harmony 鸿蒙线性布局
线性布局
线性布局(LinearLayout)是开发中最常用的布局。线性布局的子组件在线性方向上(水平方向和垂直方向)依次排列。
通过线性容器Row和Column实现线性布局。Column容器内子组件按照垂直方向排列,Row组件中,子组件按照水平方向排列。
线性布局的排列
线性布局的排列方向由所选容器组件决定。根据不同的排列方向,选择使用Row或Column容器创建线性布局,通过调整space,alignItems,justifyContent属性调整子组件的间距,水平垂直方向的对齐方式。 1. 通过space参数设置主轴(排列方向)上子组件的间距。达到各子组件在排列方向上的等间距效果。 2. 通过alignItems属性设置子组件在交叉轴(排列方向的垂直方向)的对齐方式。且在各类尺寸屏幕中,表现一致。其中,交叉轴为垂直方向时,取值为VerticalAlign类型,水平方向取值为HorizontalAlign类型。 3. 通过justifyContent属性设置子组件在主轴(排列方向)上的对齐方式。实现布局的自适应均分能力。取值为FlexAlign类型。
具体使用以及效果如下表所示:
| 属性名 | 描述 | Row效果图 | Column效果图 |
|---|---|---|---|
| space | - 横向布局中各子组件的在水平方向的间距 - 纵向布局中个子组件垂直方向间距 |
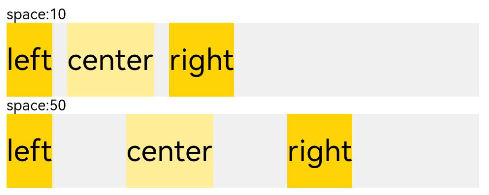 |
 |
| alignItems | 容器排列方向的垂直方向上,子组件在父容器中的对齐方式 |  |
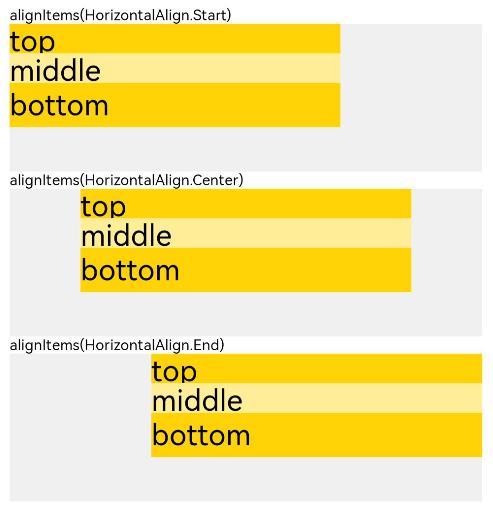 |
| justifyContent | 容器排列方向上,子组件在父容器中的对齐方式 |  |
 |
自适应拉伸
在线性布局下,常用空白填充组件Blank,在容器主轴方向自动填充空白空间,达到自适应拉伸效果。
@Entry
@Component
struct BlankExample {
build() {
Column() {
Row() {
Text('Bluetooth').fontSize(18)
Blank()
Toggle({ type: ToggleType.Switch, isOn: true })
}.backgroundColor(0xFFFFFF).borderRadius(15).padding({ left: 12 }).width('100%')
}.backgroundColor(0xEFEFEF).padding(20).width('100%')
}
}
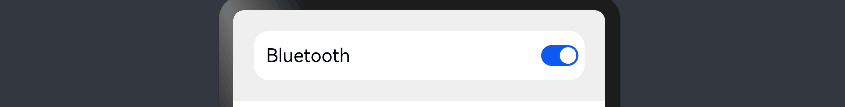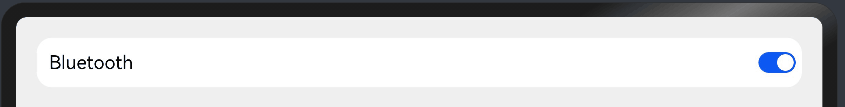
自适应缩放
自适应缩放是指在各种不同大小设备中,子组件按照预设的比例,尺寸随容器尺寸的变化而变化。在线性布局中有下列方法实现:
父容器尺寸确定时,设置了layoutWeight属性的子组件与兄弟元素占主轴尺寸按照权重进行分配,忽略元素本身尺寸设置,在任意尺寸设备下,自适应占满剩余空间。
@Entry @Component struct layoutWeightExample { build() { Column() { Text('1:2:3').width('100%') Row() { Column() { Text('layoutWeight(1)') .textAlign(TextAlign.Center) }.layoutWeight(2).backgroundColor(0xffd306).height('100%') Column() { Text('layoutWeight(2)') .textAlign(TextAlign.Center) }.layoutWeight(4).backgroundColor(0xffed97).height('100%') Column() { Text('layoutWeight(6)') .textAlign(TextAlign.Center) }.layoutWeight(6).backgroundColor(0xffd306).height('100%') }.backgroundColor(0xffd306).height('30%') Text('2:5:3').width('100%') Row() { Column() { Text('layoutWeight(2)') .textAlign(TextAlign.Center) }.layoutWeight(2).backgroundColor(0xffd306).height('100%') Column() { Text('layoutWeight(5)') .textAlign(TextAlign.Center) }.layoutWeight(5).backgroundColor(0xffed97).height('100%') Column() { Text('layoutWeight(3)') .textAlign(TextAlign.Center) }.layoutWeight(3).backgroundColor(0xffd306).height('100%') }.backgroundColor(0xffd306).height('30%') } } }
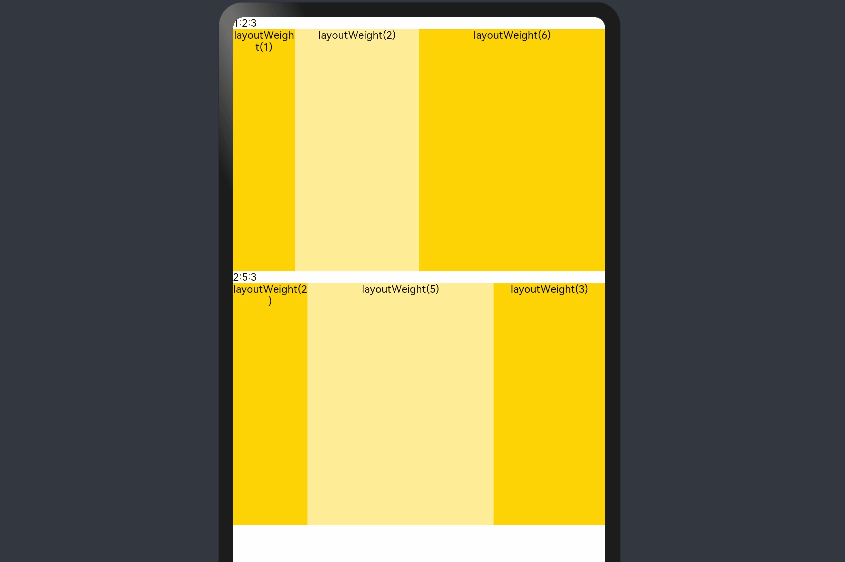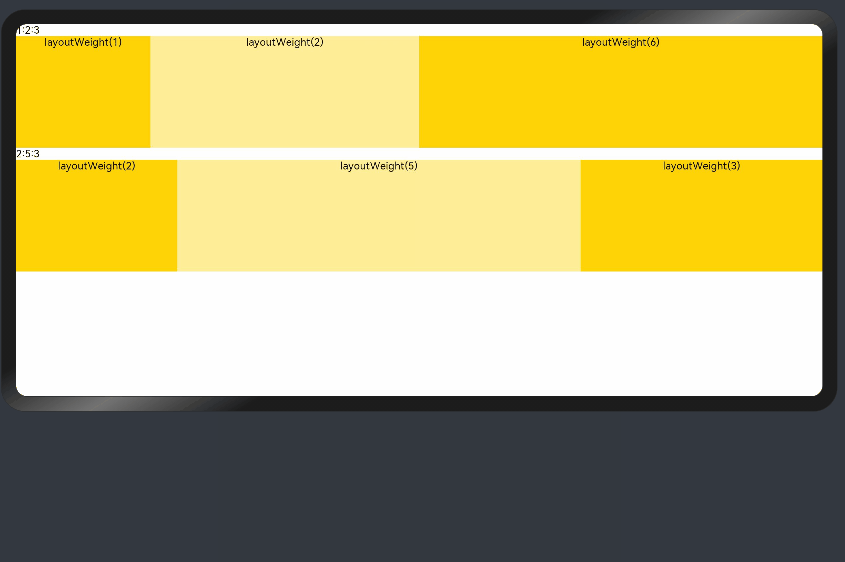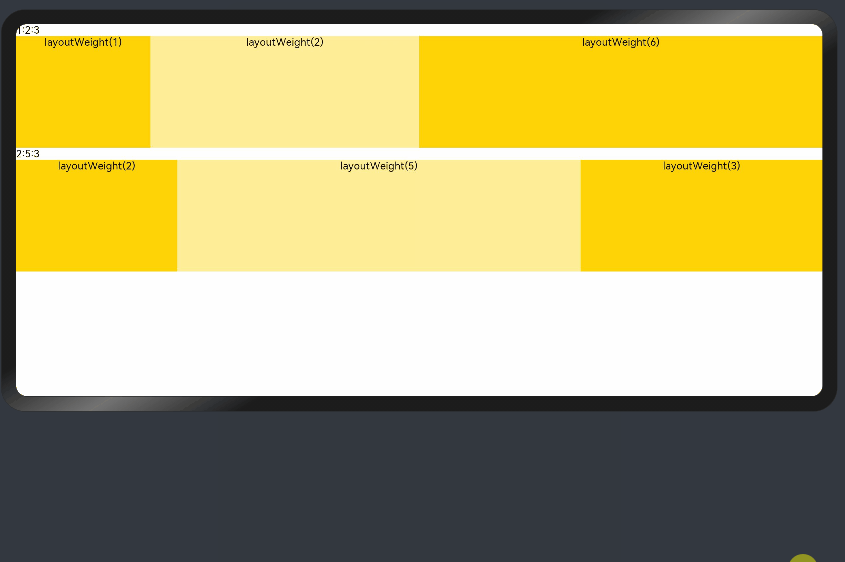
父容器尺寸确定时,使用百分比设置子组件以及兄弟组件的width宽度,可以保证各自元素在任意尺寸下的自适应占比。
@Entry @Component struct WidthExample { build() { Column() { Row() { Column() { Text('left width 20%') .textAlign(TextAlign.Center) }.width('20%').backgroundColor(0xffd306).height('100%') Column() { Text('center width 50%') .textAlign(TextAlign.Center) }.width('50%').backgroundColor(0xffed97).height('100%') Column() { Text('right width 30%') .textAlign(TextAlign.Center) }.width('30%').backgroundColor(0xffd306).height('100%') }.backgroundColor(0xffd306).height('30%') } } }
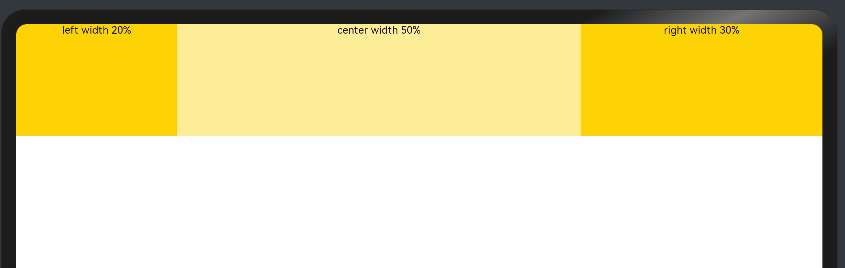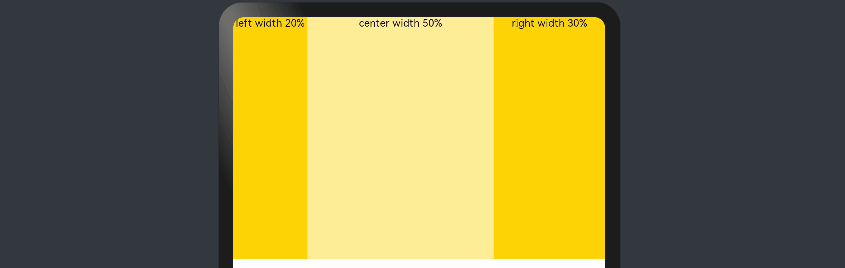
上例中,在任意大小的设备中,子组件的宽度占比固定。
定位能力
- 相对定位
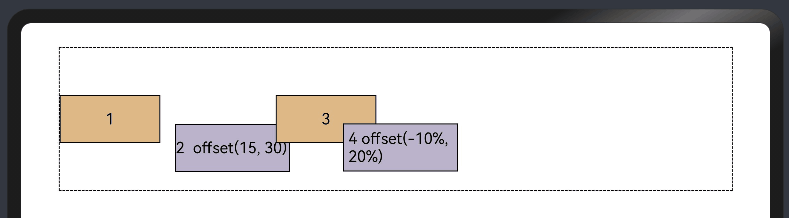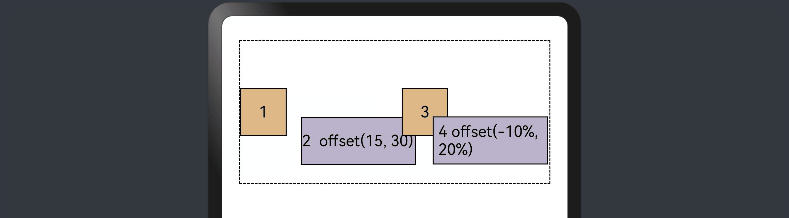
使用组件的offset属性可以实现相对定位,设置元素相对于自身的偏移量。设置该属性,不影响父容器布局,仅在绘制时进行位置调整。使用线性布局和offset可以实现大部分布局的开发。
@Entry
@Component
struct OffsetExample {
@Styles eleStyle() {
.size({ width: 120, height: '50' })
.backgroundColor(0xbbb2cb)
.border({ width: 1 })
}
build() {
Column({ space: 20 }) {
Row() {
Text('1').size({ width: '15%', height: '50' }).backgroundColor(0xdeb887).border({ width: 1 }).fontSize(16)
Text('2 offset(15, 30)')
.eleStyle()
.fontSize(16)
.align(Alignment.Start)
.offset({ x: 15, y: 30 })
Text('3').size({ width: '15%', height: '50' }).backgroundColor(0xdeb887).border({ width: 1 }).fontSize(16)
Text('4 offset(-10%, 20%)')
.eleStyle()
.fontSize(16)
.offset({ x: '-5%', y: '20%' })
}.width('90%').height(150).border({ width: 1, style: BorderStyle.Dashed })
}
.width('100%')
.margin({ top: 25 })
}
}
- 绝对定位
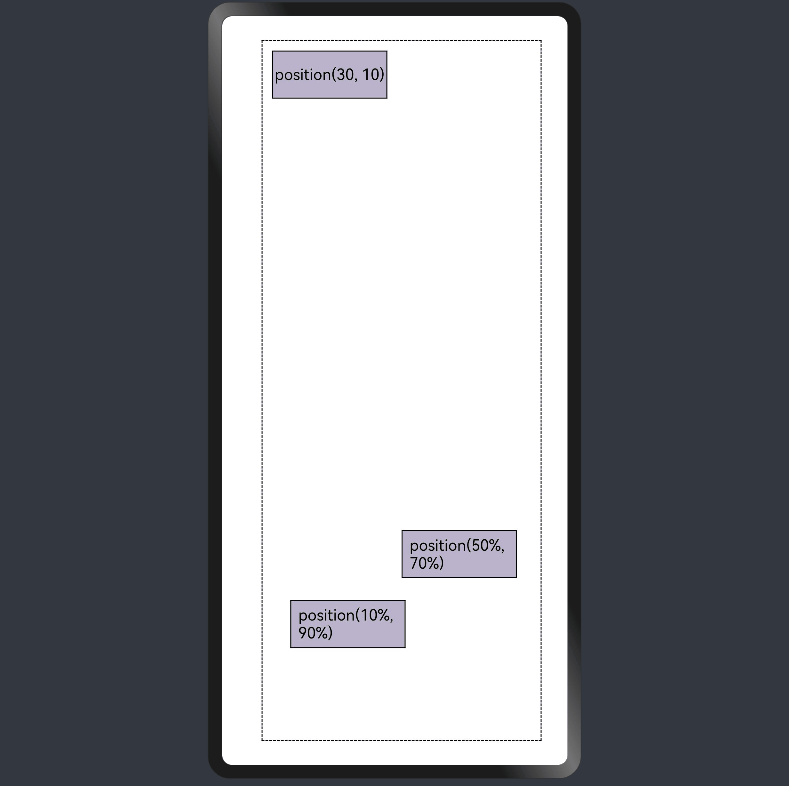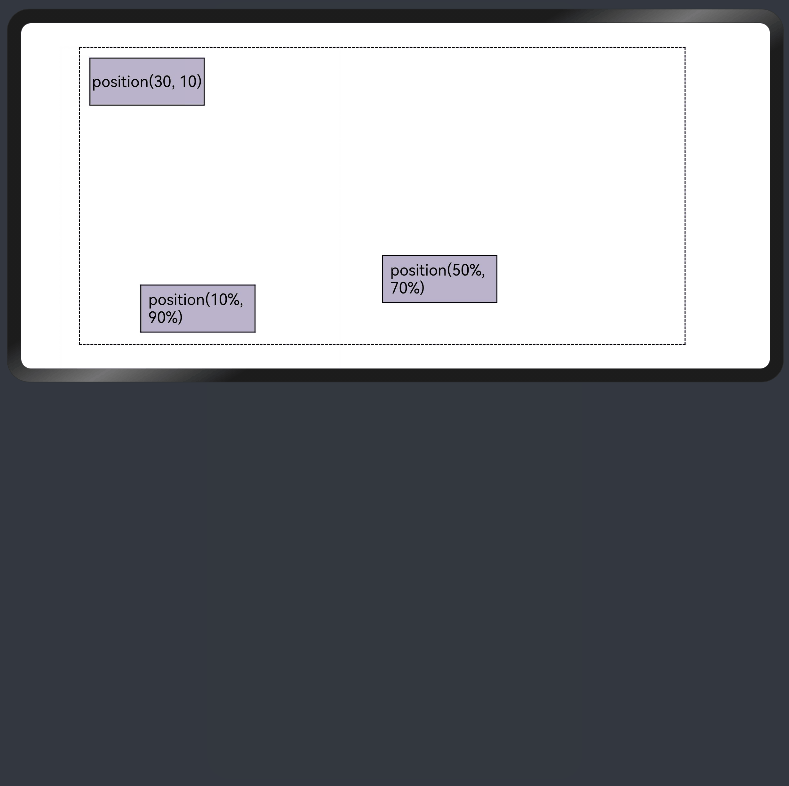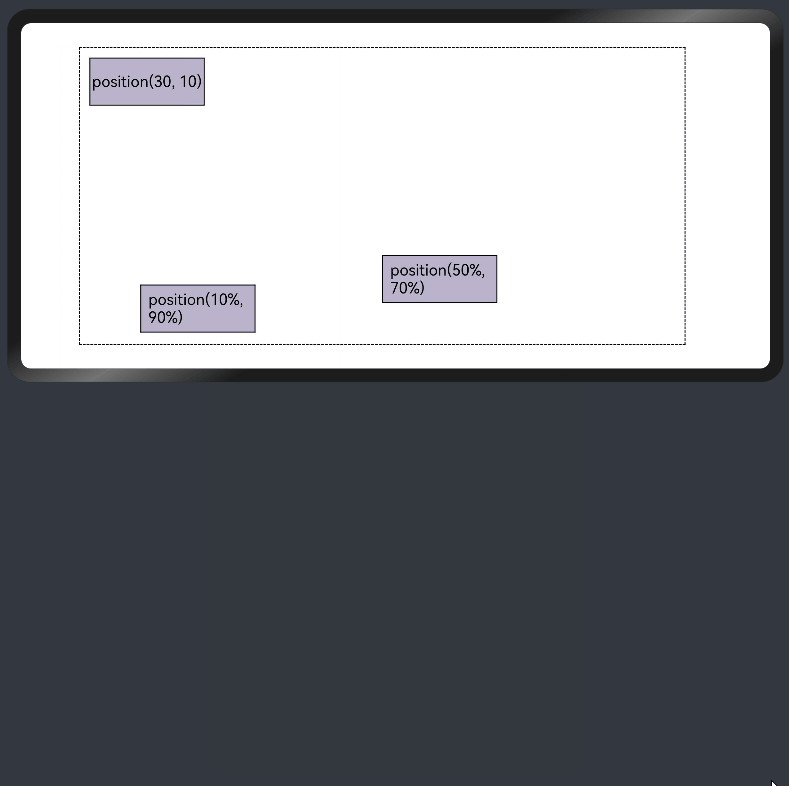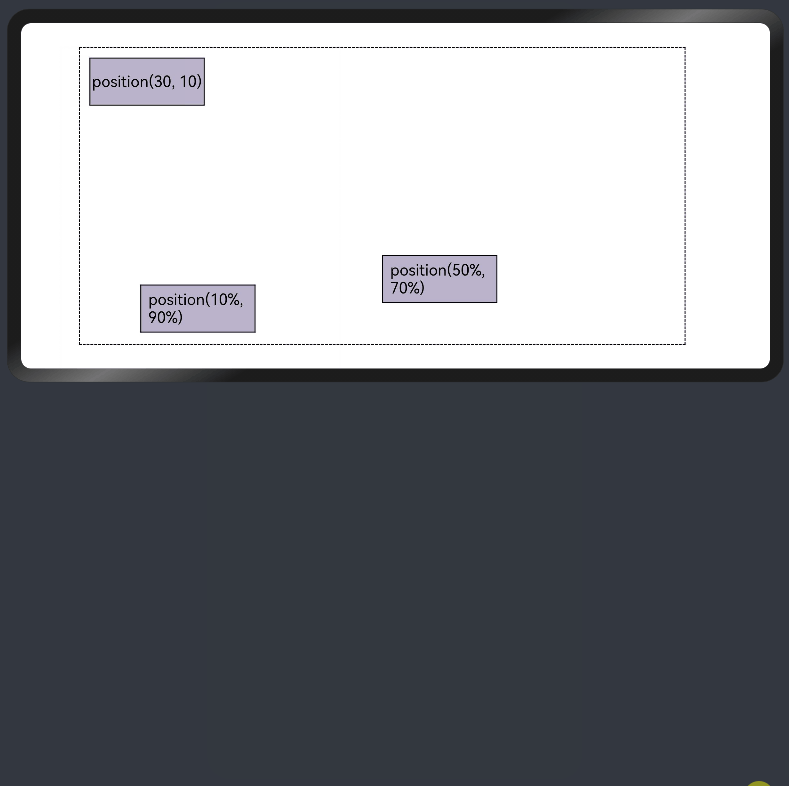
线性布局中可以使用组件的positon属性实现绝对布局(AbsoluteLayout),设置元素左上角相对于父容器左上角偏移位置。对于不同尺寸的设备,使用绝对定位的适应性会比较差,在屏幕的适配上有缺陷。
@Entry
@Component
struct PositionExample {
@Styles eleStyle(){
.backgroundColor(0xbbb2cb)
.border({ width: 1 })
.size({ width: 120, height: 50 })
}
build() {
Column({ space: 20 }) {
// 设置子组件左上角相对于父组件左上角的偏移位置
Row() {
Text('position(30, 10)')
.eleStyle()
.fontSize(16)
.position({ x: 10, y: 10 })
Text('position(50%, 70%)')
.eleStyle()
.fontSize(16)
.position({ x: '50%', y: '70%' })
Text('position(10%, 90%)')
.eleStyle()
.fontSize(16)
.position({ x: '10%', y: '80%' })
}.width('90%').height('100%').border({ width: 1, style: BorderStyle.Dashed })
}
.width('90%').margin(25)
}
}
自适应延伸
自适应延伸是在不同尺寸设备下,当页面显示内容个数不一并延伸到屏幕外时,可通过滚动条拖动展示。适用于线性布局中内容无法一屏展示的场景。常见以下两类实现方法。
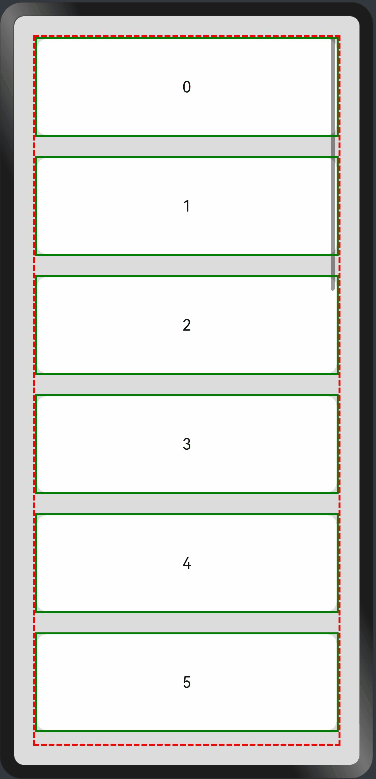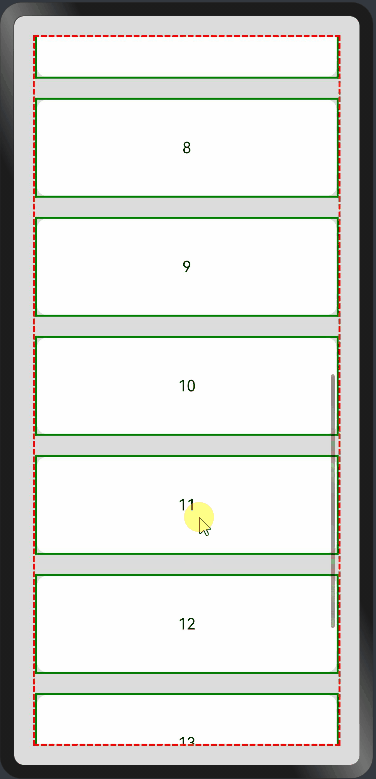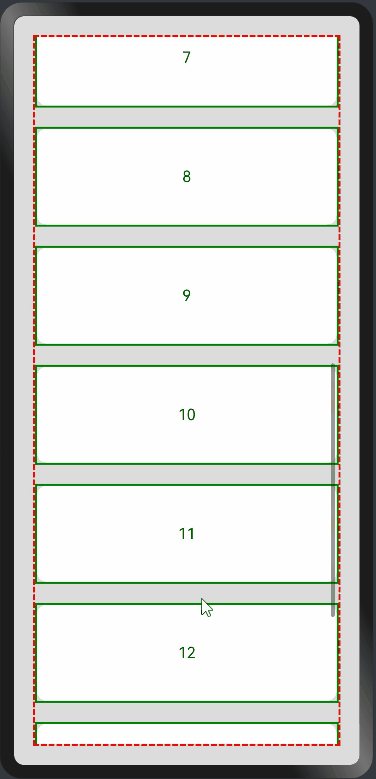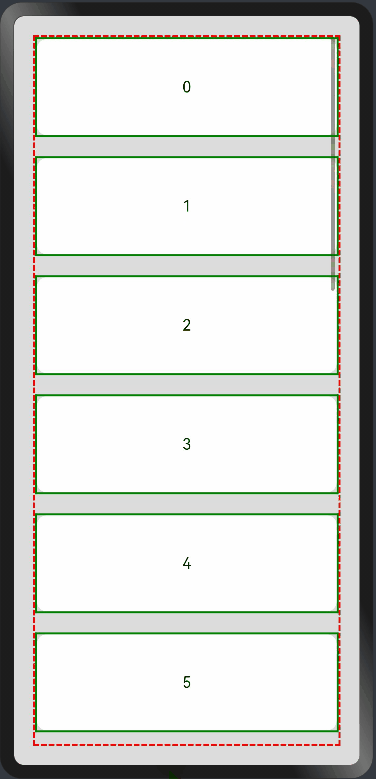
- List组件
List子项过多一屏放不下时,未展示的子项通过滚动条拖动显示。通过scrollBar属性设置滚动条的常驻状态,edgeEffect属性设置拖动到极限的回弹效果。
纵向List:
@Entry
@Component
struct ListExample1 {
@State arr: string[] = ["0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10", "11", "12", "13", "14", "15"]
@State alignListItem: ListItemAlign = ListItemAlign.Start
build() {
Column() {
List({ space: 20, initialIndex: 0 }) {
ForEach(this.arr, (item) => {
ListItem() {
Text('' + item)
.width('100%')
.height(100)
.fontSize(16)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.borderRadius(10)
.backgroundColor(0xFFFFFF)
}
.border({ width: 2, color: Color.Green })
}, item => item)
}
.border({ width: 2, color: Color.Red, style: BorderStyle.Dashed })
.scrollBar(BarState.On) // 滚动条常驻
.edgeEffect(EdgeEffect.Spring) // 滚动到边缘再拖动回弹效果
}.width('100%').height('100%').backgroundColor(0xDCDCDC).padding(20)
}
}
横向List:
@Entry
@Component
struct ListExample2 {
@State arr: string[] = ["0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10", "11", "12", "13", "14", "15"]
@State alignListItem: ListItemAlign = ListItemAlign.Start
build() {
Column() {
List({ space: 20, initialIndex: 0 }) {
ForEach(this.arr, (item) => {
ListItem() {
Text('' + item)
.height('100%')
.width(100)
.fontSize(16)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.borderRadius(10)
.backgroundColor(0xFFFFFF)
}
.border({ width: 2, color: Color.Green })
}, item => item)
}
.border({ width: 2, color: Color.Red, style: BorderStyle.Dashed })
.scrollBar(BarState.On) // 滚动条常驻
.edgeEffect(EdgeEffect.Spring) // 滚动到边缘再拖动回弹效果
.listDirection(Axis.Horizontal) // 列表水平排列
}.width('100%').height('100%').backgroundColor(0xDCDCDC).padding(20)
}
}
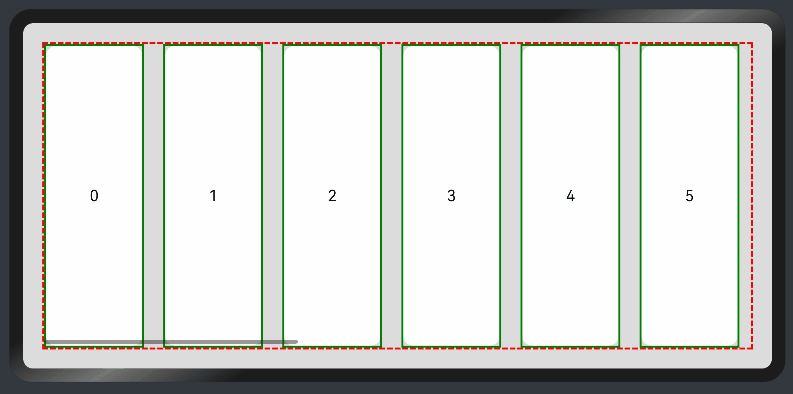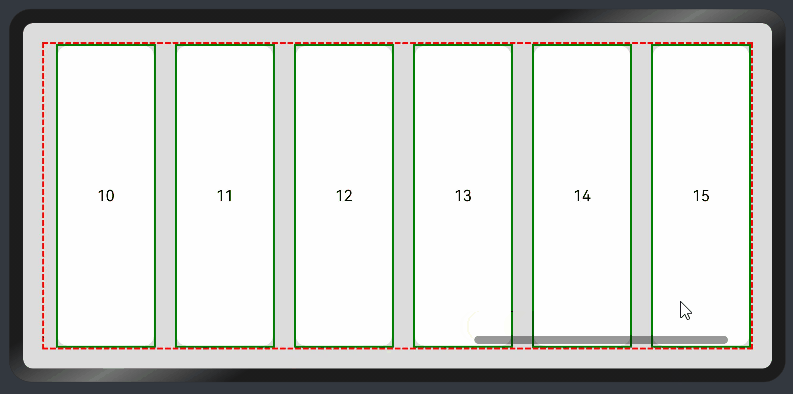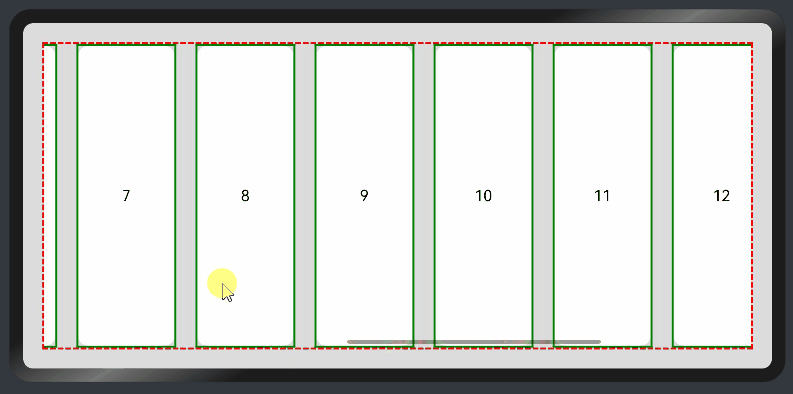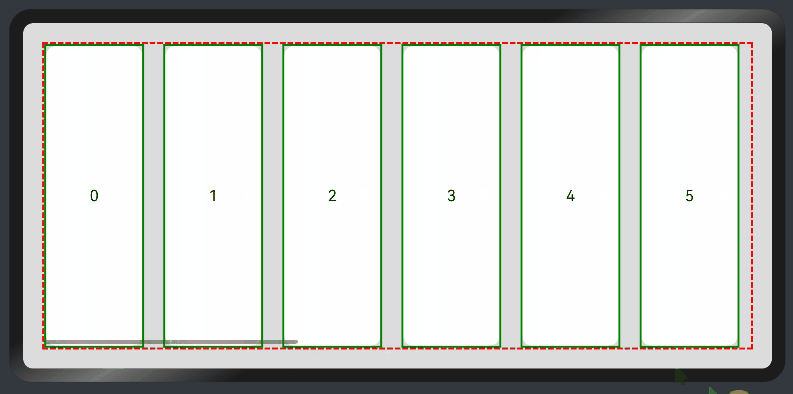
- Scroll组件
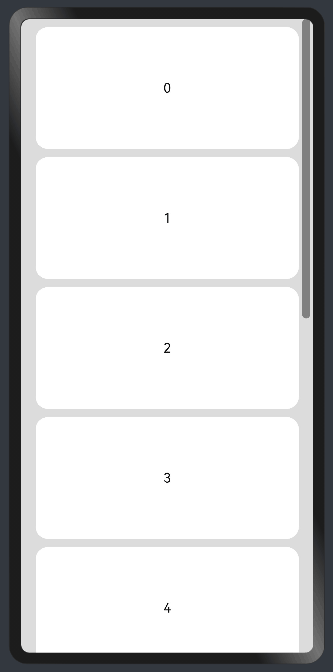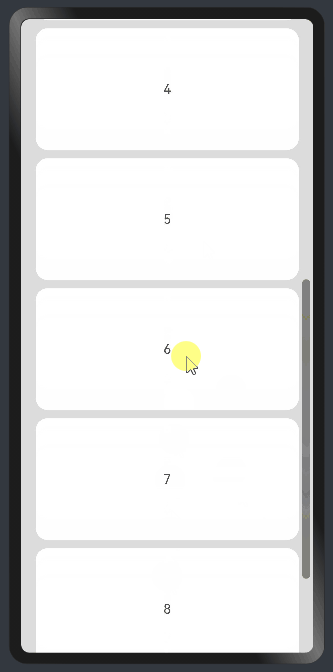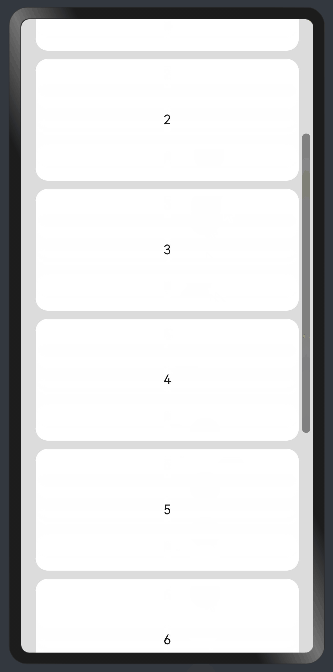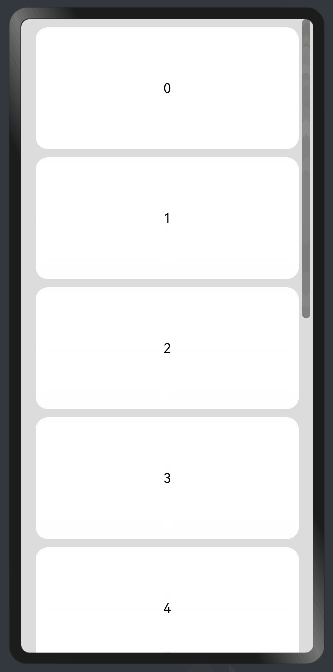
线性布局中,当子组件的布局尺寸超过父组件的尺寸时,内容可以滚动。在Column或者Row外层包裹一个可滚动的容器组件Scroll实现。
纵向Scroll:
@Entry
@Component
struct ScrollExample {
scroller: Scroller = new Scroller();
private arr: number[] = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
build() {
Scroll(this.scroller) {
Column() {
ForEach(this.arr, (item) => {
Text(item.toString())
.width('90%')
.height(150)
.backgroundColor(0xFFFFFF)
.borderRadius(15)
.fontSize(16)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.margin({ top: 10 })
}, item => item)
}.width('100%')
}
.backgroundColor(0xDCDCDC)
.scrollable(ScrollDirection.Vertical) // 滚动方向纵向
.scrollBar(BarState.On) // 滚动条常驻显示
.scrollBarColor(Color.Gray) // 滚动条颜色
.scrollBarWidth(30) // 滚动条宽度
.edgeEffect(EdgeEffect.Spring) // 滚动到边沿后回弹
}
}
横向Scroll:
@Entry
@Component
struct ScrollExample {
scroller: Scroller = new Scroller();
private arr: number[] = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
build() {
Scroll(this.scroller) {
Row() {
ForEach(this.arr, (item) => {
Text(item.toString())
.height('90%')
.width(150)
.backgroundColor(0xFFFFFF)
.borderRadius(15)
.fontSize(16)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.margin({ left: 10 })
}, item => item)
}.height('100%')
}
.backgroundColor(0xDCDCDC)
.scrollable(ScrollDirection.Horizontal) // 滚动方向横向
.scrollBar(BarState.On) // 滚动条常驻显示
.scrollBarColor(Color.Gray) // 滚动条颜色
.scrollBarWidth(30) // 滚动条宽度
.edgeEffect(EdgeEffect.Spring) // 滚动到边沿后回弹
}
}

你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: