harmony 鸿蒙ExtensionAbility Component
ExtensionAbility Component
The ExtensionAbility component is used for specific scenarios such as widget development and input method development.
The system defines an ExtensionAbility type for every specific scenario. You can use (implement and access) only the types that have been defined. All types of ExtensionAbility components are managed by the corresponding system services in a unified manner. For example, the InputMethodExtensionAbility component is managed by the input method management service.
The table below lists the ExtensionAbility types defined in the system.
NOTE
- The column Allow Third-Party Apps to Implement specifies whether third-party applications can inherit the ExtensionAbility parent class and implement their own service logic for a type of ExtensionAbility.
- The column Allow Third-Party Apps to Access specifies whether third-party applications can access external services provided by a type of ExtensionAbility.
- The column Allow Independent ExtensionAbility Sandbox specifies whether an independent sandbox is provided for an ExtensionAbility. In versions earlier than API version 12, an application and its ExtensionAbilities use the same sandbox. Since API version 12, a new ExtensionAbility uses an independent sandbox. Currently, the InputMethodExtensionAbility runs in an independent sandbox for security purposes.
- The column Allow ExtensionAbilities to Access Sendable Data in Strict Mode specifies whether an ExtensionAbility can access sendable data in strict mode. Sendable data is implemented by configuring data-group-ids and dataGroupIds of the application. Strict access indicates that the sendable data is read-only, and non-strict access indicates that the data can be read and written.
System applications are not restricted. They can implement all the ExtensionAbility types defined in the system and access external services provided by all the ExtensionAbility types.
| ExtensionAbility Type | Description | Allow Third-Party Apps to Implement | Allow Third-Party Apps to Access | Allow Independent ExtensionAbility Sandbox | Allow ExtensionAbilities to Access Sendable Data in Strict Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FormExtensionAbility | ExtensionAbility component of the FORM type, which provides APIs related to widgets. | Yes | No | No | In non-strict mode, sendable data can be read and written. |
| WorkSchedulerExtensionAbility | ExtensionAbility component of the WORK_SCHEDULER type, which provides callbacks for deferred tasks. | Yes | N/A | No | In non-strict mode, sendable data can be read and written. |
| InputMethodExtensionAbility | ExtensionAbility component of the INPUT_METHOD type, which is used to develop input method applications. | Yes | Yes | Yes | If full mode is enabled in input method management (in non-strict mode), sendable data can be read and written. If full mode is not enabled (in strict mode), sendable data can be read only. |
| BackupExtensionAbility | ExtensionAbility component of the BACKUP type, which provides APIs for backing up and restoring application data. | Yes | N/A | No | In non-strict mode, sendable data can be read and written. |
| DriverExtensionAbility | ExtensionAbility component of the DRIVER type, which provides the driver-related extension framework. | Yes | Yes | No | In non-strict mode, sendable data can be read and written. |
| EmbeddedUIExtensionAbility | ExtensionAbility component of the EMBEDDED_UI type, which provides the embedded UI across processes. | Yes | Yes | No | In non-strict mode, sendable data can be read and written. |
| ShareExtensionAbility | ExtensionAbility component of the SHARE type, which is used to extend the sharing template service. | Yes | Yes | No | In non-strict mode, sendable data can be read and written. |
| FenceExtension | ExtensionAbility component of the FENCE type, which provides the geofence capability. | Yes | No | No | In non-strict mode, sendable data can be read and written. |
Accessing ExtensionAbility of the Specified Type
Each type of ExtensionAbility component is started by the corresponding system management service, rather than applications, so that its lifecycle is under system control. The caller of the ExtensionAbility component does not need to care about its lifecycle.
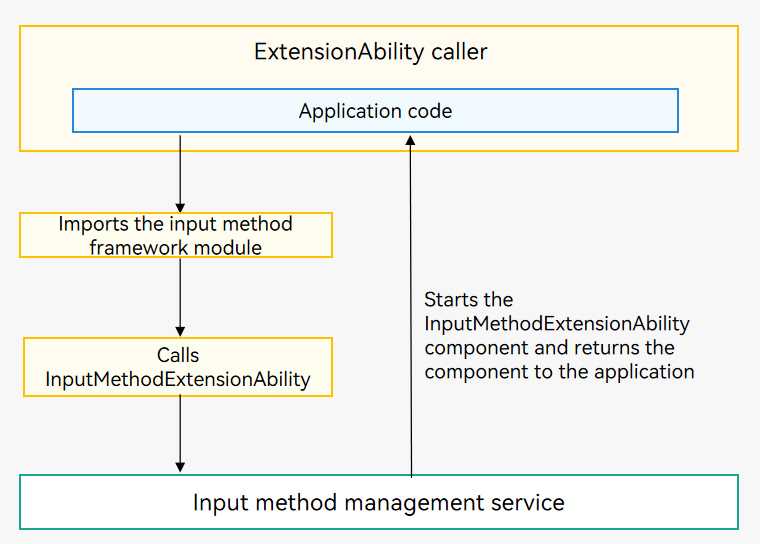
The following uses InputMethodExtensionAbility as an example. As shown in the figure below, when an application calls the InputMethodExtensionAbility component, the input method management service is called first. The input method management service starts the InputMethodExtensionAbility component, returns the component to the application, and starts to manage its lifecycle.
Figure 1 Using the InputMethodExtensionAbility component
Implementing ExtensionAbility of the Specified Type
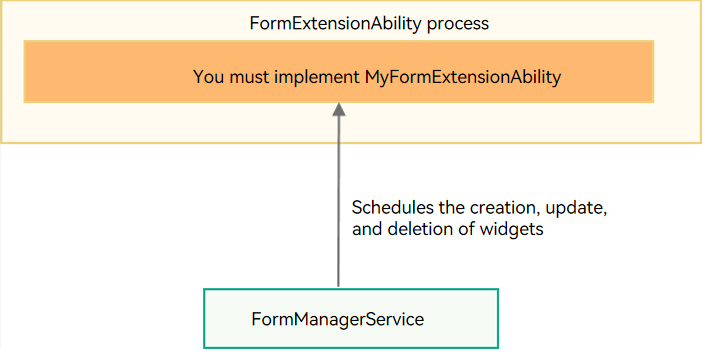
The following uses FormExtensionAbility as an example. The widget framework provides the base class FormExtensionAbility. You can derive this base class to create your own class (for example, MyFormExtensionAbility) and implement the callbacks, such as onCreate() and onUpdateForm(), to provide specific widget features. For details, see Service Widget.
You do not need to care when to add or delete a widget. The lifecycle of the FormExtensionAbility instance and the lifecycle of the ExtensionAbility process where the FormExtensionAbility instance is located are scheduled and managed by FormManagerService.
NOTE
For an application, all ExtensionAbility components of the same type run in an independent process, whereas the UIAbility, ServiceExtensionAbility, and DataShareExtensionAbility components run in another independent process. For details, see Process Model (Stage Model).
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Obtaining Reasons for Abnormal Application Exits
harmony 鸿蒙UIAbility Backup and Restore
harmony 鸿蒙Using Explicit Want to Start an Application Component
harmony 鸿蒙Introduction to Ability Kit
harmony 鸿蒙AbilityStage Component Container
harmony 鸿蒙Accessing a DataAbility
harmony 鸿蒙Accessing a DataShareExtensionAbility from the FA Model
harmony 鸿蒙Common action and entities Values (Not Recommended)
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: