harmony 鸿蒙\@Link装饰器:父子双向同步
\@Link装饰器:父子双向同步
子组件中被\@Link装饰的变量与其父组件中对应的数据源建立双向数据绑定。
在阅读\@Link文档前,建议先熟悉\@State的基本用法。最佳实践请参考状态管理最佳实践。
说明:
从API version 9开始,该装饰器支持在ArkTS卡片中使用。
从API version 11开始,该装饰器支持在原子化服务中使用。
概述
\@Link装饰的变量与其父组件中的数据源共享相同的值。
装饰器使用规则说明
| \@Link变量装饰器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 装饰器参数 | 无。 |
| 同步类型 | 双向同步。 父组件状态变量与子组件\@Link建立双向同步,当其中一方改变时,另一方也会同步更新。 |
| 允许装饰的变量类型 | Object、class、string、number、boolean、enum类型,以及这些类型的数组。 支持Date类型。 API version 11及以上支持Map、Set类型。 支持ArkUI框架定义的联合类型Length、ResourceStr、ResourceColor类型。 类型必须指定,且与双向绑定状态变量类型相同。 支持类型的场景请参考观察变化。 不支持any类型。 API version 11及以上支持上述支持类型的联合类型。例如:string |number, string |undefined或者ClassA |null,示例见Link支持联合类型实例。 注意: 使用undefined和null的时候,建议显式指定类型,遵循TypeScript类型校验。例如: @Link a : string \|undefined。 |
| 被装饰变量的初始值 | 无,禁止本地初始化。 |
变量的传递/访问规则说明
| 传递/访问 | 说明 |
|---|---|
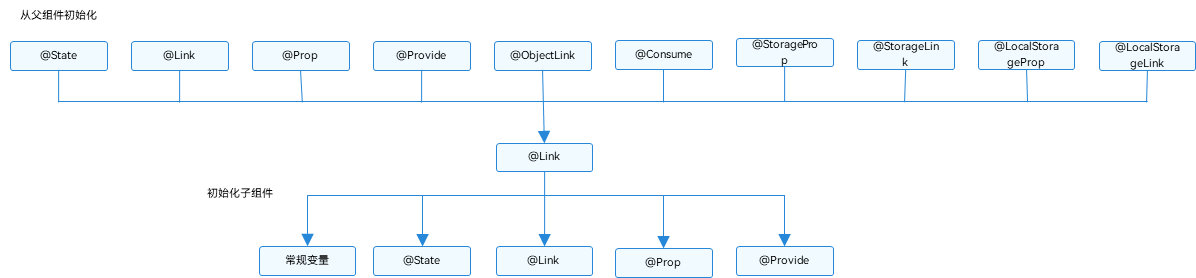
| 从父组件初始化和更新 | 必选。 - 与父组件\@State, \@StorageLink和\@Link 建立双向绑定。允许父组件中\@State、\@Link、\@Prop、\@Provide、\@Consume、\@ObjectLink、\@StorageLink、\@StorageProp、\@LocalStorageLink和\@LocalStorageProp装饰变量初始化子组件\@Link。 - 从API version 9开始,\@Link子组件从父组件初始化\@State的语法为Comp({ aLink: this.aState }),同样支持Comp({aLink: $aState})。 |
| 用于初始化子组件 | 允许,可用于初始化常规变量、\@State、\@Link、\@Prop、\@Provide。 |
| 是否支持组件外访问 | 私有,只能在所属组件内访问。 |
图1 初始化规则示意图
观察变化和行为表现
观察变化
当装饰的数据类型为boolean、string、number类型时,可以同步观察到数值的变化,示例请参考简单类型和类对象类型的@Link。
当装饰的数据类型为class或者Object时,可以观察到赋值和属性赋值的变化,即
Object.keys(observedObject)返回的所有属性,示例请参考简单类型和类对象类型的@Link。当装饰的对象是Array时,可以观察到数组添加、删除、更新数组单元的变化,示例请参考数组类型的@Link。
当装饰的对象是Date时,可以观察到Date的整体赋值,以及通过调用
setFullYear,setMonth,setDate,setHours,setMinutes,setSeconds,setMilliseconds,setTime,setUTCFullYear,setUTCMonth,setUTCDate,setUTCHours,setUTCMinutes,setUTCSeconds,setUTCMilliseconds方法更新其属性。
@Component
struct DateComponent {
@Link selectedDate: Date;
build() {
Column() {
Button(`child increase the year by 1`)
.onClick(() => {
this.selectedDate.setFullYear(this.selectedDate.getFullYear() + 1);
})
Button('child update the new date')
.margin(10)
.onClick(() => {
this.selectedDate = new Date('2023-09-09');
})
DatePicker({
start: new Date('1970-1-1'),
end: new Date('2100-1-1'),
selected: this.selectedDate
})
}
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct ParentComponent {
@State parentSelectedDate: Date = new Date('2021-08-08');
build() {
Column() {
Button('parent increase the month by 1')
.margin(10)
.onClick(() => {
this.parentSelectedDate.setMonth(this.parentSelectedDate.getMonth() + 1);
})
Button('parent update the new date')
.margin(10)
.onClick(() => {
this.parentSelectedDate = new Date('2023-07-07');
})
DatePicker({
start: new Date('1970-1-1'),
end: new Date('2100-1-1'),
selected: this.parentSelectedDate
})
DateComponent({ selectedDate:this.parentSelectedDate })
}
}
}
当装饰的变量是Map时,可以观察到Map整体的赋值,以及可通过调用Map的
set、clear、delete接口更新Map的值。详见装饰Map类型变量。当装饰的变量是Set时,可以观察Set整体的赋值,以及通过调用Set的
add、clear、delete接口更新其值。详见装饰Set类型变量。框架行为
\@Link装饰的变量和所属的自定义组件共享生命周期。
为了了解\@Link变量的初始化和更新机制,有必要先了解父组件和拥有\@Link变量的子组件的关系,以及初始渲染和双向更新的流程(以父组件为\@State为例)。
初始渲染:执行父组件的
build()函数,创建子组件的新实例。初始化过程如下:- 指定父组件中的\@State变量用于初始化子组件的\@Link变量。子组件的\@Link变量值与其父组件的数据源变量保持双向数据同步。
- 父组件的\@State状态变量包装类通过构造函数传给子组件,子组件的\@Link包装类拿到父组件的\@State的状态变量后,将当前\@Link包装类实例注册给父组件的\@State变量。
\@Link的数据源的更新:即父组件中状态变量更新,引起相关子组件的\@Link的更新。处理步骤:
- 通过初始渲染的步骤可知,子组件\@Link包装类把当前this指针注册给父组件。父组件\@State变量变更后,会遍历更新所有依赖它的系统组件和状态变量(例如:\@Link包装类)。
- 通知\@Link包装类更新后,子组件中所有依赖\@Link状态变量的系统组件都会被通知更新。以此实现父组件对子组件的状态数据同步。
\@Link的更新:当子组件中\@Link更新后,处理步骤如下(以父组件为\@State为例):
- \@Link更新后,调用父组件的\@State包装类的set方法,将数值同步回父组件。
- 子组件\@Link和父组件\@State分别遍历依赖的系统组件,更新对应的UI。从而实现子组件\@Link与父组件\@State的同步。
限制条件
\@Link装饰器不能在\@Entry装饰的自定义组件中使用。
\@Link装饰的变量禁止本地初始化,否则编译期会报错。
// 错误写法,编译报错
@Link count: number = 10;
// 正确写法
@Link count: number;
- \@Link装饰的变量的类型要和数据源类型保持一致,否则框架会抛出运行时错误。
【反例】
class Info {
info: string = 'Hello';
}
class Cousin {
name: string = 'Hello';
}
@Component
struct Child {
// 错误写法,@Link与@State数据源类型不一致
@Link test: Cousin;
build() {
Text(this.test.name)
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct LinkExample {
@State info: Info = new Info();
build() {
Column() {
// 错误写法,@Link与@State数据源类型不一致
Child({test: new Cousin()})
}
}
}
【正例】
class Info {
info: string = 'Hello';
}
@Component
struct Child {
// 正确写法
@Link test: Info;
build() {
Text(this.test.info)
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct LinkExample {
@State info: Info = new Info();
build() {
Column() {
// 正确写法
Child({test: this.info})
}
}
}
- \@Link装饰的变量仅能被状态变量初始化,不能使用常规变量初始化,否则编译期会给出告警,并在运行时崩溃。
【反例】
class Info {
info: string = 'Hello';
}
@Component
struct Child {
@Link msg: string;
@Link info: string;
build() {
Text(this.msg + this.info)
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct LinkExample {
@State message: string = 'Hello';
@State info: Info = new Info();
build() {
Column() {
// 错误写法,常规变量不能初始化@Link
Child({msg: 'World', info: this.info.info})
}
}
}
【正例】
class Info {
info: string = 'Hello';
}
@Component
struct Child {
@Link msg: string;
@Link info: Info;
build() {
Text(this.msg + this.info.info)
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct LinkExample {
@State message: string = 'Hello';
@State info: Info = new Info();
build() {
Column() {
// 正确写法
Child({msg: this.message, info: this.info})
}
}
}
- \@Link不支持装饰Function类型的变量,框架会抛出运行时错误。
使用场景
简单类型和类对象类型的\@Link
以下示例中,点击父组件ShufflingContainer中的“Parent View: Set yellowButton”和“Parent View: Set GreenButton”,可以从父组件将变化同步给子组件。
1.点击子组件GreenButton和YellowButton中的Button,子组件会发生相应变化,将变化同步给父组件。因为@Link是双向同步,会将变化同步给@State。
2.当点击父组件ShufflingContainer中的Button时,@State会发生变化,并同步给\@Link,子组件也会进行对应的刷新。
class GreenButtonState {
width: number = 0;
constructor(width: number) {
this.width = width;
}
}
@Component
struct GreenButton {
@Link greenButtonState: GreenButtonState;
build() {
Button('Green Button')
.width(this.greenButtonState.width)
.height(40)
.backgroundColor('#64bb5c')
.fontColor('#FFFFFF')
.onClick(() => {
if (this.greenButtonState.width < 700) {
// 更新class的属性,变化可以被观察到同步回父组件
this.greenButtonState.width += 60;
} else {
// 更新class,变化可以被观察到同步回父组件
this.greenButtonState = new GreenButtonState(180);
}
})
}
}
@Component
struct YellowButton {
@Link yellowButtonState: number;
build() {
Button('Yellow Button')
.width(this.yellowButtonState)
.height(40)
.backgroundColor('#f7ce00')
.fontColor('#FFFFFF')
.onClick(() => {
// 子组件的简单类型可以同步回父组件
this.yellowButtonState += 40.0;
})
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct ShufflingContainer {
@State greenButtonState: GreenButtonState = new GreenButtonState(180);
@State yellowButtonProp: number = 180;
build() {
Column() {
Flex({ direction: FlexDirection.Column, alignItems: ItemAlign.Center }) {
// 简单类型从父组件@State向子组件@Link数据同步
Button('Parent View: Set yellowButton')
.width(this.yellowButtonProp)
.height(40)
.margin(12)
.fontColor('#FFFFFF')
.onClick(() => {
this.yellowButtonProp = (this.yellowButtonProp < 700) ? this.yellowButtonProp + 40 : 100;
})
// class类型从父组件@State向子组件@Link数据同步
Button('Parent View: Set GreenButton')
.width(this.greenButtonState.width)
.height(40)
.margin(12)
.fontColor('#FFFFFF')
.onClick(() => {
this.greenButtonState.width = (this.greenButtonState.width < 700) ? this.greenButtonState.width + 100 : 100;
})
// class类型初始化@Link
GreenButton({ greenButtonState: this.greenButtonState }).margin(12)
// 简单类型初始化@Link
YellowButton({ yellowButtonState: this.yellowButtonProp }).margin(12)
}
}
}
}

数组类型的\@Link
@Component
struct Child {
@Link items: number[];
build() {
Column() {
Button(`Button1: push`)
.margin(12)
.width(312)
.height(40)
.fontColor('#FFFFFF,90%')
.onClick(() => {
this.items.push(this.items.length + 1);
})
Button(`Button2: replace whole item`)
.margin(12)
.width(312)
.height(40)
.fontColor('#FFFFFF,90%')
.onClick(() => {
this.items = [100, 200, 300];
})
}
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Parent {
@State arr: number[] = [1, 2, 3];
build() {
Column() {
Child({ items: $arr })
.margin(12)
ForEach(this.arr,
(item: number) => {
Button(`${item}`)
.margin(12)
.width(312)
.height(40)
.backgroundColor('#11a2a2a2')
.fontColor('#e6000000')
},
(item: ForEachInterface) => item.toString()
)
}
}
}

ArkUI框架可以观察到数组元素的添加、删除和替换。在该示例中,\@State和\@Link的类型均为number[],不支持将\@Link定义成number类型(\@Link item : number),并用\@State数组中的每个数据项在父组件中创建子组件。如需使用这种场景,可以参考\@Prop和\@Observed。
装饰Map类型变量
说明:
从API version 11开始,\@Link支持Map类型。
在下面的示例中,value类型为Map<number, string>,点击Button改变message的值,视图会随之刷新。
@Component
struct Child {
@Link value: Map<number, string>;
build() {
Column() {
ForEach(Array.from(this.value.entries()), (item: [number, string]) => {
Text(`${item[0]}`).fontSize(30)
Text(`${item[1]}`).fontSize(30)
Divider()
})
Button('child init map').onClick(() => {
this.value = new Map([[0, "a"], [1, "b"], [3, "c"]]);
})
Button('child set new one').onClick(() => {
this.value.set(4, "d");
})
Button('child clear').onClick(() => {
this.value.clear();
})
Button('child replace the first one').onClick(() => {
this.value.set(0, "aa");
})
Button('child delete the first one').onClick(() => {
this.value.delete(0);
})
}
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct MapSample {
@State message: Map<number, string> = new Map([[0, "a"], [1, "b"], [3, "c"]]);
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Child({ value: this.message })
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
装饰Set类型变量
说明:
从API version 11开始,\@Link支持Set类型。
在下面的示例中,message类型为Set<number>,点击Button改变message的值,视图会随之刷新。
@Component
struct Child {
@Link message: Set<number>;
build() {
Column() {
ForEach(Array.from(this.message.entries()), (item: [number, number]) => {
Text(`${item[0]}`).fontSize(30)
Divider()
})
Button('init set').onClick(() => {
this.message = new Set([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]);
})
Button('set new one').onClick(() => {
this.message.add(5);
})
Button('clear').onClick(() => {
this.message.clear();
})
Button('delete the first one').onClick(() => {
this.message.delete(0);
})
}
.width('100%')
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct SetSample {
@State message: Set<number> = new Set([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]);
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Child({ message: this.message })
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
使用双向同步机制更改本地其他变量
通过\@Watch可以在双向同步时更改本地变量。
以下示例中,在\@Link的\@Watch里面修改了一个\@State装饰的变量memberMessage,实现父子组件间的变量同步。但是\@State装饰的变量memberMessage在本地修改不会影响到父组件中的变量改变。
@Entry
@Component
struct Parent {
@State sourceNumber: number = 0;
build() {
Column() {
Text(`父组件的sourceNumber:` + this.sourceNumber)
Child({ sourceNumber: this.sourceNumber })
Button('父组件更改sourceNumber')
.onClick(() => {
this.sourceNumber++;
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
@Component
struct Child {
@State memberMessage: string = 'Hello World';
@Link @Watch('onSourceChange') sourceNumber: number;
onSourceChange() {
this.memberMessage = this.sourceNumber.toString();
}
build() {
Column() {
Text(this.memberMessage)
Text(`子组件的sourceNumber:` + this.sourceNumber.toString())
Button('子组件更改memberMessage')
.onClick(() => {
this.memberMessage = 'Hello memberMessage';
})
}
}
}
Link支持联合类型实例
@Link支持联合类型、undefined和null。在以下示例中,name类型为string|undefined。点击父组件Index中的按钮可以改变name的属性或类型,Child组件也会相应刷新。
@Component
struct Child {
@Link name: string|undefined;
build() {
Column() {
Button('Child change name to Bob')
.onClick(() => {
this.name = "Bob";
})
Button('Child change name to undefined')
.onClick(() => {
this.name = undefined;
})
}.width('100%')
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State name: string|undefined = "mary";
build() {
Column() {
Text(`The name is ${this.name}`).fontSize(30)
Child({ name: this.name })
Button('Parents change name to Peter')
.onClick(() => {
this.name = "Peter";
})
Button('Parents change name to undefined')
.onClick(() => {
this.name = undefined;
})
}
}
}
常见问题
\@Link装饰状态变量类型错误
在子组件中使用\@Link装饰状态变量时,需要保证该变量与数据源类型完全相同。数据源必须是被@State等装饰器装饰的状态变量。
【反例】
@Observed
class Info {
public age: number = 0;
constructor(age: number) {
this.age = age;
}
}
@Component
struct LinkChild {
@Link testNum: number;
build() {
Text(`LinkChild testNum ${this.testNum}`)
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Parent {
@State info: Info = new Info(1);
build() {
Column() {
Text(`Parent testNum ${this.info.age}`)
.onClick(() => {
this.info.age += 1;
})
// @Link装饰的变量需要和数据源@State类型一致
LinkChild({ testNum: this.info.age })
}
}
}
\@Link testNum: number从父组件的LinkChild({testNum:this.info.age})初始化。\@Link的数据源必须是装饰器装饰的状态变量,简而言之,\@Link装饰的数据必须和数据源类型相同,例如:\@Link: T和\@State : T。所以,此处应该改为\@Link testNum: Info,从父组件初始化的方式为LinkChild({testNum: this.info})。
【正例】
@Observed
class Info {
public age: number = 0;
constructor(age: number) {
this.age = age;
}
}
@Component
struct LinkChild {
@Link testNum: Info;
build() {
Text(`LinkChild testNum ${this.testNum?.age}`)
.onClick(() => {
this.testNum.age += 1;
})
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Parent {
@State info: Info = new Info(1);
build() {
Column() {
Text(`Parent testNum ${this.info.age}`)
.onClick(() => {
this.info.age += 1;
})
// @Link装饰的变量需要和数据源@State类型一致
LinkChild({ testNum: this.info })
}
}
}
使用a.b(this.object)形式调用,不会触发UI刷新
在build方法内,当\@Link装饰的变量是Object类型且通过a.b(this.object)形式调用时,b方法内传入的是this.object的原始对象,修改其属性无法触发UI刷新。以下示例中,通过静态方法Score.changeScore1或this.changeScore2修改Child组件中的this.score.value时,UI不会刷新。
【反例】
class Score {
value: number;
constructor(value: number) {
this.value = value;
}
static changeScore1(score:Score) {
score.value += 1;
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Parent {
@State score: Score = new Score(1);
build() {
Column({space:8}) {
Text(`The value in Parent is ${this.score.value}.`)
.fontSize(30)
.fontColor(Color.Red)
Child({ score: this.score })
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
@Component
struct Child {
@Link score: Score;
changeScore2(score:Score) {
score.value += 2;
}
build() {
Column({space:8}) {
Text(`The value in Child is ${this.score.value}.`)
.fontSize(30)
Button(`changeScore1`)
.onClick(()=>{
// 通过静态方法调用,无法触发UI刷新
Score.changeScore1(this.score);
})
Button(`changeScore2`)
.onClick(()=>{
// 使用this通过自定义组件内部方法调用,无法触发UI刷新
this.changeScore2(this.score);
})
}
}
}
可以通过如下先赋值、再调用新赋值的变量的方式为this.score加上Proxy代理,实现UI刷新。
【正例】
class Score {
value: number;
constructor(value: number) {
this.value = value;
}
static changeScore1(score:Score) {
score.value += 1;
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Parent {
@State score: Score = new Score(1);
build() {
Column({space:8}) {
Text(`The value in Parent is ${this.score.value}.`)
.fontSize(30)
.fontColor(Color.Red)
Child({ score: this.score })
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
@Component
struct Child {
@Link score: Score;
changeScore2(score:Score) {
score.value += 2;
}
build() {
Column({space:8}) {
Text(`The value in Child is ${this.score.value}.`)
.fontSize(30)
Button(`changeScore1`)
.onClick(()=>{
// 通过赋值添加 Proxy 代理
let score1 = this.score;
Score.changeScore1(score1);
})
Button(`changeScore2`)
.onClick(()=>{
// 通过赋值添加 Proxy 代理
let score2 = this.score;
this.changeScore2(score2);
})
}
}
}
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙\@AnimatableExtend装饰器:定义可动画属性
harmony 鸿蒙AppStorage:应用全局的UI状态存储
harmony 鸿蒙\@Builder装饰器:自定义构建函数