harmony 鸿蒙Matching Rules of Explicit Want and Implicit Want
Matching Rules of Explicit Want and Implicit Want
Both explicit Want and implicit Want can be used to match an application component to start based on certain rules. These rules determine how the parameters set in want match the configuration file declared by the target application component.
Matching Rules of Explicit Want
The table below describes the matching rules of explicit Want.
| Name | Type | Matching Item | Mandatory | Rule Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| deviceId | string | Yes | No | If this field is unspecified, only application components on the local device are matched. |
| bundleName | string | Yes | Yes | If abilityName is specified but bundleName is unspecified, the matching fails. |
| moduleName | string | Yes | No | If this field is unspecified and multiple modules with the same ability name exist in the application, the first application component is matched by default. |
| abilityName | string | Yes | Yes | To use explicit Want, this field must be specified. |
| uri | string | No | No | This field is not used for matching. It is passed to the target application component as a parameter. |
| type | string | No | No | This field is not used for matching. It is passed to the target application component as a parameter. |
| action | string | No | No | This field is not used for matching. It is passed to the target application component as a parameter. |
| entities | Array<string> | No | No | This field is not used for matching. It is passed to the target application component as a parameter. |
| flags | number | No | No | This field is not used for matching and is directly transferred to the system for processing. It is generally used to set runtime information, such as URI data authorization. |
| parameters | {[key: string]: Object} | No | No | This field is not used for matching. It is passed to the target application component as a parameter. |
Matching Rules of Implicit Want
The table below describes the matching rules of implicit Want.
| Name | Type | Matching Item | Mandatory | Rule Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| deviceId | string | Yes | No | Implicit invoking is not supported across devices. |
| abilityName | string | No | No | To use implicit Want, this field must be left unspecified. |
| bundleName | string | Yes | No | This field is used to match the target application component in the given bundle. |
| moduleName | string | Yes | No | This field is used to match the target application component in the given module. |
| uri | string | Yes | No | For details, see Matching Rules of uri and type in the want Parameter. |
| type | string | Yes | No | For details, see Matching Rules of uri and type in the want Parameter. |
| action | string | Yes | No | For details, see Matching Rules of action in the want Parameter. |
| entities | Array<string> | Yes | No | For details, see Matching Rules of entities in the want Parameter. |
| flags | number | No | No | This field is not used for matching and is directly transferred to the system for processing. It is generally used to set runtime information, such as URI data authorization. |
| parameters | {[key: string]: Object} | Yes | No | This field is used to transfer custom data to the target application component. Currently, only the parameter with the key set to linkFeature is used for matching. When linkFeature is not null, a matching against linkFeature is carried out preferentially. |
Get familiar with the following about implicit Want:
The want parameter passed by the caller indicates the operation to be performed by the caller. It also provides data and application type restrictions.
The skills field declares the capabilities of the target application component. For details, see the skills tag in the module.json5 file.
The system matches the want parameter (including the action, entities, uri, type, and parameters attributes) passed by the caller against the skills configuration (including the actions, entities, uris, and type attributes) of the application components. If none of the five attributes in the want parameter is configured, implicit matching fails. - If the linkFeature field in parameters is not null, a matching against linkFeature is carried out preferentially. - If linkFeature is matched and uri or type in the want parameter is configured, the system continues to match uri or type. If they are matched, the implicit matching is successful. Otherwise, the matching fails. If neither uri nor type in the want parameter is configured, the implicit matching is successful. - If linkFeature is not matched, no matching is performed and the matching fails. - If the linkFeature field in parameters is not specified or is null, the matching is successful only when the action, entities, uri, and type attributes are all matched.
Matching Rules of action in the want Parameter
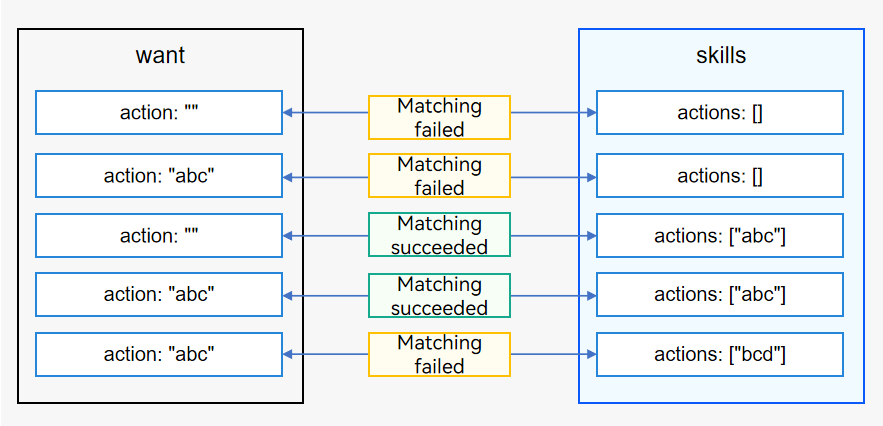
The system matches the action attribute in the want parameter passed by the caller against actions under skills of the application components.
If action in the passed want parameter is null and actions under skills of an application component is null, the matching fails.
If action in the passed want parameter is not null but actions under skills of an application component is null, the matching fails.
If action in the passed want parameter is null but actions under skills of an application component is not null, the matching is successful.
If action in the passed want parameter is not null, and actions under skills of an application component is not null and contains action in the passed want parameter, the matching is successful.
If action in the passed want parameter is not null, and actions under skills of an application component is not null but does not contain action in the passed want parameter, the matching fails.
Figure 1 Matching rules of action in the want parameter
Matching Rules of entities in the want Parameter
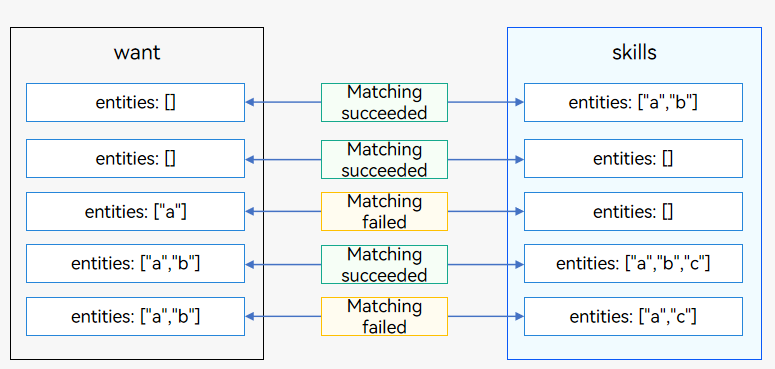
The system matches the entities attribute in the want parameter passed by the caller against entities under skills of the application components.
If entities in the passed want parameter is null but entities under skills of an application component is not null, the matching is successful.
If entities in the passed want parameter is null but entities under skills of an application component is null, the matching is successful.
If entities in the passed want parameter is not null but entities under skills of an application component is null, the matching fails.
If entities in the passed want parameter is not null, and entities under skills of an application component is not null and contains entities in the passed want parameter, the matching is successful.
If entities in the passed want parameter is not null, and entities under skills of an application component is not null but does not contain entities in the passed want parameter, the matching fails.
Figure 2 Matching rules of entities in the want parameter
Matching Rules of uri and type in the want Parameter
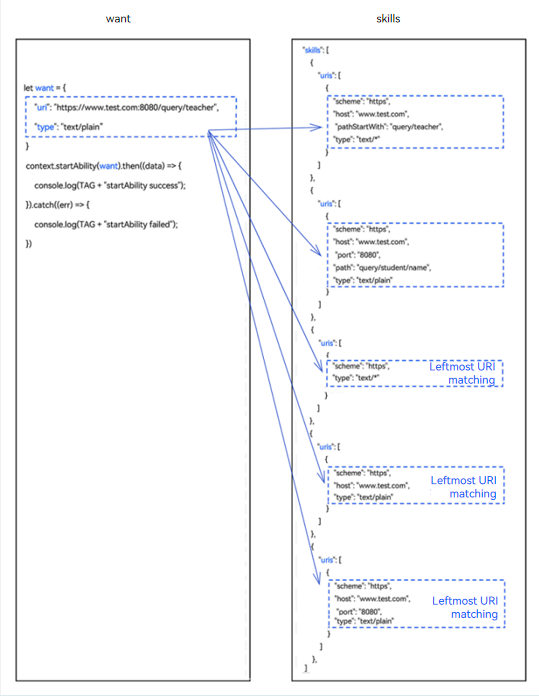
When the uri and type parameters are not null in the want parameter to initiate an application component startup request, the system traverses the list of installed components and matches the uris array under skills of the application components one by one. If one of the uris arrays under skills matches the uri and type in the passed want, the matching is successful.
There are four combinations of uri and type settings. The matching rules are as follows:
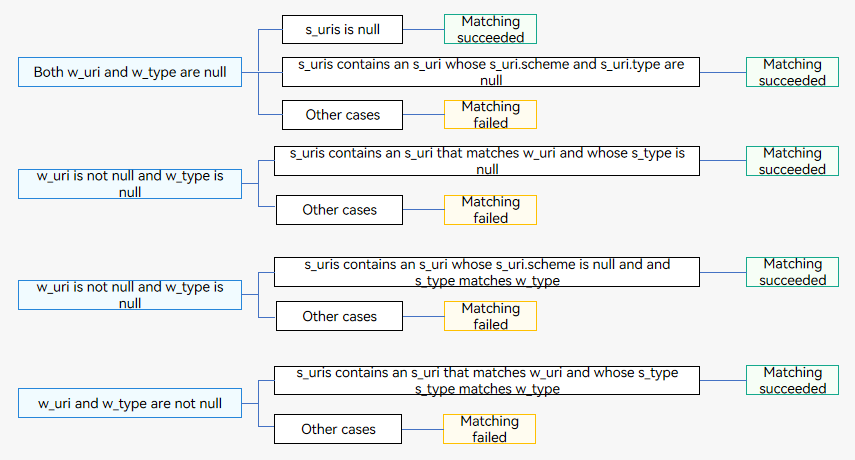
Both uri and type are null in the want parameter.
- If the uris array under skills of an application component is null, the matching is successful.
- If the uris array under skills of an application component contains an URI element whose scheme and type are null, the matching is successful.
- In other cases, the matching fails.
Only uri is not null in the want parameter.
- If the uris array under skills of an application component is null, the matching fails.
- If the uris array under skills of an application component contains an element whose uri is matched and type is null, the matching is successful. Otherwise, the matching fails.
- If the matching fails for the preceding two scenarios and the input URI is a file path URI, the system obtains the MIME type of the file based on the file name extension. If the MIME type matches type configured under skills, the matching is successful.
Only type is not null in the want parameter.
- If the uris array under skills of an application component is null, the matching fails.
- If the uris array under skills of an application component contains an URI element whose scheme is null and type is matched, the matching is successful. Otherwise, the matching fails.
Both uri and type are not null in the want parameter, as shown below.
- If the uris array under skills of an application component is null, the matching fails.
- If the uris array under skills of an application component contains an element whose uri is matched and type is matched, the matching is successful. Otherwise, the matching fails.
Leftmost URI matching: When only scheme, a combination of scheme and host, or a combination of scheme, host, and port is configured in the uris array under skills of the application component, the matching is successful only if the leftmost URI in the passed want parameter matches scheme, the combination of scheme and host, or the combination of scheme, host, and port.
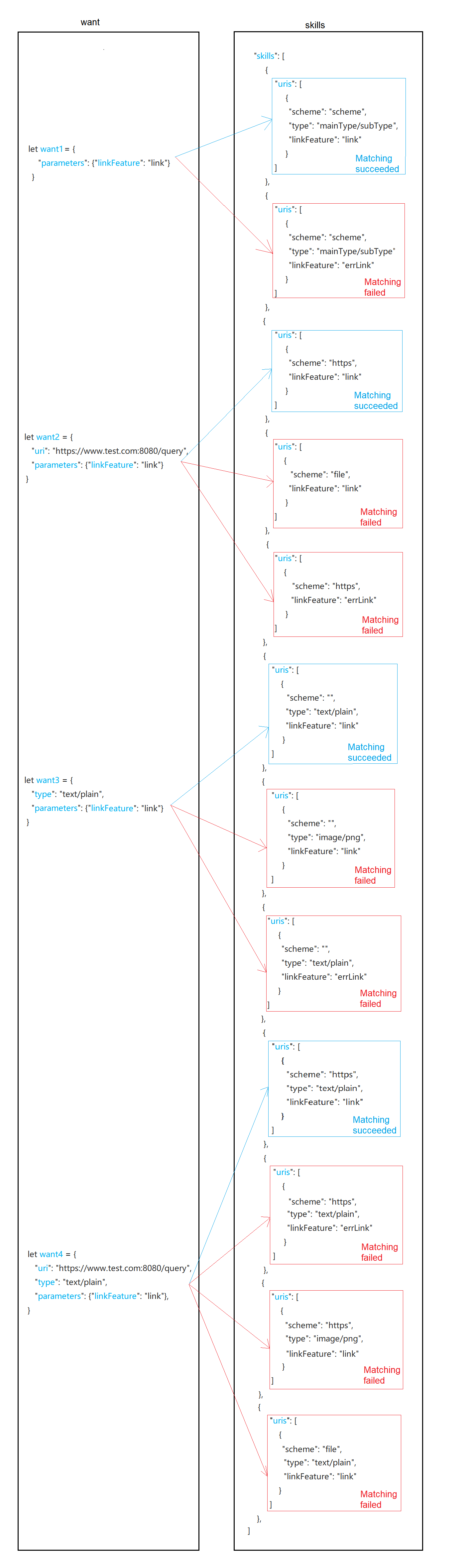
Figure 3 Matching rules when uri and type are not null in the want parameter
To simplify the description:
- uri in the want parameter passed in by the caller is called w_uri; each element in the uris array under skills of the application component to match is called s_uri.
- type in the want parameter passed in by the caller is called w_type; the type in the uris array under skills of the application component to match is called s_type.
Figure 4 Matching rules of uri and type in the want parameter
Matching Rules of uri
The matching rules are as follows:
If scheme of s_uri is null and w_uri is null, the matching is successful. Otherwise, the matching fails.
If host of s_uri is null and scheme of w_uri and scheme of s_uri are the same, the matching is successful. Otherwise, the matching fails.
If port of s_uri is null and the combination of scheme and host of w_uri is the same as the combination of scheme and host of s_uri, the matching is successful. Otherwise, the matching fails.
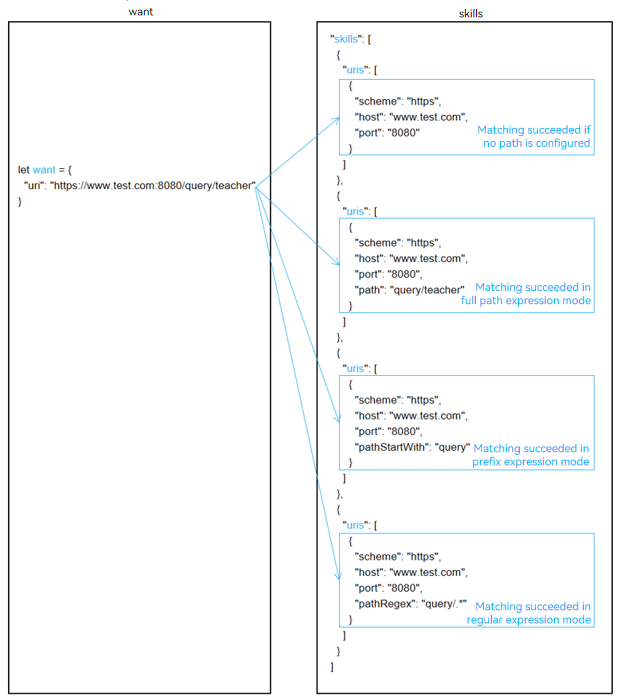
If path, pathStartWith, and pathRegex of s_uri are null and the combination of scheme, host, and port of w_uri is the same as the combination of scheme, host, and port of s_uri, the matching is successful. Otherwise, the matching fails.
If path of s_uri is not null and the full path expressions of w_uri and s_uri are the same, the matching is successful. Otherwise, the matching of pathStartWith continues.
If pathStartWith of s_uri is not null and w_uri contains the prefix expression of s_uri, the matching is successful. Otherwise, pathRegex matching continues.
If pathRegex of s_uri is not null and w_uri meets the regular expression of s_uri, the matching is successful. Otherwise, the matching fails.
NOTE
The scheme, host, port, path, pathStartWith, and pathRegex attributes of uris under skills of an application component are concatenated. If path, pathStartWith, and pathRegex are declared in sequence, uris can be concatenated into the following expressions:
- Prefix URI expression: When only scheme, a combination of scheme and host, or a combination of scheme, host, and port is configured in the configuration file, the matching is successful if a URI prefixed with the configuration file is passed in.
scheme://scheme://hostscheme://host:port- Full path expression:
scheme://host:port/path- Prefix expression:
scheme://host:port/pathStartWith- Regular expression:
scheme://host:port/pathRegexFor system applications, scheme of their URIs starts with ohos, for example, ohosclock://. The URI of a third-party application cannot be the same as that of a system application. Otherwise, the third-party application cannot be started using the URI.
Figure 5 Example of the matching rules of uri in the want parameter
Matching Rules of type
NOTE
The matching rules of type described in this section are based on the fact that type in the want parameter is not null. If type is null, follow the matching rules of uri and type in the want parameter.
The matching rules are as follows:
If s_type is null, the matching fails.
If s_type or w_type contains the wildcard
*/*, the matching is successful.If the last character of s_type is the wildcard
*, for example,prefixType/*, the matching is successful only when w_type containsprefixType/.If the last character of w_type is the wildcard
*, for example,prefixType/*, the matching is successful only when s_type containsprefixType/.
Matching Rules of linkFeature
NOTE
The linkFeature matching rules described below apply to the scenario where parameters in the want parameter contains the linkFeature key and the value of the key is not null.
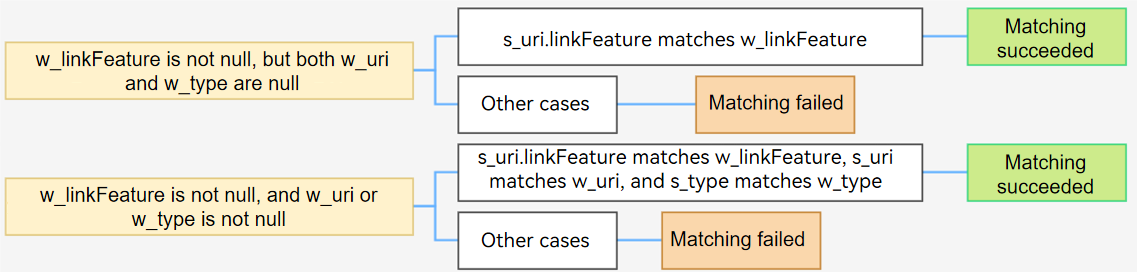
The system matches parameters in the want parameter passed by the caller against uris under skills of the application components. To simplify the description, linkFeature in the want parameter passed in by the caller is called w_linkFeature. The matching rules are as follows: - If both uri and type in the want parameter are null, only linkFeature is used for matching. If the value of w_linkFeature matches that of s_uri, the matching is successful. Otherwise, the matching fails. - If uri or type in the want parameter is not null, the system matches linkFeature, uri, and type in sequence. For details, see Matching Rules of uri and type in the want Parameter. If all the three fields are matched, the matching is successful. Otherwise, the matching fails.
Figure 6 Matching rules of linkFeature in the want parameter
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Obtaining Reasons for Abnormal Application Exits
harmony 鸿蒙UIAbility Backup and Restore
harmony 鸿蒙Using Explicit Want to Start an Application Component
harmony 鸿蒙Introduction to Ability Kit
harmony 鸿蒙AbilityStage Component Container
harmony 鸿蒙Accessing a DataAbility
harmony 鸿蒙Accessing a DataShareExtensionAbility from the FA Model
harmony 鸿蒙Common action and entities Values (Not Recommended)
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: