harmony 鸿蒙Stage Model Development Overview
Stage Model Development Overview
Basic Concepts
The following figure illustrates the stage model.
Figure 1 Stage model
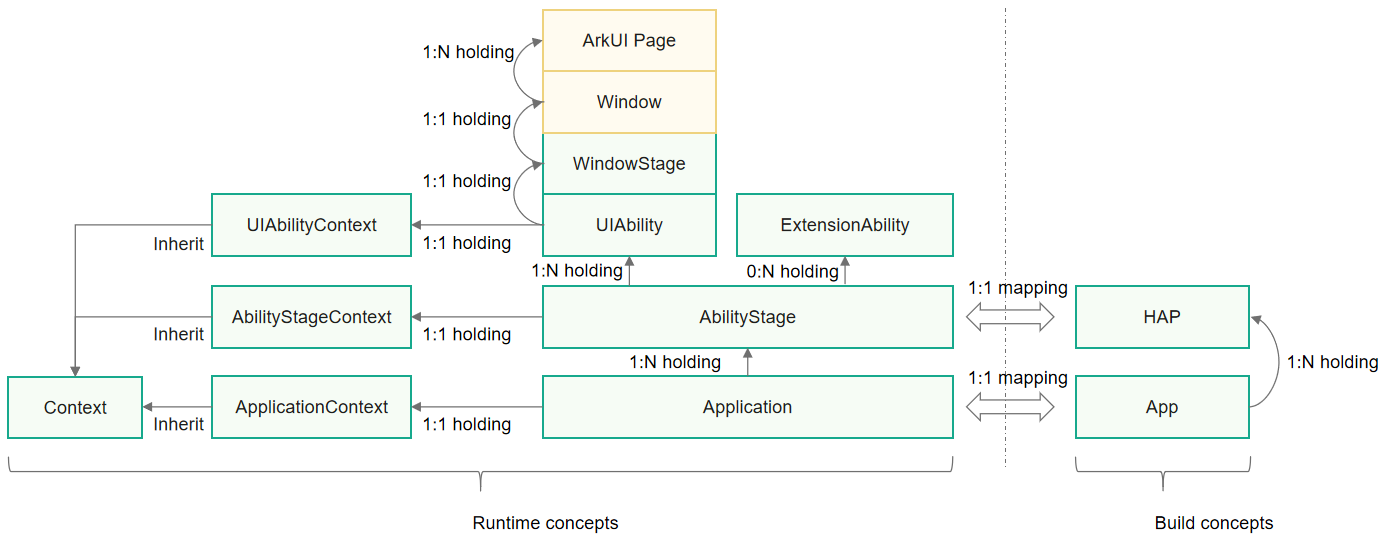
Each HAP of the Entry or Feature type has an instance of the AbilityStage class at runtime. When the code in the HAP is loaded to a process for the first time, the system creates an AbilityStage instance first.
- UIAbility and ExtensionAbility components
The stage model provides two types of application components: UIAbility and ExtensionAbility. Both have specific classes and support object-oriented development.
UIAbility is a type of application component that provides the UI for user interaction. For example, with UIAbility, the Gallery application can display images in the liquid layout. After a user selects an image, it uses a new UI to display the image details. The user can touch the Back button to return to the liquid layout. The lifecycle of the UIAbility component contains the Create, Destroy, Foreground, and Background states. Display-related states are exposed through WindowStage events.
ExtensionAbility is used for specific scenarios. You cannot derive directly from ExtensionAbility. Instead, use the derived classes of ExtensionAbility for your scenarios, such as FormExtensionAbility for widget scenarios, InputMethodExtensionAbility for input method scenarios, and WorkSchedulerExtensionAbility for deferred task scenarios. For example, to enable a user to create an application widget on the home screen, you must derive a class from FormExtensionAbility, implement callbacks, and configure the capability in the configuration file. The derived class instances are created by applications and their lifecycles are managed by the system. In the stage model, you must use the derived classes of ExtensionAbility to develop custom services of third-party applications based on your service scenarios.
Each UIAbility instance is bound to a WindowStage instance, which functions as the window manager in the application process. The WindowStage class instance contains a main window. That is, a UIAbility instance holds a main window through WindowStage, and this window provides a rendering area for ArkUI.
In the stage model, Context and its derived classes provide a variety of resources and capabilities that can be called during the runtime. The UIAbility component and ExtensionAbility derived classes have different Context classes. These classes, which all inherit from the base class Context, provide different capabilities.
How to Develop
During application development based on the stage model, the following tasks are involved in the application model.
Table 1 Stage model development process
| Task | Description | Guide |
|---|---|---|
| Application component development | Use the UIAbility and ExtensionAbility components of the stage model to develop your application. | - Application- or Component-Level Configuration - UIAbility Component - ExtensionAbility Component - AbilityStage Container Component - Context - Component Startup Rules |
| Process model development | Learn the process model and common IPC modes of the stage model. | Process Model Overview |
| Thread model development | Learn the thread model and common inter-thread communication modes of the stage model. | Thread Model Overview |
| Configuration file development | Learn the requirements for developing application configuration files in the stage model. | Application Configuration File |
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Obtaining Reasons for Abnormal Application Exits
harmony 鸿蒙UIAbility Backup and Restore
harmony 鸿蒙Using Explicit Want to Start an Application Component
harmony 鸿蒙Introduction to Ability Kit
harmony 鸿蒙AbilityStage Component Container
harmony 鸿蒙Accessing a DataAbility
harmony 鸿蒙Accessing a DataShareExtensionAbility from the FA Model
harmony 鸿蒙Common action and entities Values (Not Recommended)
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: