harmony 鸿蒙Repeat:可复用的循环渲染
Repeat:可复用的循环渲染
说明:
Repeat从API version 12开始支持。
本文档仅为开发指南。组件接口规范见Repeat API参数说明。
概述
Repeat基于数组类型数据来进行循环渲染,一般与容器组件配合使用。
Repeat根据容器组件的有效加载范围(屏幕可视区域+预加载区域)加载子组件。当容器滑动/数组改变时,Repeat会根据父容器组件的布局过程重新计算有效加载范围,并管理列表子组件节点的创建与销毁。Repeat通过组件节点更新/复用从而优化性能表现,详细描述见节点更新/复用能力说明。
说明:
Repeat与LazyForEach组件的区别: - Repeat直接监听状态变量的变化,而LazyForEach需要开发者实现IDataSource接口,手动管理子组件内容/索引的修改。 - Repeat还增强了节点复用能力,提高了长列表滑动和数据更新的渲染性能。 - Repeat增加了渲染模板(template)的能力,在同一个数组中,根据开发者自定义的模板类型(template type)渲染不同的子组件。
使用限制
- Repeat必须在滚动类容器组件内使用,仅有List、Grid、Swiper以及WaterFlow组件支持Repeat懒加载场景。
循环渲染只允许创建一个子组件,子组件应当是允许包含在容器组件中的子组件。例如:Repeat与List组件配合使用时,子组件必须为ListItem组件。 - Repeat不支持V1装饰器,混用V1装饰器会导致渲染异常。
- 滚动容器组件内只能包含一个Repeat。以List为例,同时包含ListItem、ForEach、LazyForEach的场景是不推荐的;同时包含多个Repeat也是不推荐的。
- 当Repeat与自定义组件或@Builder函数混用时,必须将RepeatItem类型整体进行传参,组件才能监听到数据变化。详见Repeat与@Builder混用。
循环渲染能力说明
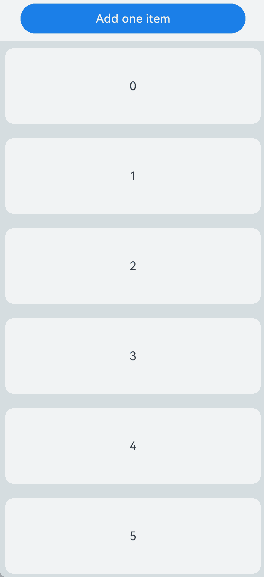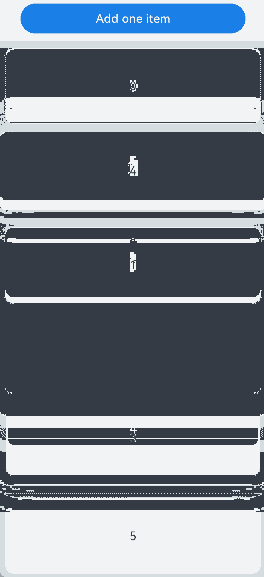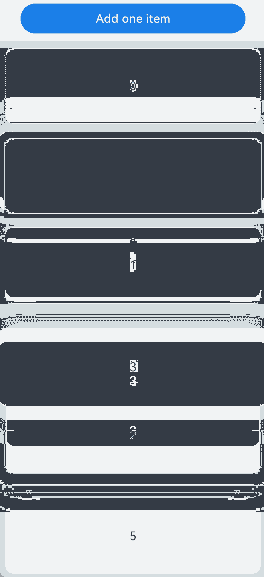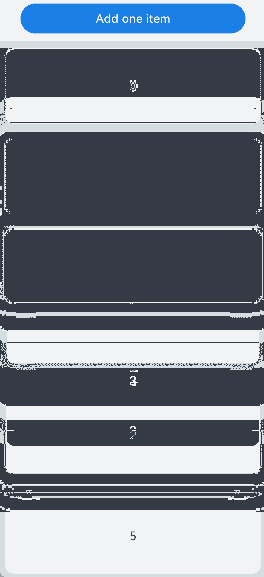
Repeat子组件由.each()和.template()属性定义,只允许包含一个子组件。当页面首次渲染时,Repeat根据当前的有效加载范围(屏幕可视区域+预加载区域)按需创建子组件。如下图所示:

.each()适用于只需要循环渲染一种子组件的场景。下列示例代码使用Repeat组件进行简单的循环渲染。
// 在List容器组件中使用Repeat
@Entry
@ComponentV2 // 推荐使用V2装饰器
struct RepeatExample {
@Local dataArr: Array<string> = []; // 数据源
aboutToAppear(): void {
for (let i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
this.dataArr.push(`data_${i}`); // 为数组添加一些数据
}
}
build() {
Column() {
List() {
Repeat<string>(this.dataArr)
.each((ri: RepeatItem<string>) => {
ListItem() {
Text('each_' + ri.item).fontSize(30)
}
})
.virtualScroll({ totalCount: this.dataArr.length }) // 打开懒加载,totalCount为期望加载的数据长度
}
.cachedCount(2) // 容器组件的预加载区域大小
.height('70%')
.border({ width: 1 }) // 边框
}
}
}
运行后界面如下图所示:

Repeat提供渲染模板(template)能力,可以在同一个数据源中渲染多种子组件。每个数据项会根据.templateId()得到template type,从而渲染type对应的.template()中的子组件。
- 如果
.templateId()缺省,则type默认为空字符串。 - 当多个template type相同时,Repeat会覆盖先定义的
.template()函数,仅生效最后定义的.template()。 - 如果找不到对应的template type,Repeat会优先渲染type为空的
.template()中的子组件,如果没有,则渲染.each()中的子组件。 - 只有相同template的节点可以互相复用。
下列示例代码中使用Repeat组件进行循环渲染,并使用了多个渲染模板。
// 在List容器组件中使用Repeat
@Entry
@ComponentV2 // 推荐使用V2装饰器
struct RepeatExampleWithTemplates {
@Local dataArr: Array<string> = []; // 数据源
aboutToAppear(): void {
for (let i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
this.dataArr.push(`data_${i}`); // 为数组添加一些数据
}
}
build() {
Column() {
List() {
Repeat<string>(this.dataArr)
.each((ri: RepeatItem<string>) => { // 默认渲染模板
ListItem() {
Text('each_' + ri.item).fontSize(30).fontColor('rgb(161,10,33)') // 文本颜色为红色
}
})
.key((item: string, index: number): string => JSON.stringify(item)) // 键值生成函数
.virtualScroll({ totalCount: this.dataArr.length }) // 打开懒加载,totalCount为期望加载的数据长度
.templateId((item: string, index: number): string => { // 根据返回值寻找对应的模板子组件进行渲染
return index <= 4 ? 'A' : (index <= 10 ? 'B' : ''); // 前5个节点模板为A,接下来的5个为B,其余为默认模板
})
.template('A', (ri: RepeatItem<string>) => { // 'A'模板
ListItem() {
Text('A_' + ri.item).fontSize(30).fontColor('rgb(23,169,141)') // 文本颜色为绿色
}
}, { cachedCount: 3 }) // 'A'模板的缓存列表容量为3
.template('B', (ri: RepeatItem<string>) => { // 'B'模板
ListItem() {
Text('B_' + ri.item).fontSize(30).fontColor('rgb(39,135,217)') // 文本颜色为蓝色
}
}, { cachedCount: 4 }) // 'B'模板的缓存列表容量为4
}
.cachedCount(2) // 容器组件的预加载区域大小
.height('70%')
.border({ width: 1 }) // 边框
}
}
}
运行后界面如下图所示:

节点更新/复用能力说明
说明:
Repeat子组件的节点操作分为四种:节点创建、节点更新、节点复用、节点销毁。其中,节点更新和节点复用的区别为:
- 节点更新:节点不销毁,状态变量驱动节点属性更新。
