harmony 鸿蒙USB DDK Development
USB DDK Development
Overview
The USB Driver Development Kit (DDK) is a toolset that helps you develop USB device drivers at the application layer based on the user mode. It provides a series of device access APIs, for example, opening and closing USB interfaces, and performing non-isochronous transfer, isochronous transfer, control transfer, and interrupt transfer over USB pipes.
The USB DDK can be used to develop device drivers for all devices that use the USB protocol to transfer data over a USB bus. For the peripherals that are not supported by standard kernel drivers, you can use the peripheral driver application developed based on the USB DDK to implement unique device capabilities.
Basic Concepts
Before developing the USB DDK, you must understand the following basic concepts:
- USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is a widely used interface technology that connects a computer to various external devices, such as a keyboard, mouse, printer, storage device, and smartphone. The USB is designed to provide a standardized, efficient, and easy-to-use connection mode that replaces the traditional serial and parallel interface communication.
- DDK
DDK is a tool package provided by OpenHarmony for developing drivers for non-standard USB serial port devices based on the peripheral framework.
Implementation Principles
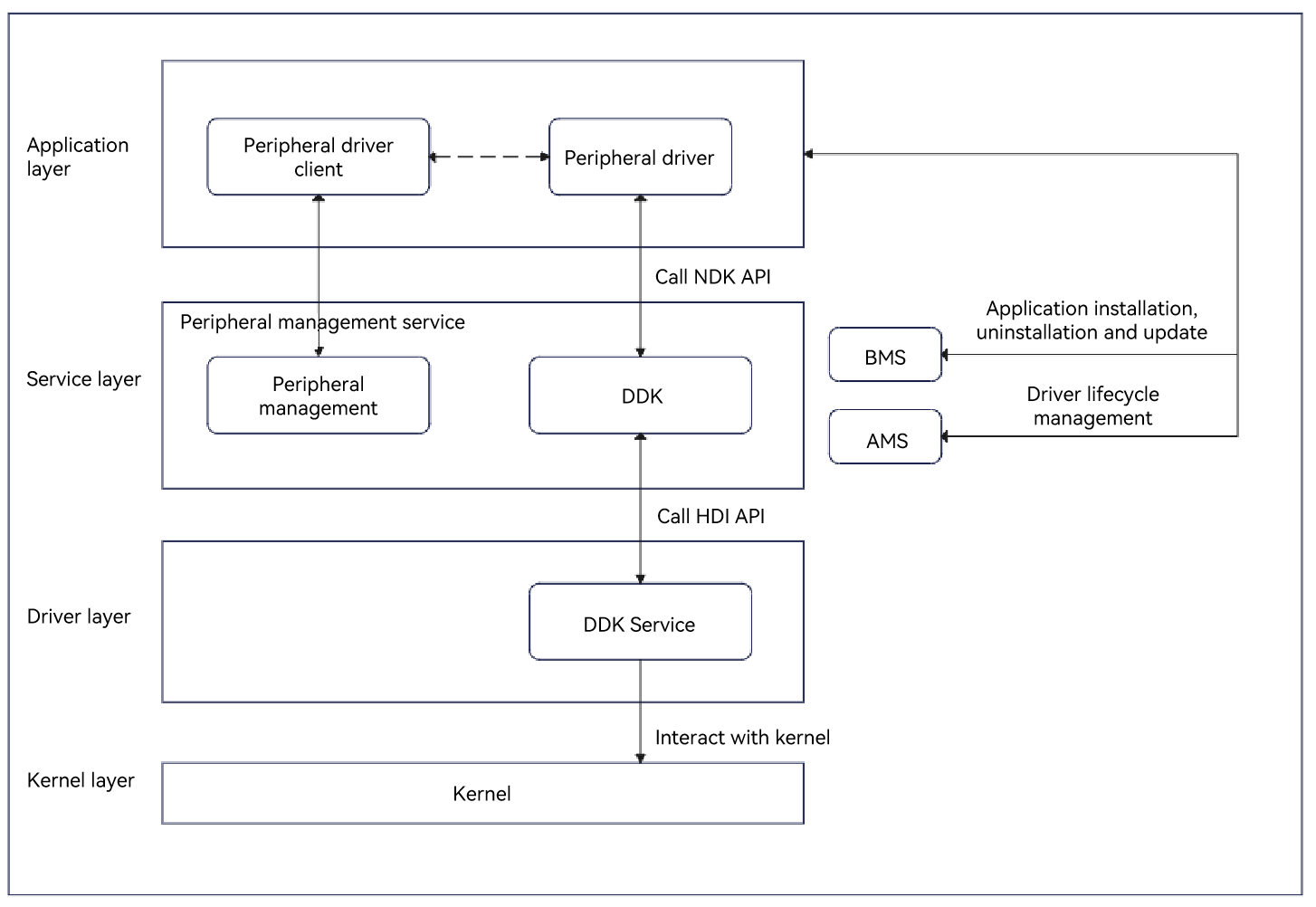
A non-standard peripheral application obtains the USB device ID by using the peripheral management service, and delivers the ID and the action to the USB driver application through RPC. The USB driver application can obtain or set the device descriptor and initiate a control transfer or interrupt transfer request by calling the USB DDK API. Then, the DDK API uses the HDI service to deliver instructions to the kernel driver, and the kernel driver uses instructions to communicate with the device.
Figure 1 Principles of invoking the USB DDK
Constraints
The open APIs of USB DDK can be used to develop drivers of non-standard USB peripherals.
The open APIs of USB DDK can be used only within the lifecycle of DriverExtensionAbility.
To use the open APIs of the USB DDK, you need to declare the matching ACL permissions in module.json5, for example, ohos.permission.ACCESS_DDK_USB.
Environment Setup
Before you get started, make necessary preparations by following instructions in Environment Preparation.
How to Develop
Available APIs
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| OH_Usb_Init(void) | Initializes the USB DDK. |
| OH_Usb_Release(void) | Releases the USB DDK. |
| OH_Usb_GetDeviceDescriptor(uint64_t deviceId, struct UsbDeviceDescriptor *desc) | Obtains the device descriptor of a USB device. |
| OH_Usb_GetConfigDescriptor(uint64_t deviceId, uint8_t configIndex, struct UsbDdkConfigDescriptor **const config) | Obtains a USB configuration descriptor. To avoid memory leakage, use OH_Usb_FreeConfigDescriptor() to release a descriptor after use. |
| OH_Usb_FreeConfigDescriptor(const struct UsbDdkConfigDescriptor *const config) | Releases a configuration descriptor. To avoid memory leakage, release a descriptor in time after use. |
| OH_Usb_ClaimInterface(uint64_t deviceId, uint8_t interfaceIndex, uint64_t *interfaceHandle) | Declares a USB interface. |
| OH_Usb_SelectInterfaceSetting(uint64_t interfaceHandle, uint8_t settingIndex) | Activates the alternate setting of a USB interface. |
| OH_Usb_GetCurrentInterfaceSetting(uint64_t interfaceHandle, uint8_t *settingIndex) | Obtains the alternate setting of a USB interface. |
| OH_Usb_SendControlReadRequest(uint64_t interfaceHandle, const struct UsbControlRequestSetup *setup, uint32_t timeout, uint8_t *data, uint32_t *dataLen) | Sends a control read transfer request. This API returns the result synchronously. |
| OH_Usb_SendControlWriteRequest(uint64_t interfaceHandle, const struct UsbControlRequestSetup *setup, uint32_t, const uint8_t *data, uint32_t dataLen) | Sends a control write transfer request. This API returns the result synchronously. |
| OH_Usb_ReleaseInterface(uint64_t interfaceHandle) | Releases a USB interface. |
| OH_Usb_SendPipeRequest(const struct UsbRequestPipe *pipe, UsbDeviceMemMap *devMmap) | Sends a pipe request. This API returns the result synchronously. It applies to interrupt transfer and bulk transfer. |
| OH_Usb_CreateDeviceMemMap(uint64_t deviceId, size_t size, UsbDeviceMemMap **devMmap) | Create a buffer. To avoid resource leakage, use OH_Usb_DestroyDeviceMemMap() to destroy a buffer after use. |
| OH_Usb_DestroyDeviceMemMap(UsbDeviceMemMap *devMmap) | Destroy a buffer. To avoid resource leakage, destroy a buffer in time after use. |
| OH_Usb_GetDevices(struct Usb_DeviceArray *devices) | Obtains the USB device ID list. Ensure that the input pointer is valid and the number of devices does not exceed 128. To prevent resource leakage, release the member memory after usage. Besides, make sure that the obtained USB device ID has been filtered by vid in the driver configuration information. |
For details about the APIs, see USB DDK.
How to Develop
To develop a USB driver using the USB DDK, perform the following steps:
Adding Dynamic Link Libraries
Add the following libraries to CMakeLists.txt.
libusb_ndk.z.so
Including Header Files
#include <usb/usb_ddk_api.h>
#include <usb/usb_ddk_types.h>
Obtain the device descriptor of a USB device.
Call OH_Usb_Init of usb_ddk_api.h to initialize the USB DDK, and call OH_Usb_GetDeviceDescriptor to obtain the device descriptor.
// Initialize the USB DDK. OH_Usb_Init(); struct UsbDeviceDescriptor devDesc; uint64_t deviceId = 0; // Obtain the device descriptor. OH_Usb_GetDeviceDescriptor(deviceId, &devDesc);Obtain a configuration descriptor, and declare the USB interface.
Call OH_Usb_GetConfigDescriptor of usb_ddk_api.h to obtain the configuration descriptor config, and call OH_Usb_ClaimInterface to declare claiming of the USB interface.
struct UsbDdkConfigDescriptor *config = nullptr; // Obtain the configuration descriptor. OH_Usb_GetConfigDescriptor(deviceId, 1, &config); // Obtain the index of the target USB interface based on the configuration descriptor. uint8_t interfaceIndex = 0; // Declare the USB interface. uint64_t interfaceHandle = 0; OH_Usb_ClaimInterface(deviceId, interfaceIndex, &interfaceHandle); // Release the configuration descriptor. OH_Usb_FreeConfigDescriptor(config);Obtain the activated alternate setting of a USB interface.
Call OH_Usb_GetCurrentInterfaceSetting of usb_ddk_api.h to obtain the alternate setting, and call OH_Usb_SelectInterfaceSetting to activate it.
uint8_t settingIndex = 0; // Obtain the alternate setting. OH_Usb_GetCurrentInterfaceSetting(interfaceHandle, &settingIndex); // Activate the alternate setting. OH_Usb_SelectInterfaceSetting(interfaceHandle, &settingIndex);Send control read requests and control write requests.
Call OH_Usb_SendControlReadRequest of usb_ddk_api.h to send a control read request, or call OH_Usb_SendControlWriteRequest to send a control write request.
// Timeout interval. Set it to 1s. uint32_t timeout = 1000; struct UsbControlRequestSetup setupRead; setupRead.bmRequestType = 0x80; setupRead.bRequest = 0x08; setupRead.wValue = 0; setupRead.wIndex = 0; setupRead.wLength = 0x01; uint8_t dataRead[256] = {0}; uint32_t dataReadLen = 256; // Send a control read request. OH_Usb_SendControlReadRequest(interfaceHandle, &setupRead, timeout, dataRead, &dataReadLen); struct UsbControlRequestSetup setupWrite; setupWrite.bmRequestType = 0; setupWrite.bRequest = 0x09; setupWrite.wValue = 1; setupWrite.wIndex = 0; setupWrite.wLength = 0; uint8_t dataWrite[256] = {0}; uint32_t dataWriteLen = 256; // Send a control write request. OH_Usb_SendControlWriteRequest(interfaceHandle, &setupWrite, timeout, dataWrite, &dataWriteLen);Create a buffer, and send a request.
Call OH_Usb_CreateDeviceMemMap of usb_ddk_api.h to create the buffer devMmap, and call OH_Usb_SendPipeRequest to send a request.
struct UsbDeviceMemMap *devMmap = nullptr; // Create a buffer for storing data. size_t bufferLen = 10; OH_Usb_CreateDeviceMemMap(deviceId, bufferLen, &devMmap); struct UsbRequestPipe pipe; pipe.interfaceHandle = interfaceHandle; // Obtain the target endpoint based on the configuration descriptor. pipe.endpoint = 128; pipe.timeout = UINT32_MAX; // Send a request. OH_Usb_SendPipeRequest(&pipe, devMmap);Release resources.
After all requests are processed and before the application exits, call OH_Usb_DestroyDeviceMemMap of usb_ddk_api.h to destroy the buffer, call OH_Usb_ReleaseInterface to release the USB interface, , and call OH_Usb_Release to release the USB DDK.
// Destroy the buffer. OH_Usb_DestroyDeviceMemMap(devMmap); // Release the USB interface. OH_Usb_ReleaseInterface(interfaceHandle); // Release the USB DDK. OH_Usb_Release();(Optional) Obtain the USB device ID list.
After the driver is started, call OH_Usb_GetDevices to obtain the device ID that matches the VID in the driver configuration for subsequent application development. (VID is the ID of the device vendor and is configured in the driver application to indicate the applicable devices. The queried device IDs need to be filtered by VID.)
OH_Usb_Init(); constexpr size_t MAX_USB_DEVICE_NUM = 128; struct Usb_DeviceArray deviceArray; deviceArray.deviceIds = new uint64_t[MAX_USB_DEVICE_NUM]; // Obtain the USB device list. OH_Usb_GetDevices(&deviceArray);
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Driver Development Kit
harmony 鸿蒙Introduction to Driver Development Kit
harmony 鸿蒙UI-free Driver Development
harmony 鸿蒙Setting Up the Environment
harmony 鸿蒙UI-based Driver Development
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: