harmony 鸿蒙Context (Stage Model)
Context (Stage Model)
Overview
Context is the context of an object in an application. It provides basic information about the application, such as resourceManager (resource management), applicationInfo (application information), dir (application file path), and area (encryption level). It also provides basic methods such as createBundleContext() and getApplicationContext(). The UIAbility component and ExtensionAbility derived class components have their own Context classes, for example, the base class Context, ApplicationContext, AbilityStageContext, UIAbilityContext, ServiceExtensionContext, and ExtensionContext.
NOTE
UIContext refers to the context of a UI instance, which is used to associate windows with UI pages. It is not directly related to the application context discussed in this topic and does not involve inheritance or holding relationships.
- The figure below illustrates the inheritance relationship of application contexts.
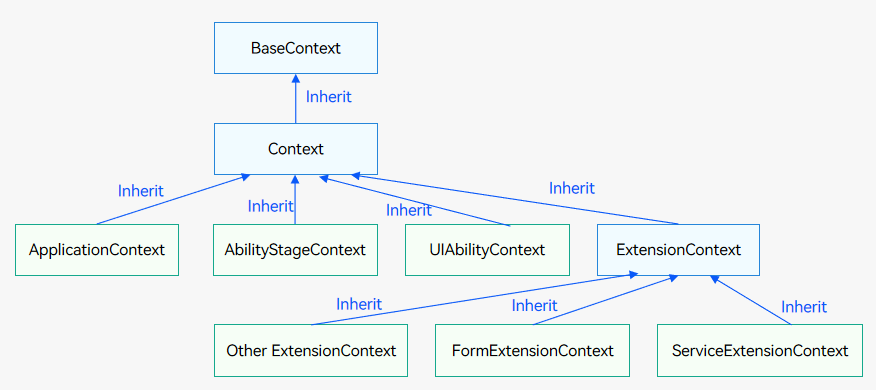
- The figure below illustrates the holding relationship of application contexts.

The following describes how to obtain different contexts.
- UIAbilityContext: Each UIAbility has the Context attribute, which provides APIs to operate an application component, obtain the application component configuration, and more.
import { UIAbility, AbilityConstant, Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit'; export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility { onCreate(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam): void { let uiAbilityContext = this.context; //... } }NOTE
For details about how to obtain the context of a UIAbility instance on the page, see Obtaining the Context of UIAbility. - Scenario-specific ExtensionContext: For example, FormExtensionContext, inherited from ExtensionContext, provides APIs related to widget services.
import { FormExtensionAbility, formBindingData } from '@kit.FormKit'; import { Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit'; export default class MyFormExtensionAbility extends FormExtensionAbility { onAddForm(want: Want) { let formExtensionContext = this.context; // ... let dataObj1: Record<string, string> = { 'temperature': '11c', 'time': '11:00' }; let obj1: formBindingData.FormBindingData = formBindingData.createFormBindingData(dataObj1); return obj1; } }- AbilityStageContext: module-level context. It provides HapModuleInfo and Configuration in addition to those provided by the base class Context.
import { AbilityStage } from '@kit.AbilityKit'; export default class MyAbilityStage extends AbilityStage { onCreate(): void { let abilityStageContext = this.context; //... } }- ApplicationContext: application-level context. It provides APIs for subscribing to application component lifecycle changes, system memory changes, and system environment changes, setting the application language and color mode, clearing application data, and revoking permissions requested from users. It can be obtained from UIAbility, ExtensionAbility, and AbilityStage.
import { UIAbility, AbilityConstant, Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit'; export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility { onCreate(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam): void { let applicationContext = this.context.getApplicationContext(); //... } }
Typical Usage Scenarios of Context
This topic describes how to use the context in the following scenarios:
- Obtaining Application File Paths
- Obtaining and Modifying Encryption Levels
- Obtaining the Context of Other Modules in the Current Application
- Subscribing to UIAbility Lifecycle Changes in a Process
Obtaining Application File Paths
The base class Context provides the capability of obtaining application file paths. ApplicationContext, AbilityStageContext, UIAbilityContext, and ExtensionContext inherit this capability. However, the specific paths retrieved can differ based on the type of the context used.
ApplicationContext: This context provides access to the application-level file path, which is used to store global application information. Files in this path are removed when the application is uninstalled.
AbilityStageContext, UIAbilityContext, and ExtensionContext: These contexts provide access to module-level file paths. Files in these paths are removed when the corresponding HAP or HSP module is uninstalled. Uninstalling an HAP or HSP module does not affect files under the application-level path unless all HAP and HSP modules of the application are uninstalled.
- UIAbilityContext: This context can be used to obtain the file paths of the module containing the UIAbility.
- ExtensionContext: This context can be used to obtain the file paths of the module containing the ExtensionAbility.
- AbilityStageContext: Given that AbilityStageContext is initialized earlier than UIAbilityContext and ExtensionContext, it is typically used to obtain file paths within the AbilityStage.
NOTE
The application file paths are a type of application sandbox paths. For details, see Application Sandbox Directory.
Table 1 Description of application file paths obtained by different types of contexts
|Name|Description|Path Obtained by ApplicationContext|Path Obtained by AbilityStageContext, UIAbilityContext, and ExtensionContext|
|——–|——–|——–|——–|
|bundleCodeDir|Bundle code directory.|<Path prefix>/el1/bundle|<Path prefix>/el1/bundle|
|cacheDir|Cache directory.|<Path prefix>/<Encryption level>/base/cache|<Path prefix>/<Encryption level>/base/haps/<module-name>/cache|
|filesDir|File directory.|<Path prefix>/<Encryption level>/base/files|<Path prefix>/<Encryption level>/base/haps/<module-name>/files|
|preferencesDir|Preferences directory.|<Path prefix>/<Encryption level>/base/preferences|<Path prefix>/<Encryption level>/base/haps/<module-name>/preferences|
|tempDir|Temporary directory.|<Path prefix>/<Encryption level>/base/temp|<Path prefix>/<Encryption level>/base/haps/<module-name>/temp|
|databaseDir|Database directory.|<Path prefix>/<Encryption level>/database|<Path prefix>/<Encryption level>/database/<module-name>|
|distributedFilesDir|Distributed file directory.|<Path prefix>/el2/distributedFiles|<Path prefix>/el2/distributedFiles/|
|resourceDir11+|Resource directory.
NOTE
You are required to manually create the resfile directory in <module-name>\resource.|N/A|<Path prefix>/el1/bundle/<module-name>/resources/resfile|
|cloudFileDir12+|Cloud file directory.|<Path prefix>/el2/cloud|<Path prefix>/el2/cloud/|
This section uses ApplicationContext as an example to describe how to obtain the application file path, create a file in the path, and read and write the file. The sample code is as follows:
import { common } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
import { buffer } from '@kit.ArkTS';
import { fileIo, ReadOptions } from '@kit.CoreFileKit';
import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit';
const TAG: string = '[Page_Context]';
const DOMAIN_NUMBER: number = 0xFF00;
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State message: string = 'Hello World';
private context = this.getUIContext().getHostContext() as common.UIAbilityContext;
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Text(this.message)
// ...
Button() {
Text('create file')
// ...
.onClick(() => {
let applicationContext = this.context.getApplicationContext();
// Obtain the application file path.
let filesDir = applicationContext.filesDir;
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `filePath: ${filesDir}`);
// Create and open the file if it does not exist. Open the file if it already exists.
let file = fileIo.openSync(filesDir + '/test.txt', fileIo.OpenMode.READ_WRITE|fileIo.OpenMode.CREATE);
// Write data to the file.
let writeLen = fileIo.writeSync(file.fd, "Try to write str.");
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `The length of str is: ${writeLen}`);
// Create an ArrayBuffer object with a size of 1024 bytes to store the data read from the file.
let arrayBuffer = new ArrayBuffer(1024);
// Set the offset and length to read.
let readOptions: ReadOptions = {
offset: 0,
length: arrayBuffer.byteLength
};
// Read the file content to the ArrayBuffer object and return the number of bytes that are actually read.
let readLen = fileIo.readSync(file.fd, arrayBuffer, readOptions);
// Convert the ArrayBuffer object into a Buffer object and output it as a string.
let buf = buffer.from(arrayBuffer, 0, readLen);
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `the content of file: ${buf.toString()}`);
// Close the file.
fileIo.closeSync(file);
})
}
// ...
}
// ...
}
// ...
}
}
Obtaining and Modifying Encryption Levels
Encrypting application files enhances data security by preventing files from unauthorized access. Different application files require different levels of protection.
In practice, you need to select a proper encryption level based on scenario-specific requirements to protect application data security. For details about the permissions required for a specific encryption level, see AreaMode in ContextConstant.
- EL1: For private files, such as alarms and wallpapers, the application can place them in a directory with the device-level encryption (EL1) to ensure that they can be accessed before the user enters the password.
- EL2: For sensitive files, such as personal privacy data, the application can place them in a directory with the user-level encryption (EL2).
- EL3: For step recording, file download, or music playback that needs to read, write, and create files when the screen is locked, the application can place these files in EL3.
- EL4: For files that are related to user security information and do not need to be read, written, or created when the screen is locked, the application can place them in EL4.
- EL5: By default, sensitive user privacy files cannot be read or written on the lock screen. If such files need to be read or written on the lock screen, you can call Access to apply for reading or writing files before the screen is locked or create new files that can be read and written after the screen is locked. It is more appropriate to place these files in EL5.
You can obtain and set the encryption level by reading and writing the area attribute in Context.
// EntryAbility.ets
import { UIAbility, contextConstant, AbilityConstant, Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
onCreate(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam) {
// Before storing common information, switch the encryption level to EL1.
this.context.area = contextConstant.AreaMode.EL1; // Change the encryption level.
// Store common information.
// Before storing sensitive information, switch the encryption level to EL2.
this.context.area = contextConstant.AreaMode.EL2; // Change the encryption level.
// Store sensitive information.
// Before storing sensitive information, switch the encryption level to EL3.
this.context.area = contextConstant.AreaMode.EL3; // Change the encryption level.
// Store sensitive information.
// Before storing sensitive information, switch the encryption level to EL4.
this.context.area = contextConstant.AreaMode.EL4; // Change the encryption level.
// Store sensitive information.
// Before storing sensitive information, switch the encryption level to EL5.
this.context.area = contextConstant.AreaMode.EL5; // Change the encryption level.
// Store sensitive information.
}
}
// Index.ets
import { contextConstant, common } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
@Entry
@Component
struct Page_Context {
private context = this.getUIContext().getHostContext() as common.UIAbilityContext;
build() {
Column() {
//...
List({ initialIndex: 0 }) {
//...
ListItem() {
Row() {
//...
}
.onClick(() => {
// Before storing common information, switch the encryption level to EL1.
if (this.context.area === contextConstant.AreaMode.EL2) { // Obtain the encryption level.
this.context.area = contextConstant.AreaMode.EL1; // Change the encryption level.
this.getUIContext().getPromptAction().showToast({
message: 'SwitchToEL1'
});
}
// Store common information.
})
}
//...
ListItem() {
Row() {
//...
}
.onClick(() => {
// Before storing sensitive information, switch the encryption level to EL2.
if (this.context.area === contextConstant.AreaMode.EL1) { // Obtain the encryption level.
this.context.area = contextConstant.AreaMode.EL2; // Change the encryption level.
this.getUIContext().getPromptAction().showToast({
message: 'SwitchToEL2'
});
}
// Store sensitive information.
})
}
//...
}
//...
}
//...
}
}
Obtaining the Context of Other Modules in the Current Application
Call createModuleContext(context: Context, moduleName: string) to obtain the context of another module in the current application. After obtaining the context, you can obtain the resource information of that module.
import { common, application } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
let storageEventCall = new LocalStorage();
@Entry(storageEventCall)
@Component
struct Page_Context {
private context = this.getUIContext().getHostContext() as common.UIAbilityContext;
build() {
Column() {
//...
List({ initialIndex: 0 }) {
ListItem() {
Row() {
//...
}
.onClick(() => {
let moduleName2: string = 'entry';
application.createModuleContext(this.context, moduleName2)
.then((data: common.Context) => {
console.info(`CreateModuleContext success, data: ${JSON.stringify(data)}`);
if (data !== null) {
this.getUIContext().getPromptAction().showToast({
message: ('Context obtained')
});
}
})
.catch((err: BusinessError) => {
console.error(`CreateModuleContext failed, err code:${err.code}, err msg: ${err.message}`);
});
})
}
//...
}
//...
}
//...
}
}
Subscribing to UIAbility Lifecycle Changes in a Process
In the DFX statistics scenario of an application, if you need to collect statistics on the stay duration and access frequency of a page, you can subscribe to UIAbility lifecycle changes in a process.
ApplicationContext provides APIs for subscribing to UIAbility lifecycle changes in a process. When the UIAbility lifecycle changes in a process, for example, being created or destroyed, becoming visible or invisible, or gaining or losing focus, the corresponding callback is triggered. Each time the callback is registered, a listener lifecycle ID is returned, with the value incremented by 1 each time. When the number of listeners exceeds the upper limit (2^63-1), -1 is returned. The following uses UIAbilityContext as an example.
import { AbilityConstant, AbilityLifecycleCallback, UIAbility, Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit';
import { window } from '@kit.ArkUI';
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
const TAG: string = '[LifecycleAbility]';
const DOMAIN_NUMBER: number = 0xFF00;
export default class LifecycleAbility extends UIAbility {
// Define a lifecycle ID.
lifecycleId: number = -1;
onCreate(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam): void {
// Define a lifecycle callback object.
let abilityLifecycleCallback: AbilityLifecycleCallback = {
// Called when a UIAbility is created.
onAbilityCreate(uiAbility) {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `onAbilityCreate uiAbility.launchWant: ${JSON.stringify(uiAbility.launchWant)}`);
},
// Called when a window is created.
onWindowStageCreate(uiAbility, windowStage: window.WindowStage) {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `onWindowStageCreate uiAbility.launchWant: ${JSON.stringify(uiAbility.launchWant)}`);
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `onWindowStageCreate windowStage: ${JSON.stringify(windowStage)}`);
},
// Called when the window becomes active.
onWindowStageActive(uiAbility, windowStage: window.WindowStage) {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `onWindowStageActive uiAbility.launchWant: ${JSON.stringify(uiAbility.launchWant)}`);
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `onWindowStageActive windowStage: ${JSON.stringify(windowStage)}`);
},
// Called when the window becomes inactive.
onWindowStageInactive(uiAbility, windowStage: window.WindowStage) {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `onWindowStageInactive uiAbility.launchWant: ${JSON.stringify(uiAbility.launchWant)}`);
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `onWindowStageInactive windowStage: ${JSON.stringify(windowStage)}`);
},
// Called when the window is destroyed.
onWindowStageDestroy(uiAbility, windowStage: window.WindowStage) {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `onWindowStageDestroy uiAbility.launchWant: ${JSON.stringify(uiAbility.launchWant)}`);
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `onWindowStageDestroy windowStage: ${JSON.stringify(windowStage)}`);
},
// Called when the UIAbility is destroyed.
onAbilityDestroy(uiAbility) {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `onAbilityDestroy uiAbility.launchWant: ${JSON.stringify(uiAbility.launchWant)}`);
},
// Called when the UIAbility is switched from the background to the foreground.
onAbilityForeground(uiAbility) {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `onAbilityForeground uiAbility.launchWant: ${JSON.stringify(uiAbility.launchWant)}`);
},
// Called when the UIAbility is switched from the foreground to the background.
onAbilityBackground(uiAbility) {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `onAbilityBackground uiAbility.launchWant: ${JSON.stringify(uiAbility.launchWant)}`);
},
// Called when UIAbility is continued on another device.
onAbilityContinue(uiAbility) {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `onAbilityContinue uiAbility.launchWant: ${JSON.stringify(uiAbility.launchWant)}`);
}
};
// Obtain the application context.
let applicationContext = this.context.getApplicationContext();
try {
// Register the application lifecycle callback.
this.lifecycleId = applicationContext.on('abilityLifecycle', abilityLifecycleCallback);
} catch (err) {
let code = (err as BusinessError).code;
let message = (err as BusinessError).message;
hilog.error(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `Failed to register applicationContext. Code is ${code}, message is ${message}`);
}
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `register callback number: ${this.lifecycleId}`);
}
//...
onDestroy(): void {
// Obtain the application context.
let applicationContext = this.context.getApplicationContext();
try {
// Deregister the application lifecycle callback.
applicationContext.off('abilityLifecycle', this.lifecycleId);
} catch (err) {
let code = (err as BusinessError).code;
let message = (err as BusinessError).message;
hilog.error(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `Failed to unregister applicationContext. Code is ${code}, message is ${message}`);
}
}
}
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Obtaining Reasons for Abnormal Application Exits
harmony 鸿蒙UIAbility Backup and Restore
harmony 鸿蒙Using Explicit Want to Start an Application Component
harmony 鸿蒙Introduction to Ability Kit
harmony 鸿蒙AbilityStage Component Container
harmony 鸿蒙Accessing a DataAbility
harmony 鸿蒙Accessing a DataShareExtensionAbility from the FA Model
harmony 鸿蒙Common action and entities Values (Not Recommended)
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: