harmony 鸿蒙自定义组件冻结功能
自定义组件冻结功能
当@ComponentV2装饰的自定义组件处于非激活状态时,状态变量将不响应更新,即@Monitor不会调用,状态变量关联的节点不会刷新。该冻结机制在复杂UI场景下能显著优化性能,避免非激活组件因状态变量更新进行无效刷新,从而减少资源消耗。通过freezeWhenInactive属性来决定是否使用冻结功能,不传参数时默认不使用。支持的场景有:页面路由、TabContent、Navigation、Repeat。
在阅读本文档前,开发者需要了解\@ComponentV2基本语法。建议提前阅读:\@ComponentV2。
说明:
从API version 12开始,支持@ComponentV2装饰的自定义组件冻结功能。
从API version 18开始,支持自定义组件冻结功能的混用场景冻结。
与@Component的组件冻结不同,@ComponentV2装饰的自定义组件不支持在LazyForEach场景下缓存节点组件冻结。
当前支持的场景
页面路由
说明:
本示例使用了router进行页面跳转,建议开发者使用组件导航(Navigation)代替页面路由(router)来实现页面切换。Navigation提供了更多的功能和更灵活的自定义能力。请参考使用Navigation的组件冻结用例。
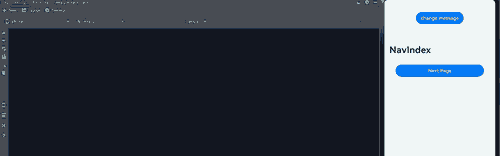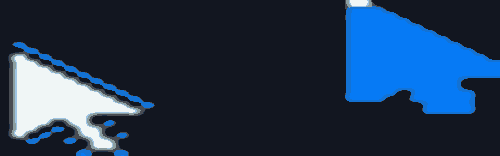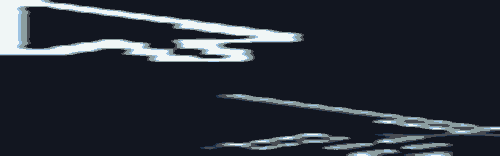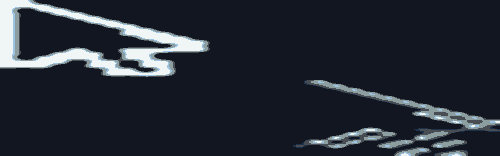
- 当页面1调用router.pushUrl接口跳转到页面2时,页面1为隐藏不可见状态,此时如果更新页面1中的状态变量,不会触发页面1刷新。 图示如下:
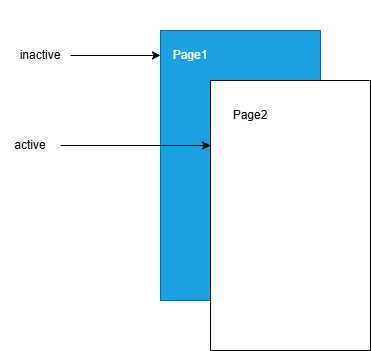
页面1:
@ObservedV2
export class Book {
@Trace name: string = "100";
constructor(page: string) {
this.name = page;
}
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2({ freezeWhenInactive: true })
export struct Page1 {
@Local bookTest: Book = new Book("A Midsummer Night’s Dream");
@Monitor("bookTest.name")
onMessageChange(monitor: IMonitor) {
console.log(`The book name change from ${monitor.value()?.before} to ${monitor.value()?.now}`);
}
build() {
Column() {
Text(`Book name is ${this.bookTest.name}`).fontSize(25)
Button('changeBookName').fontSize(25)
.onClick(() => {
this.bookTest.name = "The Old Man and the Sea";
})
Button('go to next page').fontSize(25)
.onClick(() => {
this.getUIContext().getRouter().pushUrl({ url: 'pages/Page2' });
setTimeout(() => {
this.bookTest = new Book("Jane Austen's Pride and Prejudice");
}, 1000)
})
}
}
}
页面2:
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Page2 {
build() {
Column() {
Text(`This is the page2`).fontSize(25)
Button('Back')
.onClick(() => {
this.getUIContext().getRouter().back();
})
}
}
}
在上面的示例中:
点击页面1中的Button “changeBookName”,bookTest变量的name属性改变,@Monitor中注册的方法onMessageChange会被调用。
点击页面1中的Button “go to next page”,跳转到页面2,然后延迟1s更新状态变量“bookTest”。在更新“bookTest”的时候,已经跳转到页面2,页面1处于inactive状态,状态变量
@Local bookTest将不响应更新,其@Monitor不会调用,状态变量关联的节点不会刷新。
Trace如下:
- 点击“back”,页面2被销毁,页面1的状态由inactive变为active。状态变量“bookTest”的更新被观察到,@Monitor中注册的方法onMessageChange被调用,对应的Text显示内容改变。

TabContent
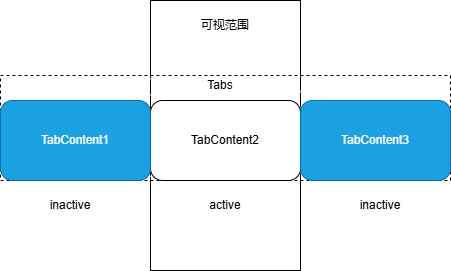
对Tabs中当前不可见的TabContent进行冻结,不会触发组件的更新。
需要注意的是:在首次渲染的时候,Tab只会创建当前正在显示的TabContent,当切换全部的TabContent后,TabContent才会被全部创建。
图示如下:
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct TabContentTest {
@Local message: number = 0;
@Local data: number[] = [0, 1];
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Button('change message').onClick(() => {
this.message++;
})
Tabs() {
ForEach(this.data, (item: number) => {