- 节点复用:旧节点不销毁,存储在空闲节点缓存池;需要创建新节点时,直接从缓存池中获取可复用的旧节点,并做相应的节点属性更新。
当滚动容器组件滑动/数组改变时,Repeat将失效的子组件节点(离开有效加载范围)加入空闲节点缓存池中,即断开组件节点与页面组件树的连接但不销毁节点。在需要生成新的组件时,对缓存池里的组件节点进行复用。
Repeat组件默认开启节点复用功能。从API version 18开始,可以通过配置reusable字段选择是否启用复用功能。为了提高渲染性能,建议开发者保持节点复用。代码示例见VirtualScrollOptions对象说明。
从API version 18开始,Repeat支持L2缓存自定义组件冻结。详细描述见缓存池自定义组件冻结。
下面通过典型的滑动场景和数据更新场景示例来展示Repeat子组件的渲染逻辑。图中L1缓存为Repeat有效加载区域,L2缓存为每个循环渲染模板的空闲节点缓存池。
定义长度为20的数组,数组前5项的template type为aa,其余项为bb。aa缓存池容量为3,bb缓存池容量为4。容器组件的预加载区域大小为2。为了便于理解,在aa和bb缓存池中分别加入一个和两个空闲节点。
首次渲染,列表的节点状态如下图所示。
滑动场景
将屏幕向右滑动(屏幕内容右移)一个节点的距离,Repeat将开始复用缓存池中的节点。index=10的节点进入有效加载范围,计算出其template type为bb。由于bb缓存池非空,Repeat会从bb缓存池中取出一个空闲节点进行复用,更新其节点属性,该子组件中涉及数据item和索引index的其他孙子组件会根据V2状态管理的规则做同步更新。其他节点仍在有效加载范围,均只更新索引index。
index=0的节点滑出了有效加载范围。当UI主线程空闲时,会检查aa缓存池是否已满,此时aa缓存池未满,将该节点加入到对应的缓存池中。
如果此时对应template type的缓存池已满,Repeat会销毁掉多余的节点。
数据更新场景
在上一小节的基础上做如下的数组更新操作,删除index=4的节点,修改节点数据item_7为new_7。
首先,删除index=4的节点后,失效节点加入aa缓存池。后面的列表节点前移,新进入有效加载区域的节点item_11会复用bb缓存池中的空闲节点,其他节点均只更新索引index。如下图所示。
其次,节点item_5前移,索引index更新为4。根据template type的计算规则,节点item_5的template type变为aa,需要从aa缓存池中复用空闲节点,并且将旧节点加入bb缓存池。如下图所示。
键值生成函数
Repeat的.key()属性为每个子组件生成一个键值。Repeat通过键值识别数组增加、删除哪些数据以及哪些数据改变了位置(索引)。
注意:
键值(key)与索引(index)的区别:键值是数据项的唯一标识符,Repeat根据键值是否发生变化判断数据项是否更新;索引只标识数据项在数组中的位置。
当.key()缺省时,Repeat会生成新的随机键值。当发现有重复key时,Repeat会在已有键值的基础上递归生成新的键值,直到没有重复键值。
键值生成函数.key()的使用限制:
- 即使数组发生变化,开发者也必须保证键值key唯一。
- 每次执行
.key()函数时,使用相同的数据项作为输入,输出必须是一致的。 - 允许在
.key()中使用index,但不建议开发者这样做。因为在数据项移动时索引index发生变化的同时key值也会改变,导致Repeat认为数据发生变化,从而触发子组件重新渲染,降低性能表现。 - 推荐将简单类型数组转换为类对象数组,并添加一个
readonly id属性,在构造函数中初始化唯一值。
数据精准懒加载
当数据源总长度较长,或数据项加载耗时较长时,可使用Repeat数据精准懒加载特性,避免在初始化时加载所有数据。
开发者可以设置.virtualScroll()的totalCount属性值或onTotalCount自定义方法用于计算期望的数据源长度,设置onLazyLoading属性实现数据精准懒加载,实现在节点首次渲染时加载对应的数据。详细说明和注意事项见VirtualScrollOptions对象说明。
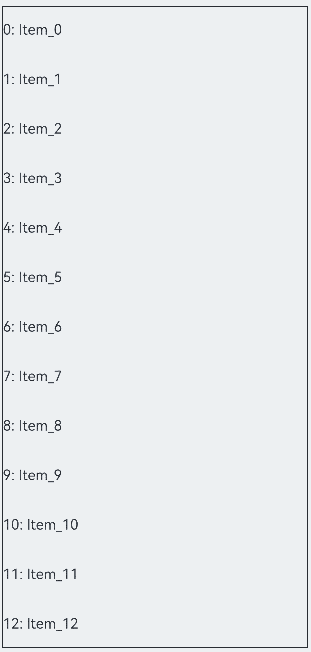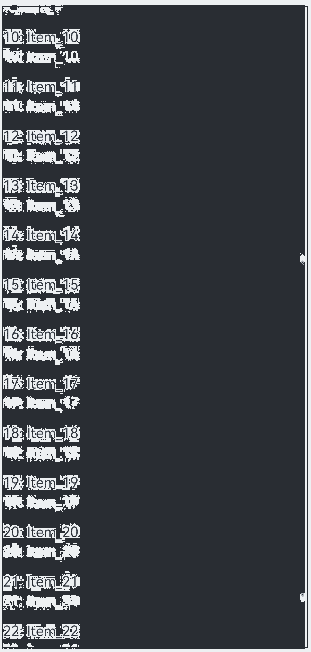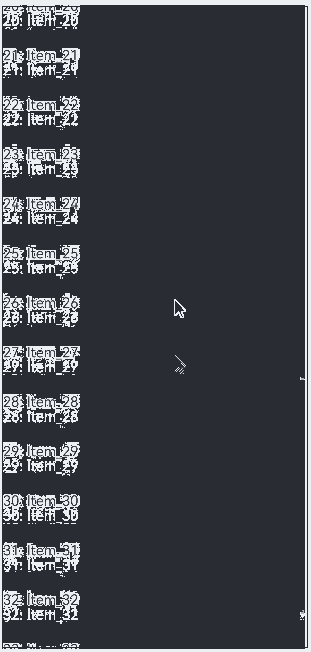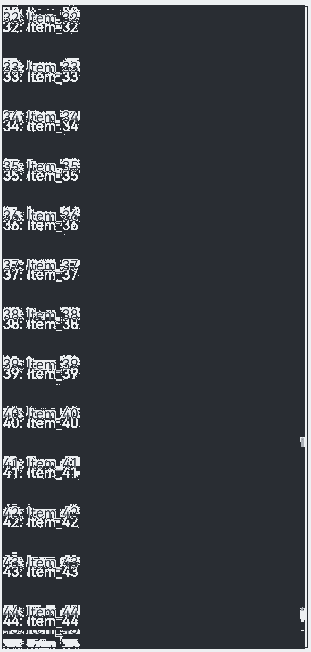
示例1
数据源总长度较长,在首次渲染、滑动屏幕、跳转显示区域时,动态加载对应区域内的数据。
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct RepeatLazyLoading {
// 假设数据源总长度较长,为1000。初始数组未提供数据。
@Local arr: Array<string> = [];
scroller: Scroller = new Scroller();
build() {
Column({ space: 5 }) {
// 初始显示位置为index = 100,数据可通过懒加载自动获取。
List({ scroller: this.scroller, space: 5, initialIndex: 100 }) {
Repeat(this.arr)
.virtualScroll({
// 期望的数据源总长度为1000。
onTotalCount: () => { return 1000; },
// 实现数据懒加载。
onLazyLoading: (index: number) => { this.arr[index] = index.toString(); }
})
.each((obj: RepeatItem<string>) => {
ListItem() {
Row({ space: 5 }) {
Text(`${obj.index}: Item_${obj.item}`)
}
}
.height(50)
})
}
.height('80%')
.border({ width: 1})
// 显示位置跳转至index = 500,数据可通过懒加载自动获取。
Button('ScrollToIndex 500')
.onClick(() => { this.scroller.scrollToIndex(500); })
}
}
}
运行效果:

示例2
数据加载耗时长,在onLazyLoading方法中,首先为数据项创建占位符,再通过异步任务加载数据。
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct RepeatLazyLoading {
@Local arr: Array<string> = [];
build() {
Column({ space: 5 }) {
List({ space: 5 }) {
Repeat(this.arr)
.virtualScroll({
onTotalCount: () => { return 100; },
// 实现数据懒加载。
onLazyLoading: (index: number) => {
// 创建占位符。
this.arr[index] = '';
// 模拟高耗时加载过程,通过异步任务加载数据。
setTimeout(() => { this.arr[index] = index.toString(); }, 1000);
}
})
.each((obj: RepeatItem<string>) => {
ListItem() {
Row({ space: 5 }) {
Text(`${obj.index}: Item_${obj.item}`)
}
}
.height(50)
})
}
.height('100%')
.border({ width: 1})
}
}
}
运行效果:
示例3
使用数据懒加载,并配合设置onTotalCount: () => { return this.arr.length + 1; },可实现数据无限懒加载。
注意:
- 此场景下,开发者需要提供首屏显示所需的初始数据,并建议设置父容器组件
cachedCount > 0,否则将会导致渲染异常。- 若与Swiper-Loop模式同时使用,停留在
index = 0处时,将导致onLazyLoading方法被持续触发,建议避免与Swiper-Loop模式同时使用。- 开发者需要关注内存消耗情况,避免因数据持续加载而导致内存过量消耗。
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct RepeatLazyLoading {
@Local arr: Array<string> = [];
// 提供首屏显示所需的初始数据。
aboutToAppear(): void {
for (let i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
this.arr.push(i.toString());
}
}
build() {
Column({ space: 5 }) {
List({ space: 5 }) {
Repeat(this.arr)
.virtualScroll({
// 数据无限懒加载。
onTotalCount: () => { return this.arr.length + 1; },
onLazyLoading: (index: number) => { this.arr[index] = index.toString(); }
})
.each((obj: RepeatItem<string>) => {
ListItem() {
Row({ space: 5 }) {
Text(`${obj.index}: Item_${obj.item}`)
}
}
.height(50)
})
}
.height('100%')
.border({ width: 1})
// 建议设置cachedCount > 0。
.cachedCount(1)
}
}
}
运行效果:
拖拽排序
当Repeat在List组件下使用,并且设置了onMove事件,Repeat每次迭代都生成一个ListItem时,可以使能拖拽排序。Repeat拖拽排序特性从API version 19开始支持。
注意:
- 拖拽排序离手后,如果数据位置发生变化,则会触发onMove事件,上报数据移动原始索引号和目标索引号。
在onMove事件中,需要根据上报的起始索引号和目标索引号修改数据源。数据源修改前后,要保持每个数据的键值不变,只是顺序发生变化,才能保证落位动画正常执行。- 拖拽排序过程中,在离手之前,不允许修改数据源。
示例代码:
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct RepeatVirtualScrollOnMove {
@Local simpleList: Array<string> = [];
aboutToAppear(): void {
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
this.simpleList.push(`${i}`);
}
}
build() {
Column() {
List() {
Repeat<string>(this.simpleList)
// 通过设置onMove,使能拖拽排序。
.onMove((from: number, to: number) => {
let temp = this.simpleList.splice(from, 1);
this.simpleList.splice(to, 0, temp[0]);
})
.each((obj: RepeatItem<string>) => {
ListItem() {
Text(obj.item)
.fontSize(16)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.size({height: 100, width: "100%"})
}.margin(10)
.borderRadius(10)
.backgroundColor("#FFFFFFFF")
})
.key((item: string, index: number) => {
return item;
})
.virtualScroll({ totalCount: this.simpleList.length })
}
.border({ width: 1 })
.backgroundColor("#FFDCDCDC")
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
}
运行效果:
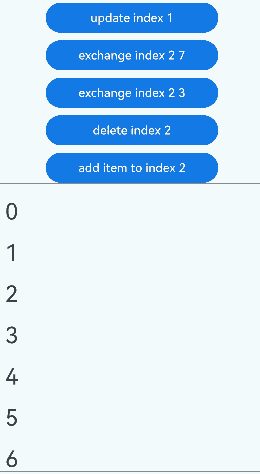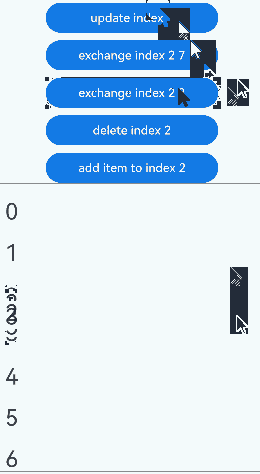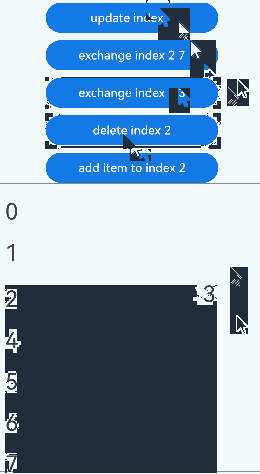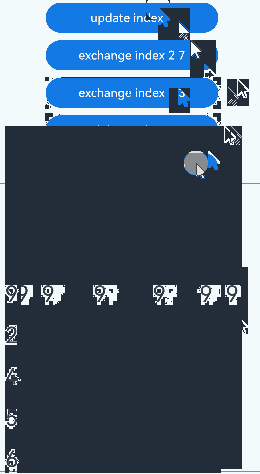
动画
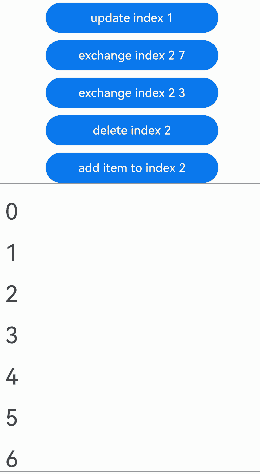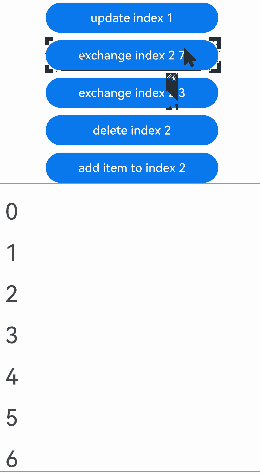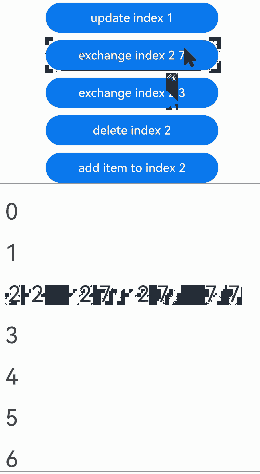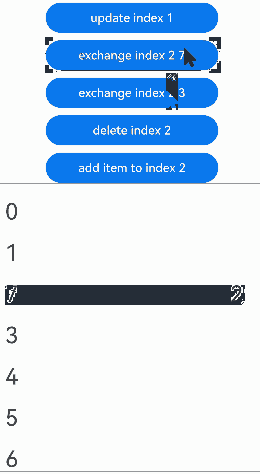
从API version 20开始,当父容器为滚动容器组件时,可视区内Repeat子组件的插入、删除、交换操作均支持animateTo动画,子组件更新操作不支持animateTo动画。Repeat子组件在动画过程中不会复用。滚动容器组件的cachedCount(count: number, show: boolean)属性包含两个参数,count设置预加载数量,show设置是否显示预加载的组件(show设置为true,可视区包含预加载的组件)。
示例
@ObservedV2
class DemoData {
@Trace key: string;
@Trace value: string;
constructor(key: string, value: string) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct AnimateToDemo {
@Local simpleList: Array<DemoData> = [];
aboutToAppear(): void {
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
this.simpleList.push(new DemoData(i.toString(), i.toString()));
}
}
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Button('update index 1').onClick(() => {
this.getUIContext()?.animateTo({ duration: 3000 }, () => {
this.simpleList[1].value = Math.random().toPrecision(2).toString();
});
}).fontSize(16).width(230).margin({ top: 10 })
Button('exchange index 2 7').onClick(() => {
this.getUIContext()?.animateTo({ duration: 3000 }, () => {
let temp = this.simpleList[2];
this.simpleList[2] = this.simpleList[7];
this.simpleList[7] = temp;
});
}).fontSize(16).width(230).margin({ top: 10 })
Button('exchange index 2 3').onClick(() => {
this.getUIContext()?.animateTo({ duration: 3000 }, () => {
let temp = this.simpleList[2];
this.simpleList[2] = this.simpleList[3];
this.simpleList[3] = temp;
});
}).fontSize(16).width(230).margin({ top: 10 })
Button('delete index 2').onClick(() => {
this.getUIContext()?.animateTo({ duration: 3000 }, () => {
this.simpleList.splice(2, 1);
});
}).fontSize(16).width(230).margin({ top: 10 })
Button('add item to index 2').onClick(() => {
this.getUIContext()?.animateTo({ duration: 3000 }, () => {
this.simpleList.splice(2, 0, new DemoData(this.simpleList.length.toString(), this.simpleList.length.toString()));
});
}).fontSize(16).width(230).margin({ top: 10 })
Column() {
List() {
Repeat<DemoData>(this.simpleList)
.each((obj: RepeatItem<DemoData>) => {
ListItem() {
Text(obj.item.value)
.fontSize(30)
.margin({ top: 20, left: 10 })
}
// 设置平移转场效果,组件出现或消失的位置在x=300处
.transition(TransitionEffect.translate({ x: 300 }))
})
.key((item: DemoData) => item.key) // 不同的数组项生成的key要具有唯一性
.virtualScroll({ totalCount: this.simpleList.length })
.templateId(() => 'a')
.template('a', (ri) => {
ListItem() {
Text(ri.item.value)
.fontSize(30)
.margin({ top: 20, left: 10 })
}
// 设置平移转场效果,组件出现或消失的位置在x=300处
.transition(TransitionEffect.translate({ x: 300 }))
})
}
// Repeat动画一般需配合滚动容器组件cachedCount属性的show参数(设置true时显示预加载的子组件)一起使用;
// 当show参数设置为false、插入数组项时,Repeat子组件离开屏幕时无动画,效果如下图(show参数设置为false、插入数组项时的动画效果)所示
.cachedCount(1, true)
.border({ width: 1 })
.height(386)
}
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
点击“udpate index 1”按钮,更新Repeat子组件没有动画效果。点击其他按钮,可视区内Repeat子组件的交换、删除、插入都有相应的动画效果:
show参数设置为false、插入数组项时的动画效果:
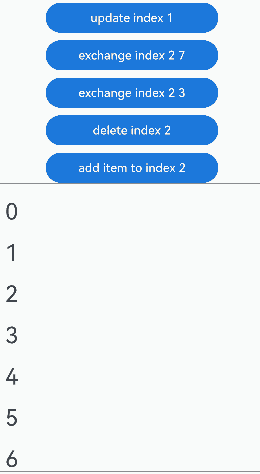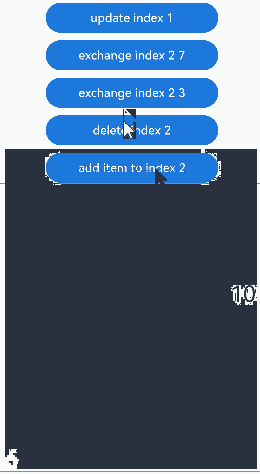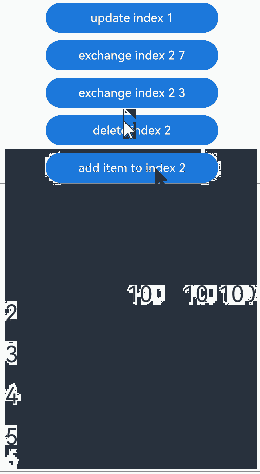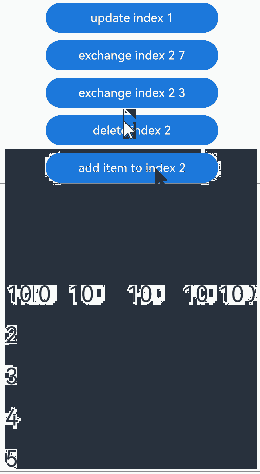
最佳实践
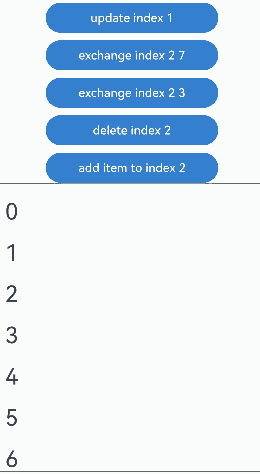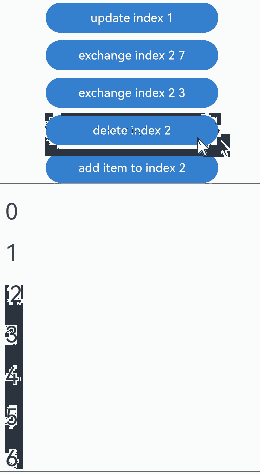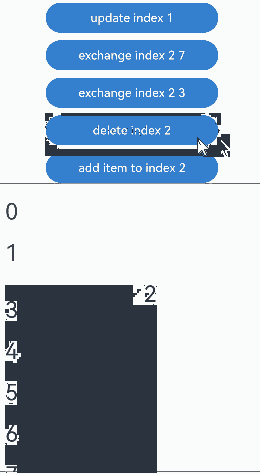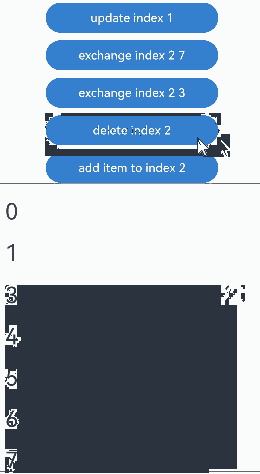
通过设置Repeat父容器组件的cachedCount属性来控制动画效果。 |操作 |设置 |动画效果|说明 | |———-|——|—-|————————————————————| |组件插入|cachedCount(0, true)|组件“6”移除动画|插入“10”后,组件“6”出可视区,下树做移除动画。| |组件插入|cachedCount(1, true)|组件“6”下移动画|插入“10”后,组件“6”进入预加载区,没有下树,做下移动画。| |组件删除|cachedCount(0, true)|组件“7”插入动画|删除“2”后,组件“7”进可视区,上树做插入动画。| |组件删除|cachedCount(1, true)|组件“7”上移动画|删除“2”后,组件“7”从预加载区进入显示区,做上移动画。| |组件交换|cachedCount(0, true)|组件“2”移除动画,组件“7”插入动画|组件“2”出可视区,下树做移除动画;组件“7”进可视区,上树做插入动画。| |组件交换|cachedCount(1, true)|组件“2”和组件“7”挤位动画|组件“2”从显示区进入预加载区,组件“7”从预加载区进入显示区。两个组件都一直在可视区,只是位置发生变化,因此做挤位动画。|
没有预加载组件时,组件插入的运行效果:
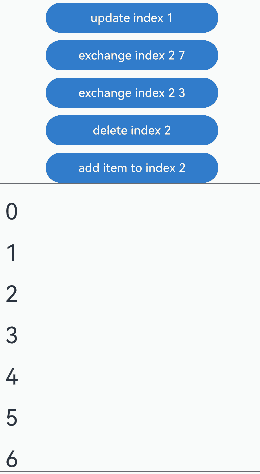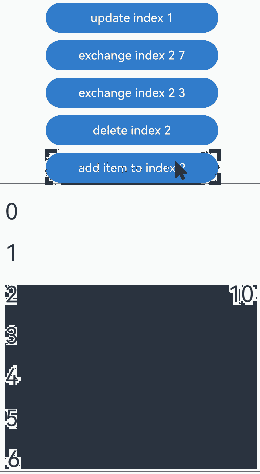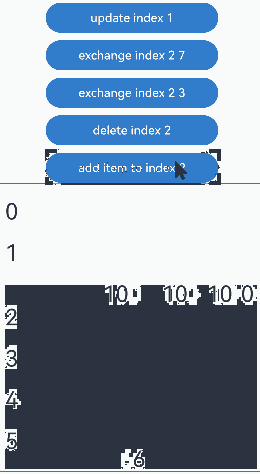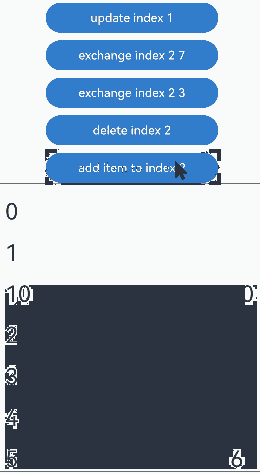
预加载组件时,组件插入的运行效果:
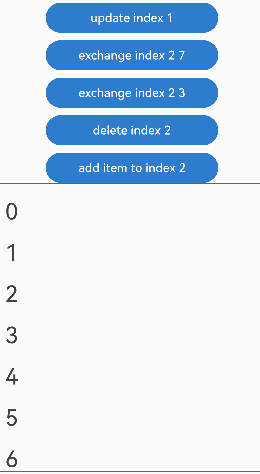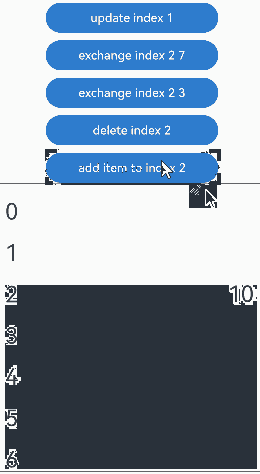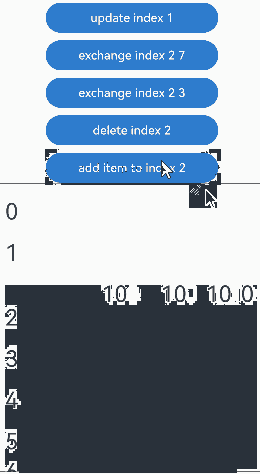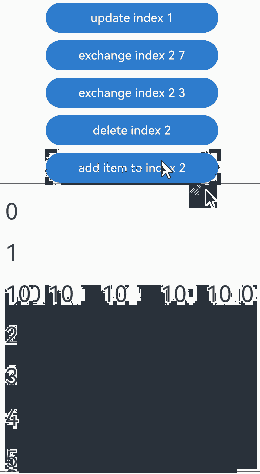
没有预加载组件时,组件删除的运行效果:

预加载组件时,组件删除的运行效果:
没有预加载组件时,组件交换的运行效果:
预加载组件时,组件交换的运行效果:

前插保持
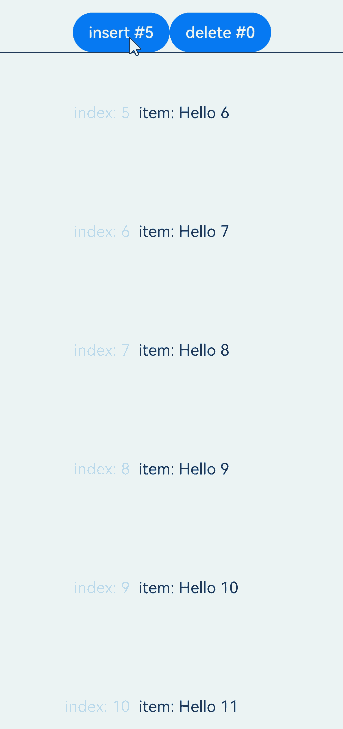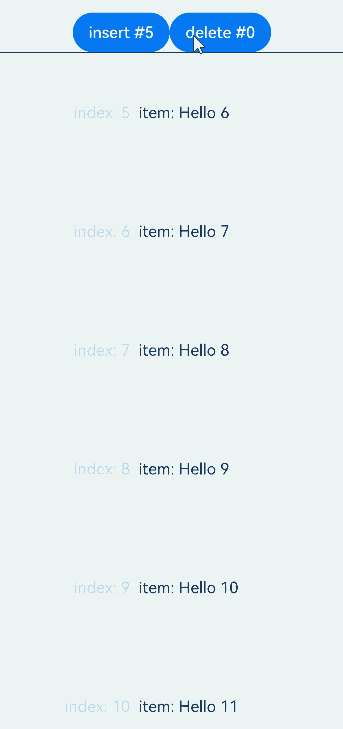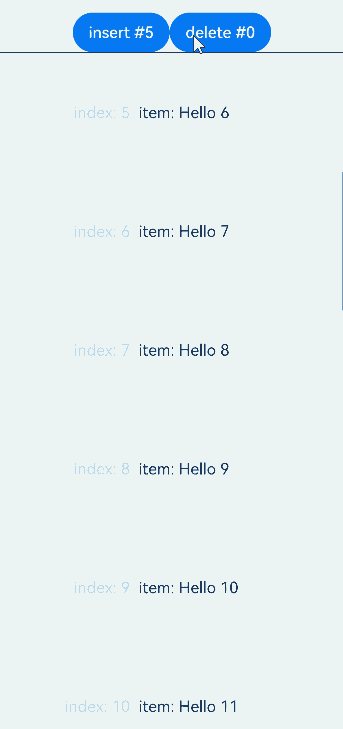
前插保持,即在显示区域之前插入或删除数据后,保持显示区域的子组件位置不变。
从API version 20开始,仅当父容器组件为List且maintainVisibleContentPosition属性设置为true后,在List显示区域之前插入或删除数据时保持List显示区域子组件位置不变。
示例代码
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct PreInsertDemo {
@Local simpleList: Array<string> = [];
private cnt: number = 1;
aboutToAppear(): void {
for (let i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
this.simpleList.push(`Hello ${this.cnt++}`);
}
}
build() {
Column() {
Row() {
Button(`insert #5`)
.onClick(() => {
this.simpleList.splice(5, 0, `Hello ${this.cnt++}`);
})
Button(`delete #0`)
.onClick(() => {
this.simpleList.splice(0, 1);
})
}
List({ initialIndex: 5 }) {
Repeat<string>(this.simpleList)
.each((obj: RepeatItem<string>) => {
ListItem() {
Row() {
Text(`index: ${obj.index} `)
.fontSize(16)
.fontColor("#70707070")
.textAlign(TextAlign.End)
.size({ height: 100, width: "40%" })
Text(`item: ${obj.item}`)
.fontSize(16)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Start)
.size({ height: 100, width: "60%" })
}
}.margin(10)
.borderRadius(10)
.backgroundColor("#FFFFFFFF")
})
.key((item: string, index: number) => item)
.virtualScroll({ totalCount: this.simpleList.length })
}
.maintainVisibleContentPosition(true) // 启用前插保持
.border({ width: 1 })
.backgroundColor("#FFDCDCDC")
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
}
示例中,通过点击按钮在显示区域上方插入或删除数据时,显示区域的节点仅index发生改变,对应数据项不变。
运行效果:
常见使用场景
数据展示&操作
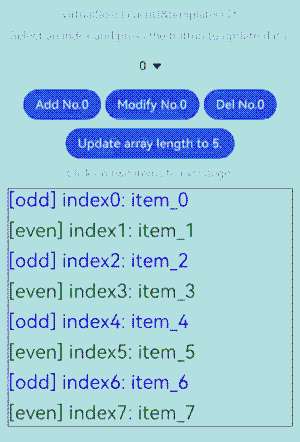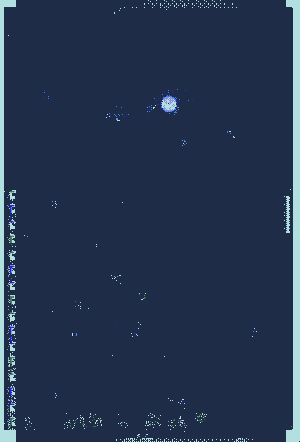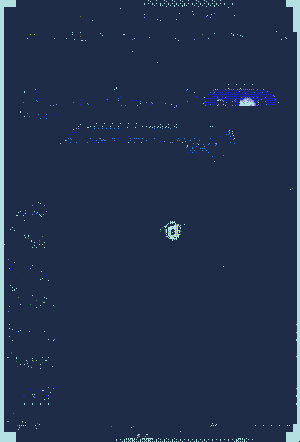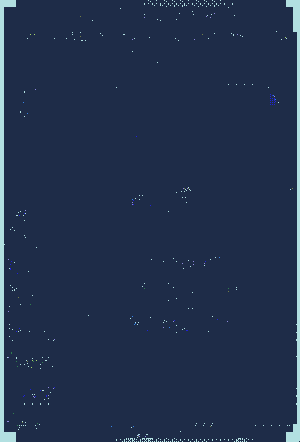
下面的代码示例展示了Repeat修改数组的常见操作,包括插入数据、修改数据、删除数据、交换数据。点击下拉框选择索引index值,点击相应的按钮即可操作数据项,依次点击两个数据项可以进行交换。
@ObservedV2
class Repeat006Clazz {
@Trace message: string = '';
constructor(message: string) {
this.message = message;
}
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct RepeatVirtualScroll2T {
@Local simpleList: Array<Repeat006Clazz> = [];
private exchange: number[] = [];
private counter: number = 0;
@Local selectOptions: SelectOption[] = [];
@Local selectIdx: number = 0;
@Monitor("simpleList")
reloadSelectOptions(): void {
this.selectOptions = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.simpleList.length; ++i) {
this.selectOptions.push({ value: i.toString() });
}
if (this.selectIdx >= this.simpleList.length) {
this.selectIdx = this.simpleList.length - 1;
}
}
aboutToAppear(): void {
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
this.simpleList.push(new Repeat006Clazz(`item_${i}`));
}
this.reloadSelectOptions();
}
handleExchange(idx: number): void { // 点击交换子组件
this.exchange.push(idx);
if (this.exchange.length === 2) {
let _a = this.exchange[0];
let _b = this.exchange[1];
let temp: Repeat006Clazz = this.simpleList[_a];
this.simpleList[_a] = this.simpleList[_b];
this.simpleList[_b] = temp;
this.exchange = [];
}
}
build() {
Column({ space: 10 }) {
Text('virtualScroll each()&template() 2t')
.fontSize(15)
.fontColor(Color.Gray)
Text('Select an index and press the button to update data.')
.fontSize(15)
.fontColor(Color.Gray)
Select(this.selectOptions)
.selected(this.selectIdx)
.value(this.selectIdx.toString())
.key('selectIdx')
.onSelect((index: number) => {
this.selectIdx = index;
})
Row({ space: 5 }) {
Button('Add No.' + this.selectIdx)
.onClick(() => {
this.simpleList.splice(this.selectIdx, 0, new Repeat006Clazz(`${this.counter++}_add_item`));
this.reloadSelectOptions();
})
Button('Modify No.' + this.selectIdx)
.onClick(() => {
this.simpleList.splice(this.selectIdx, 1, new Repeat006Clazz(`${this.counter++}_modify_item`));
})
Button('Del No.' + this.selectIdx)
.onClick(() => {
this.simpleList.splice(this.selectIdx, 1);
this.reloadSelectOptions();
})
}
Button('Update array length to 5.')
.onClick(() => {
this.simpleList = this.simpleList.slice(0, 5);
this.reloadSelectOptions();
})
Text('Click on two items to exchange.')
.fontSize(15)
.fontColor(Color.Gray)
List({ space: 10 }) {
Repeat<Repeat006Clazz>(this.simpleList)
.each((obj: RepeatItem<Repeat006Clazz>) => {
ListItem() {
Text(`[each] index${obj.index}: ${obj.item.message}`)
.fontSize(25)
.onClick(() => {
this.handleExchange(obj.index);
})
}
})
.key((item: Repeat006Clazz, index: number) => {
return item.message;
})
.virtualScroll({ totalCount: this.simpleList.length })
.templateId((item: Repeat006Clazz, index: number) => {
return (index % 2 === 0) ? 'odd' : 'even';
})
.template('odd', (ri) => {
Text(`[odd] index${ri.index}: ${ri.item.message}`)
.fontSize(25)
.fontColor(Color.Blue)
.onClick(() => {
this.handleExchange(ri.index);
})
}, { cachedCount: 3 })
.template('even', (ri) => {
Text(`[even] index${ri.index}: ${ri.item.message}`)
.fontSize(25)
.fontColor(Color.Green)
.onClick(() => {
this.handleExchange(ri.index);
})
}, { cachedCount: 1 })
}
.cachedCount(2)
.border({ width: 1 })
.width('95%')
.height('40%')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
该示例代码展示了100项自定义类RepeatClazz的message字符串属性,List组件的cachedCount属性设为2,模板’odd’和’even’的空闲节点缓存池大小分别设为3和1。运行后界面如下图所示:
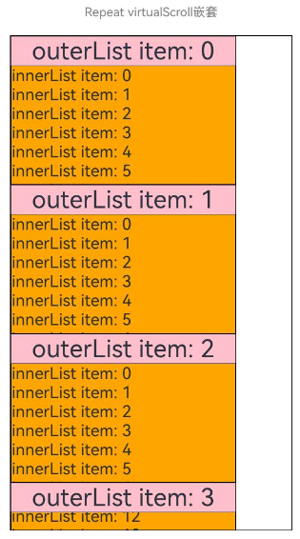
Repeat嵌套
Repeat支持嵌套使用,示例代码如下:
// Repeat嵌套
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct RepeatNest {
@Local outerList: string[] = [];
@Local innerList: number[] = [];
aboutToAppear(): void {
for (let i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
this.outerList.push(i.toString());
this.innerList.push(i);
}
}
build() {
Column({ space: 20 }) {
Text('Repeat virtualScroll嵌套')
.fontSize(15)
.fontColor(Color.Gray)
List() {
Repeat<string>(this.outerList)
.each((obj) => {
ListItem() {
Column() {
Text('outerList item: ' + obj.item)
.fontSize(30)
List() {
Repeat<number>(this.innerList)
.each((subObj) => {
ListItem() {
Text('innerList item: ' + subObj.item)
.fontSize(20)
}
})
.key((item) => "innerList_" + item)
.virtualScroll()
}
.width('80%')
.border({ width: 1 })
.backgroundColor(Color.Orange)
}
.height('30%')
.backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
}
.border({ width: 1 })
})
.key((item) => "outerList_" + item)
.virtualScroll()
}
.width('80%')
.border({ width: 1 })
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width('90%')
.height('80%')
}
}
运行效果:
父容器组件应用场景
本节展示Repeat与滚动容器组件的常见应用场景。
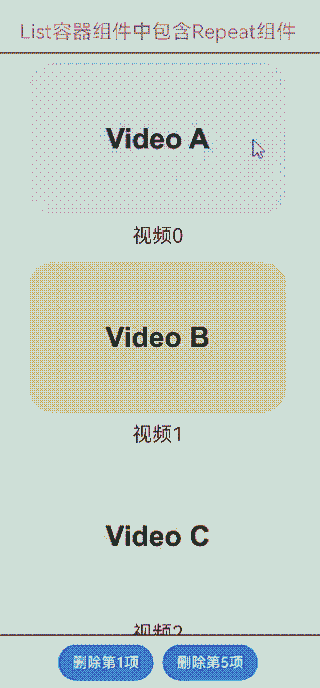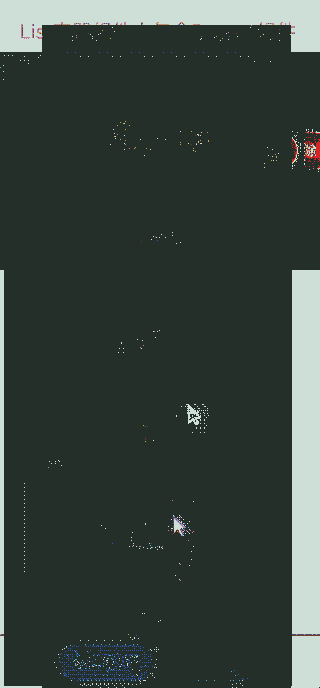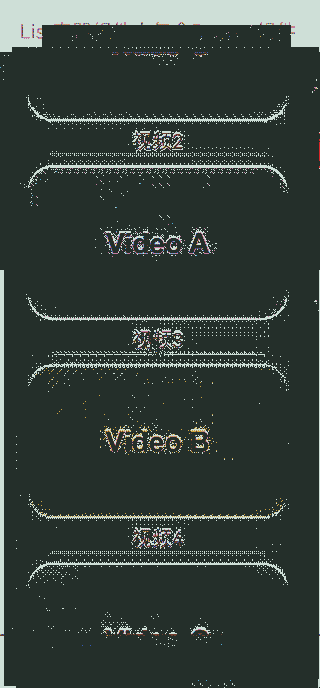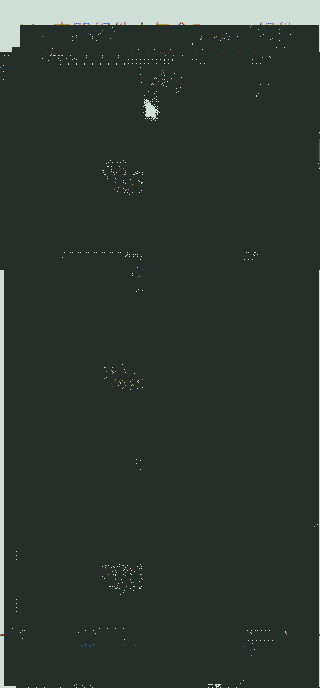
与List组合使用
在List容器组件中使用Repeat,示例代码如下:
class DemoListItemInfo {
name: string;
icon: Resource;
constructor(name: string, icon: Resource) {
this.name = name;
this.icon = icon;
}
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct DemoList {
@Local videoList: Array<DemoListItemInfo> = [];
aboutToAppear(): void {
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// 此处app.media.listItem0、app.media.listItem1、app.media.listItem2仅作示例,请开发者自行替换
this.videoList.push(new DemoListItemInfo('视频' + i,
i % 3 == 0 ? $r("app.media.listItem0") :
i % 3 == 1 ? $r("app.media.listItem1") : $r("app.media.listItem2")));
}
}
@Builder
itemEnd(index: number) {
Button('删除')
.backgroundColor(Color.Red)
.onClick(() => {
this.videoList.splice(index, 1);
})
}
build() {
Column({ space: 10 }) {
Text('List容器组件中包含Repeat组件')
.fontSize(15)
.fontColor(Color.Gray)
List({ space: 5 }) {
Repeat<DemoListItemInfo>(this.videoList)
.each((obj: RepeatItem<DemoListItemInfo>) => {
ListItem() {
Column() {
Image(obj.item.icon)
.width('80%')
.margin(10)
Text(obj.item.name)
.fontSize(20)
}
}
.swipeAction({
end: {
builder: () => {
this.itemEnd(obj.index);
}
}
})
.onAppear(() => {
console.info('AceTag', obj.item.name);
})
})
.key((item: DemoListItemInfo) => item.name)
.virtualScroll()
}
.cachedCount(2)
.height('90%')
.border({ width: 1 })
.listDirection(Axis.Vertical)
.alignListItem(ListItemAlign.Center)
.divider({
strokeWidth: 1,
startMargin: 60,
endMargin: 60,
color: '#ffe9f0f0'
})
Row({ space: 10 }) {
Button('删除第1项')
.onClick(() => {
this.videoList.splice(0, 1);
})
Button('删除第5项')
.onClick(() => {
this.videoList.splice(4, 1);
})
}
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
}
右滑并点击按钮,或点击底部按钮,可删除视频卡片:
与Grid组合使用
在Grid容器组件中使用Repeat,示例如下:
class DemoGridItemInfo {
name: string;
icon: Resource;
constructor(name: string, icon: Resource) {
this.name = name;
this.icon = icon;
}
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct DemoGrid {
@Local itemList: Array<DemoGridItemInfo> = [];
@Local isRefreshing: boolean = false;
private layoutOptions: GridLayoutOptions = {
regularSize: [1, 1],
irregularIndexes: [10]
}
private GridScroller: Scroller = new Scroller();
private num: number = 0;
aboutToAppear(): void {
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// 此处app.media.gridItem0、app.media.gridItem1、app.media.gridItem2仅作示例,请开发者自行替换
this.itemList.push(new DemoGridItemInfo('视频' + i,
i % 3 == 0 ? $r("app.media.gridItem0") :
i % 3 == 1 ? $r("app.media.gridItem1") : $r("app.media.gridItem2")));
}
}
build() {
Column({ space: 10 }) {
Text('Grid容器组件中包含Repeat组件')
.fontSize(15)
.fontColor(Color.Gray)
Refresh({ refreshing: $$this.isRefreshing }) {
Grid(this.GridScroller, this.layoutOptions) {
Repeat<DemoGridItemInfo>(this.itemList)
.each((obj: RepeatItem<DemoGridItemInfo>) => {
if (obj.index === 10 ) {
GridItem() {
Text('先前浏览至此,点击刷新')
.fontSize(20)
}
.height(30)
.border({ width: 1 })
.onClick(() => {
this.GridScroller.scrollToIndex(0);
this.isRefreshing = true;
})
.onAppear(() => {
console.info('AceTag', obj.item.name);
})
} else {
GridItem() {
Column() {
Image(obj.item.icon)
.width('100%')
.height(80)
.objectFit(ImageFit.Cover)
.borderRadius({ topLeft: 16, topRight: 16 })
Text(obj.item.name)
.fontSize(15)
.height(20)
}
}
.height(100)
.borderRadius(16)
.backgroundColor(Color.White)
.onAppear(() => {
console.info('AceTag', obj.item.name);
})
}
})
.key((item: DemoGridItemInfo) => item.name)
.virtualScroll()
}
.columnsTemplate('repeat(auto-fit, 150)')
.cachedCount(4)
.rowsGap(15)
.columnsGap(10)
.height('100%')
.padding(10)
.backgroundColor('#F1F3F5')
}
.onRefreshing(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
this.itemList.splice(10, 1);
this.itemList.unshift(new DemoGridItemInfo('refresh', $r('app.media.gridItem0'))); // 此处app.media.gridItem0仅作示例,请开发者自行替换
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// 此处app.media.gridItem0、app.media.gridItem1、app.media.gridItem2仅作示例,请开发者自行替换
this.itemList.unshift(new DemoGridItemInfo('新视频' + this.num,
i % 3 == 0 ? $r("app.media.gridItem0") :
i % 3 == 1 ? $r("app.media.gridItem1") : $r("app.media.gridItem2")));
this.num++;
}
this.isRefreshing = false;
}, 1000);
console.info('AceTag', 'onRefreshing');
})
.refreshOffset(64)
.pullToRefresh(true)
.width('100%')
.height('85%')
Button('刷新')
.onClick(() => {
this.GridScroller.scrollToIndex(0);
this.isRefreshing = true;
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
}
下拉屏幕,或点击刷新按钮,或点击“先前浏览至此,点击刷新”,可加载新的视频内容:

与Swiper组合使用
在Swiper容器组件中使用Repeat,示例如下:
const remotePictures: Array<string> = [
'https://www.example.com/xxx/0001.jpg', // 请填写具体的网络图片地址
'https://www.example.com/xxx/0002.jpg',
'https://www.example.com/xxx/0003.jpg',
'https://www.example.com/xxx/0004.jpg',
'https://www.example.com/xxx/0005.jpg',
'https://www.example.com/xxx/0006.jpg',
'https://www.example.com/xxx/0007.jpg',
'https://www.example.com/xxx/0008.jpg',
'https://www.example.com/xxx/0009.jpg'
];
@ObservedV2
class DemoSwiperItemInfo {
id: string;
@Trace url: string = 'default';
constructor(id: string) {
this.id = id;
}
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct DemoSwiper {
@Local pics: Array<DemoSwiperItemInfo> = [];
aboutToAppear(): void {
for (let i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
this.pics.push(new DemoSwiperItemInfo('pic' + i));
}
setTimeout(() => {
this.pics[0].url = remotePictures[0];
}, 1000);
}
build() {
Column() {
Text('Swiper容器组件中包含Repeat组件')
.fontSize(15)
.fontColor(Color.Gray)
Stack() {
Text('图片加载中')
.fontSize(15)
.fontColor(Color.Gray)
Swiper() {
Repeat(this.pics)
.each((obj: RepeatItem<DemoSwiperItemInfo>) => {
Image(obj.item.url)
.onAppear(() => {
console.info('AceTag', obj.item.id);
})
})
.key((item: DemoSwiperItemInfo) => item.id)
.virtualScroll()
}
.cachedCount(9)
.height('50%')
.loop(false)
.indicator(true)
.onChange((index) => {
setTimeout(() => {
this.pics[index].url = remotePictures[index];
}, 1000);
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor(Color.Black)
}
}
}
定时1秒后加载图片,模拟网络延迟:

关闭懒加载
当关闭Repeat的.virtualScroll()属性时(即省略该属性),Repeat在初始化页面时加载列表中的所有子组件,适合短数据列表/组件全部加载的场景。对于长数据列表(数据长度大于30),如果关闭懒加载,Repeat会一次性加载全量子组件,此操作耗时长,不建议使用。
注意:
- 渲染模板特性(template)不可用。
- 不受滚动容器组件的限制,可以在任意场景使用。
- 支持与V1装饰器混用。
- 页面刷新取决于键值变化:如果键值相同,即使数据改变,页面也不会刷新。详见节点更新能力说明。
节点更新能力说明
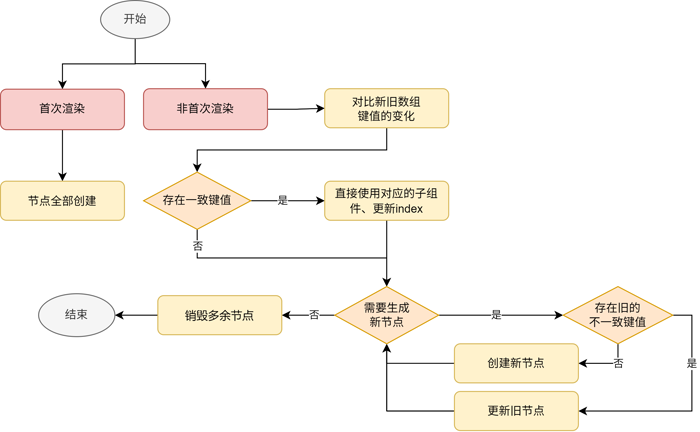
(关闭懒加载后)页面首次渲染时,Repeat子组件全部创建。数组发生改变后,Repeat对子组件节点的处理分为以下几个步骤:
首先,遍历旧数组键值。如果新数组中没有该键值,将其加入键值集合deletedKeys。
其次,遍历新数组键值。依次判断以下条件,进行符合条件的操作:
- 若在旧数组中能找到相同键值,直接使用对应的子组件节点,并更新索引index。
- 若deletedKeys非空,按照先进后出的顺序,更新该集合中的键值所对应的节点。
- 若deletedKeys为空,则表示没有可以更新的节点,需要创建新节点。
最后,如果新数组键值遍历结束后,deletedKeys非空,则销毁集合中的键值所对应的节点。
以下图中的数组变化为例,图中的item_X表示数据项的键值key。
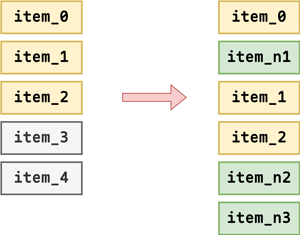
根据上述判断逻辑:item_0没有变化,item_1和item_2只更新了索引,item_n1和item_n2分别由item_4和item_3进行节点更新获得,item_n3为新创建的节点。
说明:
Repeat关闭懒加载场景与ForEach组件的区别: - 针对特定数组更新场景的渲染性能进行了优化 - 将子组件的内容/索引管理职责转移至框架层面
示例
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Parent {
@Local simpleList: Array<string> = ['one', 'two', 'three'];
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Text('点击修改第3个数组项的值')
.fontSize(24)
.fontColor(Color.Red)
.onClick(() => {
this.simpleList[2] = 'new three';
})
Repeat<string>(this.simpleList)
.each((obj: RepeatItem<string>)=>{
ChildItem({ item: obj.item })
.margin({top: 20})
})
.key((item: string) => item)
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor(0xF1F3F5)
}
}
@ComponentV2
struct ChildItem {
@Param @Require item: string;
build() {
Text(this.item)
.fontSize(30)
}
}

点击红色字体,第三个数据项发生变化(直接使用旧的组件节点,仅刷新数据)。
常见问题
屏幕外的列表数据发生变化时,保证滚动条位置不变
以下示例中,屏幕外的数据源变化将影响屏幕中List列表Scroller停留的位置: 在List组件中声明Repeat组件,实现key值生成逻辑和each逻辑(如下示例代码),点击按钮“insert”,在屏幕显示的第一个元素前面插入一个元素,屏幕出现向下滚动。
// 定义一个类,标记为可观察的
// 类中自定义一个数组,标记为可追踪的
@ObservedV2
class ArrayHolder {
@Trace arr: Array<number> = [];
// constructor,用于初始化数组个数
constructor(count: number) {
for (let i = 0; i < count; i++) {
this.arr.push(i);
}
}
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct RepeatTemplateSingle {
@Local arrayHolder: ArrayHolder = new ArrayHolder(100);
@Local totalCount: number = this.arrayHolder.arr.length;
scroller: Scroller = new Scroller();
build() {
Column({ space: 5 }) {
List({ space: 20, initialIndex: 19, scroller: this.scroller }) {
Repeat(this.arrayHolder.arr)
.virtualScroll({ totalCount: this.totalCount })
.templateId((item, index) => {
return 'number';
})
.template('number', (r) => {
ListItem() {
Text(r.index! + ":" + r.item + "Reuse");
}
})
.each((r) => {
ListItem() {
Text(r.index! + ":" + r.item + "eachMessage");
}
})
}
.height('30%')
Button(`insert totalCount ${this.totalCount}`)
.height(60)
.onClick(() => {
// 插入元素,元素位置为屏幕显示的前一个元素
this.arrayHolder.arr.splice(18, 0, this.totalCount);
this.totalCount = this.arrayHolder.arr.length;
})
}
.width('100%')
.margin({ top: 5 })
}
}
运行效果:

以下为修正后的示例: 在一些场景中,我们不希望屏幕外的数据源变化影响屏幕中List列表Scroller停留的位置,可以通过List组件的onScrollIndex事件对列表滚动动作进行监听,当列表发生滚动时,获取列表滚动位置。使用Scroller组件的scrollToIndex特性,滑动到指定index位置,实现屏幕外的数据源增加/删除数据时,Scroller停留的位置不变的效果。
示例代码仅对增加数据的情况进行展示。
// ...ArrayHolder的定义和上述demo代码一致
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct RepeatTemplateSingle {
@Local arrayHolder: ArrayHolder = new ArrayHolder(100);
@Local totalCount: number = this.arrayHolder.arr.length;
scroller: Scroller = new Scroller();
private start: number = 1;
private end: number = 1;
build() {
Column({ space: 5 }) {
List({ space: 20, initialIndex: 19, scroller: this.scroller }) {
Repeat(this.arrayHolder.arr)
.virtualScroll({ totalCount: this.totalCount })
.templateId((item, index) => {
return 'number';
})
.template('number', (r) => {
ListItem() {
Text(r.index! + ":" + r.item + "Reuse")
}
})
.each((r) => {
ListItem() {
Text(r.index! + ":" + r.item + "eachMessage")
}
})
}
.onScrollIndex((start, end) => {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
})
.height('30%')
Button(`insert totalCount ${this.totalCount}`)
.height(60)
.onClick(() => {
// 插入元素,元素位置为屏幕显示的前一个元素
this.arrayHolder.arr.splice(18, 0, this.totalCount);
let rect = this.scroller.getItemRect(this.start); // 获取子组件的大小位置
this.scroller.scrollToIndex(this.start + 1); // 滑动到指定index
this.scroller.scrollBy(0, -rect.y); // 滑动指定距离
this.totalCount = this.arrayHolder.arr.length;
})
}
.width('100%')
.margin({ top: 5 })
}
}
运行效果:

totalCount值大于数据源长度
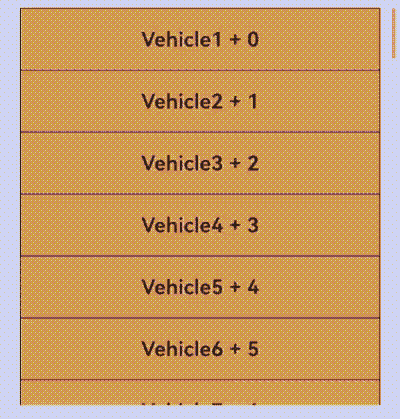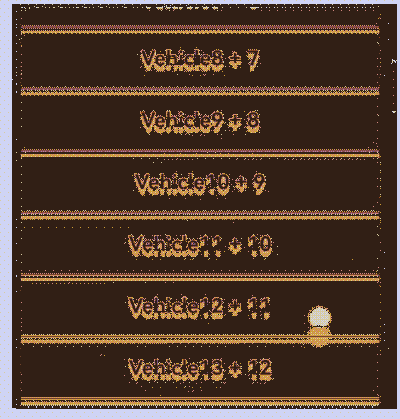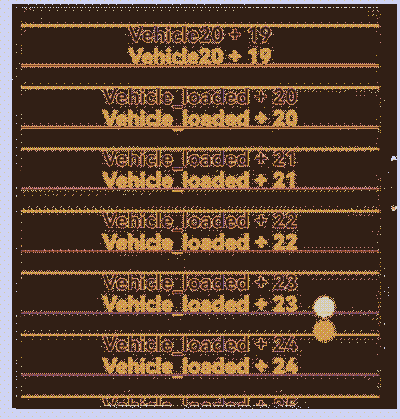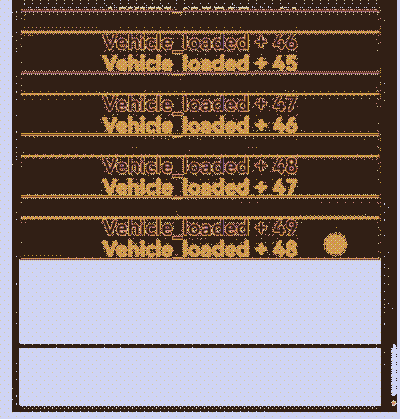
当数据源总长度很大时,会使用懒加载的方式先加载一部分数据,为了使Repeat显示正确的滚动条样式,需要将数据总长度赋值给totalCount,即数据源全部加载完成前,totalCount大于array.length。
totalCount > array.length时,在父组件容器滚动过程中,应用需要保证列表即将滑动到数据源末尾时请求后续数据,开发者需要对数据请求的错误场景(如网络延迟)进行保护操作,直到数据源全部加载完成,否则列表滑动的过程中会出现滚动效果异常。
上述规范可以通过实现父组件List/Grid的onScrollIndex属性的回调函数完成。示例代码如下:
@ObservedV2
class VehicleData {
@Trace name: string;
@Trace price: number;
constructor(name: string, price: number) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
}
@ObservedV2
class VehicleDB {
public vehicleItems: VehicleData[] = [];
constructor() {
// 数组初始化大小 20
for (let i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
this.vehicleItems.push(new VehicleData(`Vehicle${i}`, i));
}
}
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct entryCompSucc {
@Local vehicleItems: VehicleData[] = new VehicleDB().vehicleItems;
@Local listChildrenSize: ChildrenMainSize = new ChildrenMainSize(60);
@Local totalCount: number = this.vehicleItems.length;
scroller: Scroller = new Scroller();
build() {
Column({ space: 3 }) {
List({ scroller: this.scroller }) {
Repeat(this.vehicleItems)
.virtualScroll({ totalCount: 50 }) // 数组预期长度 50
.templateId(() => 'default')
.template('default', (ri) => {
ListItem() {
Column() {
Text(`${ri.item.name} + ${ri.index}`)
.width('90%')
.height(this.listChildrenSize.childDefaultSize)
.backgroundColor(0xFFA07A)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.fontSize(20)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}
}.border({ width: 1 })
}, { cachedCount: 5 })
.each((ri) => {
ListItem() {
Text("Wrong: " + `${ri.item.name} + ${ri.index}`)
.width('90%')
.height(this.listChildrenSize.childDefaultSize)
.backgroundColor(0xFFA07A)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.fontSize(20)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}.border({ width: 1 })
})
.key((item, index) => `${index}:${item}`)
}
.height('50%')
.margin({ top: 20 })
.childrenMainSize(this.listChildrenSize)
.alignListItem(ListItemAlign.Center)
.onScrollIndex((start, end) => {
console.log('onScrollIndex', start, end);
// 数据懒加载
if (this.vehicleItems.length < 50) {
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (this.vehicleItems.length < 50) {
this.vehicleItems.push(new VehicleData("Vehicle_loaded", i));
}
}
}
})
}
}
}
示例代码运行效果:
Repeat与@Builder混用
当Repeat与@Builder混用时,必须将RepeatItem类型整体进行传参,组件才能监听到数据变化,如果只传递RepeatItem.item或RepeatItem.index,将会出现UI渲染异常。
示例代码如下:
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct RepeatBuilderPage {
@Local simpleList1: Array<number> = [];
@Local simpleList2: Array<number> = [];
aboutToAppear(): void {
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
this.simpleList1.push(i);
this.simpleList2.push(i);
}
}
build() {
Column({ space: 20 }) {
Text('Repeat与@Builder混用,左边是异常场景,右边是正常场景,向下滑动一段距离可以看出差别')
.fontSize(15)
.fontColor(Color.Gray)
Row({ space: 20 }) {
List({ initialIndex: 5, space: 20 }) {
Repeat<number>(this.simpleList1)
.each((ri) => {})
.virtualScroll({ totalCount: this.simpleList1.length })
.templateId((item: number, index: number) => "default")
.template('default', (ri) => {
ListItem() {
Column() {
Text('Text id = ' + ri.item)
.fontSize(20)
this.buildItem1(ri.item) // 错误示例,为避免渲染异常,应修改为:this.buildItem1(ri)
}
}
.border({ width: 1 })
}, { cachedCount: 3 })
}
.cachedCount(1)
.border({ width: 1 })
.width('45%')
.height('60%')
List({ initialIndex: 5, space: 20 }) {
Repeat<number>(this.simpleList2)
.each((ri) => {})
.virtualScroll({ totalCount: this.simpleList2.length })
.templateId((item: number, index: number) => "default")
.template('default', (ri) => {
ListItem() {
Column() {
Text('Text id = ' + ri.item)
.fontSize(20)
this.buildItem2(ri) // 正确示例,渲染正常
}
}
.border({ width: 1 })
}, { cachedCount: 3 })
}
.cachedCount(1)
.border({ width: 1 })
.width('45%')
.height('60%')
}
}
.height('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
@Builder
// @Builder参数必须传RepeatItem类型才能正常渲染
buildItem1(item: number) {
Text('Builder1 id = ' + item)
.fontSize(20)
.fontColor(Color.Red)
.margin({ top: 2 })
}
@Builder
buildItem2(ri: RepeatItem<number>) {
Text('Builder2 id = ' + ri.item)
.fontSize(20)
.fontColor(Color.Red)
.margin({ top: 2 })
}
}
界面展示如下图,进入页面后向下滑动一段距离可以看出差别,左边是错误用法,右边是正确用法(Text组件为黑色,Builder组件为红色)。上述代码展示了开发过程中易出错的场景,即在@Builder构造函数中传参方式为值传递。

你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙\@AnimatableExtend装饰器:定义可动画属性
harmony 鸿蒙AppStorage:应用全局的UI状态存储
harmony 鸿蒙\@Builder装饰器:自定义构建函数