TabContent() {
FreezeChild({ message: this.message, index: item })
}.tabBar(`tab${item}`)
}, (item: number) => item.toString())
}
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
@ComponentV2({ freezeWhenInactive: true })
struct FreezeChild {
@Param message: number = 0;
@Param index: number = 0;
@Monitor('message') onMessageUpdated(mon: IMonitor) {
console.info(`FreezeChild message callback func ${this.message}, index: ${this.index}`);
}
build() {
Text("message" + `${this.message}, index: ${this.index}`)
.fontSize(50)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}
}
在上面的示例中:
1.点击“change message”更改message的值,当前正在显示的TabContent组件中的@Monitor中注册的方法onMessageUpdated被触发。
2.点击TabBar“tab1”切换到另外的TabContent,TabContent状态由inactive变为active,对应的@Monitor中注册的方法onMessageUpdated被触发。
3.再次点击“change message”更改message的值,仅当前显示的TabContent子组件中的@Monitor中注册的方法onMessageUpdated被触发。其他inactive的TabContent组件不会触发@Monitor。
Navigation
- 当NavDestination不可见时,会将其子自定义组件设置成非激活态,不会触发组件的刷新。当返回该页面时,其子自定义组件重新恢复成激活态,触发@Monitor回调进行刷新。
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct MyNavigationTestStack {
@Provider('pageInfo') pageInfo: NavPathStack = new NavPathStack();
@Local message: number = 0;
@Monitor('message') info() {
console.info(`freeze-test MyNavigation message callback ${this.message}`);
}
@Builder
PageMap(name: string) {
if (name === 'pageOne') {
pageOneStack({ message: this.message })
} else if (name === 'pageTwo') {
pageTwoStack({ message: this.message })
} else if (name === 'pageThree') {
pageThreeStack({ message: this.message })
}
}
build() {
Column() {
Button('change message')
.onClick(() => {
this.message++;
})
Navigation(this.pageInfo) {
Column() {
Button('Next Page', { stateEffect: true, type: ButtonType.Capsule })
.onClick(() => {
this.pageInfo.pushPath({ name: 'pageOne' }); //将name指定的NavDestination页面信息入栈
})
}
}.title('NavIndex')
.navDestination(this.PageMap)
.mode(NavigationMode.Stack)
}
}
}
@ComponentV2
struct pageOneStack {
@Consumer('pageInfo') pageInfo: NavPathStack = new NavPathStack();
@Local index: number = 1;
@Param message: number = 0;
build() {
NavDestination() {
Column() {
NavigationContentMsgStack({ message: this.message, index: this.index })
Text("cur stack size:" + `${this.pageInfo.size()}`)
.fontSize(30)
Button('Next Page', { stateEffect: true, type: ButtonType.Capsule })
.onClick(() => {
this.pageInfo.pushPathByName('pageTwo', null);
})
Button('Back Page', { stateEffect: true, type: ButtonType.Capsule })
.onClick(() => {
this.pageInfo.pop();
})
}.width('100%').height('100%')
}.title('pageOne')
.onBackPressed(() => {
this.pageInfo.pop();
return true;
})
}
}
@ComponentV2
struct pageTwoStack {
@Consumer('pageInfo') pageInfo: NavPathStack = new NavPathStack();
@Local index: number = 2;
@Param message: number = 0;
build() {
NavDestination() {
Column() {
NavigationContentMsgStack({ message: this.message, index: this.index })
Text("cur stack size:" + `${this.pageInfo.size()}`)
.fontSize(30)
Button('Next Page', { stateEffect: true, type: ButtonType.Capsule })
.onClick(() => {
this.pageInfo.pushPathByName('pageThree', null);
})
Button('Back Page', { stateEffect: true, type: ButtonType.Capsule })
.onClick(() => {
this.pageInfo.pop();
})
}
}.title('pageTwo')
.onBackPressed(() => {
this.pageInfo.pop();
return true;
})
}
}
@ComponentV2
struct pageThreeStack {
@Consumer('pageInfo') pageInfo: NavPathStack = new NavPathStack();
@Local index: number = 3;
@Param message: number = 0;
build() {
NavDestination() {
Column() {
NavigationContentMsgStack({ message: this.message, index: this.index })
Text("cur stack size:" + `${this.pageInfo.size()}`)
.fontSize(30)
Button('Next Page', { stateEffect: true, type: ButtonType.Capsule })
.height(40)
.onClick(() => {
this.pageInfo.pushPathByName('pageOne', null);
})
Button('Back Page', { stateEffect: true, type: ButtonType.Capsule })
.height(40)
.onClick(() => {
this.pageInfo.pop();
})
}
}.title('pageThree')
.onBackPressed(() => {
this.pageInfo.pop();
return true;
})
}
}
@ComponentV2({ freezeWhenInactive: true })
struct NavigationContentMsgStack {
@Param message: number = 0;
@Param index: number = 0;
@Monitor('message') info() {
console.info(`freeze-test NavigationContent message callback ${this.message}`);
console.info(`freeze-test ---- called by content ${this.index}`);
}
build() {
Column() {
Text("msg:" + `${this.message}`)
.fontSize(30)
}
}
}
在上面的示例中:
1.点击“change message”更改message的值,当前正在显示的MyNavigationTestStack组件中的@Monitor中注册的方法info被触发。
2.点击“Next Page”切换到PageOne,创建pageOneStack节点。
3.再次点击“change message”更改message的值,仅pageOneStack中的NavigationContentMsgStack子组件中的@Monitor中注册的方法info被触发。
4.再次点击“Next Page”切换到PageTwo,创建pageTwoStack节点。pageOneStack节点状态由active变为inactive。
5.再次点击“change message”更改message的值,仅pageTwoStack中的NavigationContentMsgStack子组件中的@Monitor中注册的方法info被触发。Navigation路由栈中非栈顶的NavDestination中的子自定义组件,将是inactive状态。@Monitor方法不会触发。
6.再次点击“Next Page”切换到PageThree,创建pageThreeStack节点。pageTwoStack节点状态由active变为inactive。
7.再次点击“change message”更改message的值,仅pageThreeStack中的NavigationContentMsgStack子组件中的@Monitor中注册的方法info被触发。Navigation路由栈中非栈顶的NavDestination中的子自定义组件,将是inactive状态。@Monitor方法不会触发。
8.点击“Back Page”回到PageTwo,此时,pageTwoStack节点状态由inactive变为active,其NavigationContentMsgStack子组件中的@Monitor中注册的方法info被触发。
9.再次点击“Back Page”回到PageOne,此时,pageOneStack节点状态由inactive变为active,其NavigationContentMsgStack子组件中的@Monitor中注册的方法info被触发。
10.再次点击“Back Page”回到初始页。
Repeat
说明:
Repeat从API version 18开始支持自定义组件冻结。
对Repeat缓存池中的自定义组件进行冻结,避免不必要的组件刷新。建议提前阅读Repeat节点更新/复用能力说明。
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct RepeatVirtualScrollFreeze {
@Local simpleList: Array<string> = [];
@Local bgColor: Color = Color.Pink;
aboutToAppear(): void {
for (let i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
this.simpleList.push(`item${i}`);
}
}
build() {
Column() {
Row() {
Button(`Reduce length to 5`)
.onClick(() => {
this.simpleList = this.simpleList.slice(0, 5);
})
Button(`Change bgColor`)
.onClick(() => {
this.bgColor = this.bgColor == Color.Pink ? Color.Blue : Color.Pink;
})
}
List() {
Repeat(this.simpleList)
.each((obj: RepeatItem<string>) => {
})
.key((item: string, index: number) => item)
.virtualScroll({ totalCount: this.simpleList.length })
.templateId(() => `a`)
.template(`a`, (ri) => {
ChildComponent({
message: ri.item,
bgColor: this.bgColor
})
}, { cachedCount: 2 })
}
.cachedCount(0)
.height(500)
}
.height(`100%`)
}
}
// 开启组件冻结
@ComponentV2({ freezeWhenInactive: true })
struct ChildComponent {
@Param @Require message: string = ``;
@Param @Require bgColor: Color = Color.Pink;
@Monitor(`bgColor`)
onBgColorChange(monitor: IMonitor) {
// bgColor改变时,缓存池中组件不刷新,不会打印日志
console.log(`repeat---bgColor change from ${monitor.value()?.before} to ${monitor.value()?.now}`);
}
build() {
Text(`[a]: ${this.message}`)
.fontSize(50)
.backgroundColor(this.bgColor)
}
}
在上面的示例中:
点击“Reduce length to 5”后,被移除的两个组件会进入Repeat缓存池,然后点击“Change bgColor”更改bgColor的值触发节点刷新。
开启组件冻结(freezeWhenInactive: true),只有剩余节点中@Monitor装饰的方法onBgColorChange被触发,如示例中屏上的5个节点会刷新并打印5条日志,缓存池中的节点则不会。

// 关闭组件冻结
@ComponentV2({ freezeWhenInactive: false })
struct ChildComponent {
@Param @Require message: string = ``;
@Param @Require bgColor: Color = Color.Pink;
@Monitor(`bgColor`)
onBgColorChange(monitor: IMonitor) {
// bgColor改变时,缓存池组件也会刷新,并打印日志
console.log(`repeat---bgColor change from ${monitor.value()?.before} to ${monitor.value()?.now}`);
}
build() {
Text(`[a]: ${this.message}`)
.fontSize(50)
.backgroundColor(this.bgColor)
}
}
不开启组件冻结(freezeWhenInactive: false,当未指定freezeWhenInactive参数时默认不开启组件冻结),剩余节点和缓存池节点中@Monitor装饰的方法onBgColorChange都会被触发,即会有7个节点会刷新并打印7条日志。

仅子组件开启组件冻结
如果开发者只想冻结某个子组件,可以选择只在子组件设置freezeWhenInactive为true。
// Page1.ets
@ObservedV2
class Book {
@Trace name: string = 'TS';
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name;
}
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Page1 {
pageInfo: NavPathStack = new NavPathStack();
build() {
Column() {
Navigation(this.pageInfo) {
Child()
Button('Go to next page').fontSize(30)
.onClick(() => {
this.pageInfo.pushPathByName('Page2', null);
})
}
}
}
}
@ComponentV2({ freezeWhenInactive: true })
export struct Child {
@Local bookTest: Book = new Book(`A Midsummer Night's Dream`);
@Monitor('bookTest.name')
onMessageChange(monitor: IMonitor) {
console.log(`The book name change from ${monitor.value()?.before} to ${monitor.value()?.now}`);
}
textUpdate(): number {
console.log('The text is update');
return 25;
}
build() {
Column() {
Text(`The book name is ${this.bookTest.name}`).fontSize(this.textUpdate())
Button('change BookName')
.onClick(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
this.bookTest = new Book("Jane Austen's Pride and Prejudice");
}, 3000);
})
}
}
}
// Page2.ets
@Builder
function Page2Builder() {
Page2()
}
@ComponentV2
struct Page2 {
pathStack: NavPathStack = new NavPathStack();
build() {
NavDestination() {
Column() {
Text('This is the Page2')
Button('Back').fontSize(30)
.onClick(() => {
this.pathStack.pop();
})
}
}.onReady((context: NavDestinationContext) => {
this.pathStack = context.pathStack;
})
}
}
使用Navigation时,需要添加配置系统路由表文件src/main/resources/base/profile/route_map.json,并替换pageSourceFile为Page2页面的路径,并且在module.json5中添加:”routerMap”: “$profile:route_map”。
{
"routerMap": [
{
"name": "Page2",
"pageSourceFile": "src/main/ets/pages/Page2.ets",
"buildFunction": "Page2Builder",
"data": {
"description" : "This is the Page2"
}
}
]
}
上述示例:
- Page1的子组件Child,设置freezeWhenInactive: true, 开启了组件冻结功能。
- 点击Button('change BookName'),然后3s内点击Button('Go to next page')。在更新bookTest的时候,已经跳转到Page2,Page1的组件处于inactive状态,又因为Child组件开启了组件冻结,状态变量@Local bookTest将不响应更新,其@Monitor装饰的回调方法不会被调用,状态变量关联的组件不会刷新。
- 点击Button('Back')回到前一个页面,调用@Monitor装饰的回调方法,状态变量关联的组件刷新。
混用场景
组件冻结混用场景即当支持组件冻结的场景彼此之间组合使用,对于不同的API version版本,冻结行为会有不同。给父组件设置组件冻结标志,在API version 17及以下,当父组件解冻时,会解冻自己子组件所有的节点;从API version 18开始,父组件解冻时,只会解冻子组件的屏上节点,详细说明见\@Component的自定义组件冻结的混用场景。
Navigation和TabContent的混用
@ComponentV2
struct ChildOfParamComponent {
@Require @Param child_val: number;
@Monitor('child_val') onChange(m: IMonitor) {
console.log(`Appmonitor ChildOfParamComponent: changed ${m.dirty[0]}: ${m.value()?.before} -> ${m.value()?.now}`);
}
build() {
Column() {
Text(`Child Param: ${this.child_val}`);
}
}
}
@ComponentV2
struct ParamComponent {
@Require @Param val: number;
@Monitor('val') onChange(m: IMonitor) {
console.log(`Appmonitor ParamComponent: changed ${m.dirty[0]}: ${m.value()?.before} -> ${m.value()?.now}`);
}
build() {
Column() {
Text(`val: ${this.val}`);
ChildOfParamComponent({child_val: this.val});
}
}
}
@ComponentV2
struct DelayComponent {
@Require @Param delayVal1: number;
@Monitor('delayVal1') onChange(m: IMonitor) {
console.log(`Appmonitor DelayComponent: changed ${m.dirty[0]}: ${m.value()?.before} -> ${m.value()?.now}`);
}
build() {
Column() {
Text(`Delay Param: ${this.delayVal1}`);
}
}
}
@ComponentV2 ({freezeWhenInactive: true})
struct TabsComponent {
private controller: TabsController = new TabsController();
@Local tabState: number = 47;
@Monitor('tabState') onChange(m: IMonitor) {
console.log(`Appmonitor TabsComponent: changed ${m.dirty[0]}: ${m.value()?.before} -> ${m.value()?.now}`);
}
build() {
Column({space: 10}) {
Button(`Incr state ${this.tabState}`)
.fontSize(25)
.onClick(() => {
console.log('Button increment state value');
this.tabState = this.tabState + 1;
})
Tabs({ barPosition: BarPosition.Start, index: 0, controller: this.controller}) {
TabContent() {
ParamComponent({val: this.tabState});
}.tabBar('Update')
TabContent() {
DelayComponent({delayVal1: this.tabState});
}.tabBar('DelayUpdate')
}
.vertical(false)
.scrollable(true)
.barMode(BarMode.Fixed)
.barWidth(400).barHeight(150).animationDuration(400)
.width('100%')
.height(200)
.backgroundColor(0xF5F5F5)
}
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct MyNavigationTestStack {
@Provide('pageInfo') pageInfo: NavPathStack = new NavPathStack();
@Builder
PageMap(name: string) {
if (name === 'pageOne') {
pageOneStack()
} else if (name === 'pageTwo') {
pageTwoStack()
}
}
build() {
Column() {
Navigation(this.pageInfo) {
Column() {
Button('Next Page', { stateEffect: true, type: ButtonType.Capsule })
.width('80%')
.height(40)
.margin(20)
.onClick(() => {
this.pageInfo.pushPath({ name: 'pageOne' }); //将name指定的NavDestination页面信息入栈
})
}
}.title('NavIndex')
.navDestination(this.PageMap)
.mode(NavigationMode.Stack)
}
}
}
@Component
struct pageOneStack {
@Consume('pageInfo') pageInfo: NavPathStack;
build() {
NavDestination() {
Column() {
TabsComponent();
Button('Next Page', { stateEffect: true, type: ButtonType.Capsule })
.width('80%')
.height(40)
.margin(20)
.onClick(() => {
this.pageInfo.pushPathByName('pageTwo', null);
})
}.width('100%').height('100%')
}.title('pageOne')
.onBackPressed(() => {
this.pageInfo.pop();
return true;
})
}
}
@Component
struct pageTwoStack {
@Consume('pageInfo') pageInfo: NavPathStack;
build() {
NavDestination() {
Column() {
Button('Back Page', { stateEffect: true, type: ButtonType.Capsule })
.width('80%')
.height(40)
.margin(20)
.onClick(() => {
this.pageInfo.pop();
})
}.width('100%').height('100%')
}.title('pageTwo')
.onBackPressed(() => {
this.pageInfo.pop();
return true;
})
}
}
在API version 17及以下:
点击Next page进入下一个页面并返回,会解冻Tabcontent所有的标签。
在API version 18及以上:
点击Next page进入下一个页面并返回,只会解冻对应标签的节点。
限制条件
如下面的例子所示,FreezeBuildNode中使用了自定义节点BuilderNode。BuilderNode可以通过命令式动态挂载组件,而组件冻结又是强依赖父子关系来通知是否开启组件冻结。如果父组件使用组件冻结,且组件树的中间层级上又启用了BuilderNode,则BuilderNode的子组件将无法被冻结。
import { BuilderNode, FrameNode, NodeController, UIContext } from '@kit.ArkUI';
// 定义一个Params类,用于传递参数
@ObservedV2
class Params {
// 单例模式,确保只有一个Params实例
static singleton_: Params;
// 获取Params实例的方法
static instance() {
if (!Params.singleton_) {
Params.singleton_ = new Params(0);
}
return Params.singleton_;
}
// 使用@Trace装饰器装饰message属性,以便跟踪其变化
@Trace message: string = "Hello";
index: number = 0;
constructor(index: number) {
this.index = index;
}
}
// 定义一个buildNodeChild组件,它包含一个message属性和一个index属性
@ComponentV2
struct buildNodeChild {
// 使用Params实例作为storage属性
storage: Params = Params.instance();
@Param index: number = 0;
// 使用@Monitor装饰器监听storage.message的变化
@Monitor("storage.message")
onMessageChange(monitor: IMonitor) {
console.log(`FreezeBuildNode buildNodeChild message callback func ${this.storage.message}, index:${this.index}`);
}
build() {
Text(`buildNode Child message: ${this.storage.message}`).fontSize(30)
}
}
// 定义一个buildText函数,它接收一个Params参数并构建一个Column组件
@Builder
function buildText(params: Params) {
Column() {
buildNodeChild({ index: params.index })
}
}
class TextNodeController extends NodeController {
private textNode: BuilderNode<[Params]>|null = null;
private index: number = 0;
// 构造函数接收一个index参数
constructor(index: number) {
super();
this.index = index;
}
// 创建并返回一个FrameNode
makeNode(context: UIContext): FrameNode|null {
this.textNode = new BuilderNode(context);
this.textNode.build(wrapBuilder<[Params]>(buildText), new Params(this.index));
return this.textNode.getFrameNode();
}
}
// 定义一个Index组件,它包含一个message属性和一个data数组
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Index {
// 使用Params实例作为storage属性
storage: Params = Params.instance();
private data: number[] = [0, 1];
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Button("change").fontSize(30)
.onClick(() => {
this.storage.message += 'a';
})
Tabs() {
// 使用Repeat重复渲染TabContent组件
Repeat<number>(this.data)
.each((obj: RepeatItem<number>) => {
TabContent() {
FreezeBuildNode({ index: obj.item })
.margin({ top: 20 })
}.tabBar(`tab${obj.item}`)
})
.key((item: number) => item.toString())
}
}
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
// 定义一个FreezeBuildNode组件,它包含一个message属性和一个index属性
@ComponentV2({ freezeWhenInactive: true })
struct FreezeBuildNode {
// 使用Params实例作为storage属性
storage: Params = Params.instance();
@Param index: number = 0;
// 使用@Monitor装饰器监听storage.message的变化
@Monitor("storage.message")
onMessageChange(monitor: IMonitor) {
console.log(`FreezeBuildNode message callback func ${this.storage.message}, index: ${this.index}`);
}
build() {
NodeContainer(new TextNodeController(this.index))
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor('#FFF0F0F0')
}
}
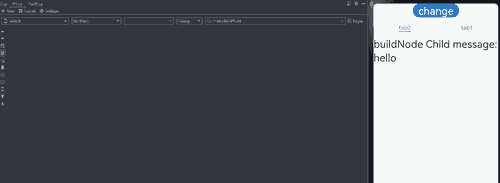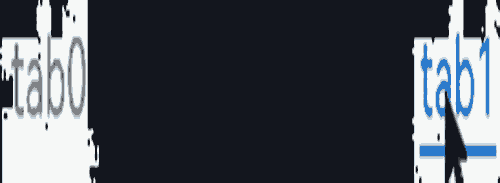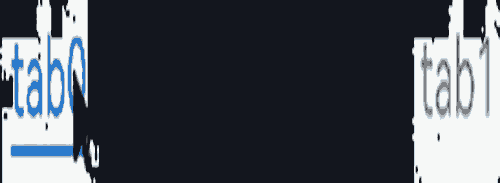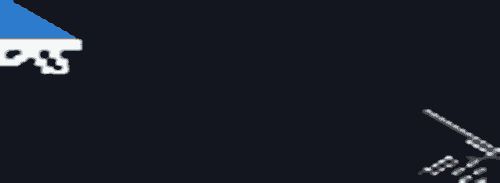
点击Button(“change”)。改变message的值,当前正在显示的TabContent组件中的@Watch中注册的方法onMessageUpdated被触发。未显示的TabContent中的BuilderNode节点下组件的@Watch方法onMessageUpdated也被触发,并没有被冻结。
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙\@AnimatableExtend装饰器:定义可动画属性
harmony 鸿蒙AppStorage:应用全局的UI状态存储
harmony 鸿蒙\@Builder装饰器:自定义构建函数