harmony 鸿蒙Development of Application Recovery
Development of Application Recovery
Overview
During application running, some unexpected behaviors are inevitable. For example, unprocessed exceptions and errors are thrown, and the call or running constraints of the recovery framework are violated.
Process exit is treated as the default exception handling method. However, if user data is generated during application use, process exit may interrupt user operations and cause data loss. If the application recovery function is enabled in AbilityStage and temporary data is saved, the previous application state and data will be restored upon next startup in the case of an abnormal exit, providing more consistent user experience. The application state includes two parts, namely, the page stack and the data saved in onSaveState.
In API version 9, application recovery is supported only for a single ability of the application developed using the stage model. Application state saving and automatic restart are performed when a JsError occurs.
In API version 10, application recovery is applicable to multiple abilities of an application developed using the stage model. Application state storage and restore are performed when an AppFreeze occurs. If an application is killed in control mode, the application state will be restored upon next startup.
Available APIs
The application recovery APIs are provided by the appRecovery module, which can be imported via import. For details, see Development Example.
Available APIs
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| enableAppRecovery(restart?: RestartFlag, saveOccasion?: SaveOccasionFlag, saveMode?: SaveModeFlag) : void9+ | Enables application recovery. After this API is called, the first ability that is displayed when the application is started from the initiator can be restored. |
| saveAppState(): boolean9+ | Saves the state of the ability that supports recovery in the current application. |
| restartApp(): void9+ | Restarts the current process and starts the ability specified by setRestartWant. If no ability is specified, a foreground ability that supports recovery is restarted. |
| saveAppState(context?: UIAbilityContext): boolean10+ | Saves the ability state specified by Context. |
| setRestartWant(want: Want): void10+ | Sets the abilities to restart when restartApp is actively called and RestartFlag is not NO_RESTART. The abilities must be under the same bundle name and must be a UIAbility. |
No error will be thrown if the preceding APIs are used in the troubleshooting scenario. The following are some notes on API usage:
enableAppRecovery: This API should be called during application initialization. For example, you can call this API in onCreate of AbilityStage. For details, see Parameter Description.
saveAppState: After this API is called, the recovery framework invokes onSaveState for all abilities that support recovery in the current process. If you choose to save data in onSaveState, the related data and ability page stack are persistently stored in the local cache of the application. To save data of the specified ability, you need to specify the context corresponding to that ability.
setRestartWant: This API specifies the ability to be restarted by appRecovery.
restartApp: After this API is called, the recovery framework kills the current process and restarts the ability specified by setRestartWant, with APP_RECOVERY set as the startup cause. In API version 9 and scenarios where an ability is not specified by setRestartWant, the last foreground ability that supports recovery is started. If the no foreground ability supports recovery, the application crashes. If a saved state is available for the restarted ability, the saved state is passed as the wantParam attribute in the want parameter of the ability’s onCreate callback. The interval between two restarts must be greater than 1 minute. If this API is called repeatedly within 1 minute, the application exits but does not restart. The behavior of automatic restart is the same as that of proactive restart.
Application State Management
Since API version 10, application recovery is not limited to automatic restart in the case of an exception. Therefore, you need to understand when the application will load the saved state. If the last exit of an application is not initiated by a user and a saved state is available for recovery, the startup reason is set to APP_RECOVERY when the application is started by the user next time, and the recovery state of the application is cleared. The application recovery status flag is set when saveAppState is actively or passively called. The flag is cleared when the application exits normally or restarts after an abnormal exit. (A normal exit is usually triggered by pressing the back key or clearing recent tasks.)
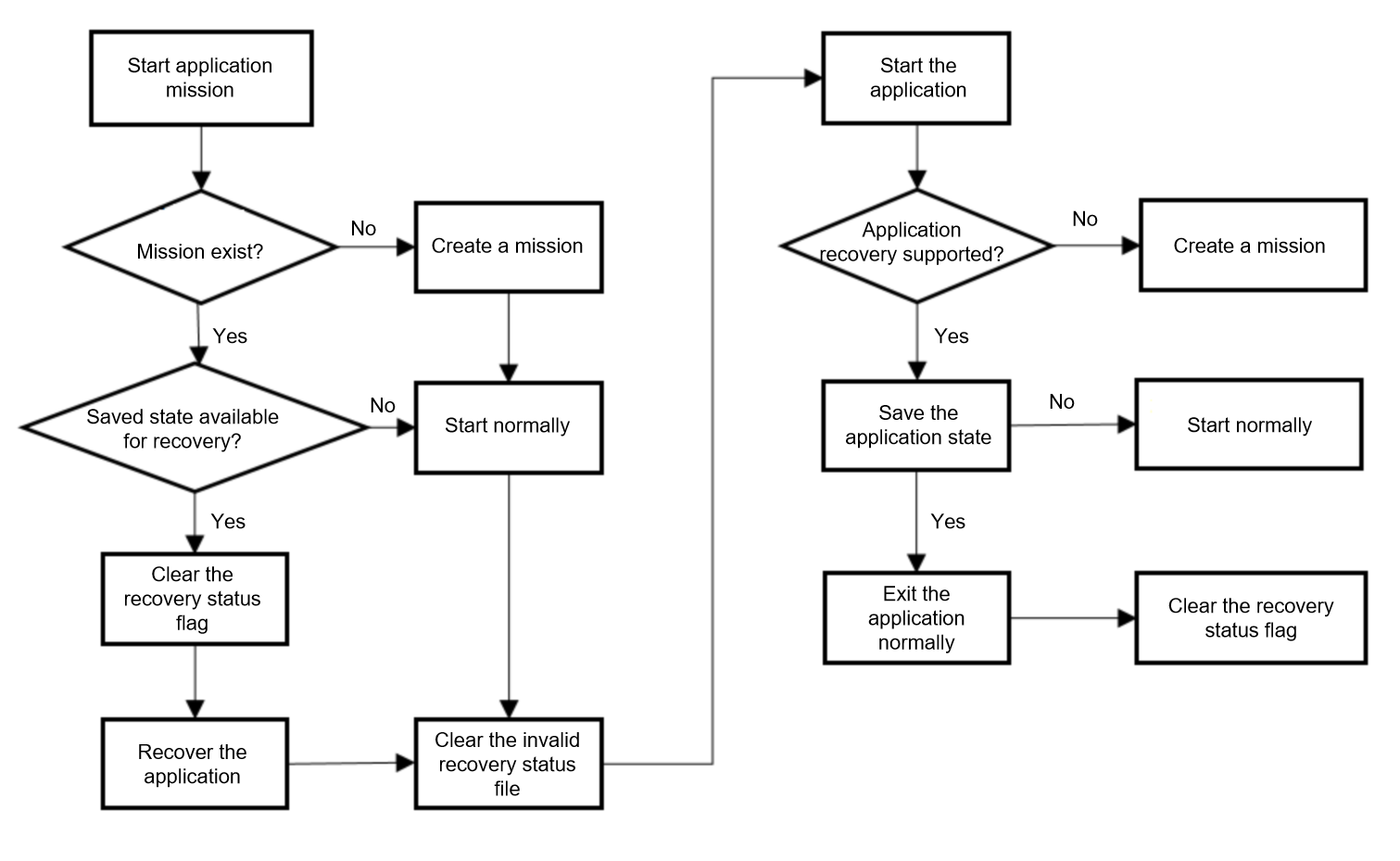
Application State Saving and Restore
API version 10 or later supports saving of the application state when an application is suspended. If a JsError occurs, onSaveState is called in the main thread. If an AppFreeze occurs, however, the main thread may be suspended, and therefore onSaveState is called in a non-main thread. The following figure shows the main service flow.
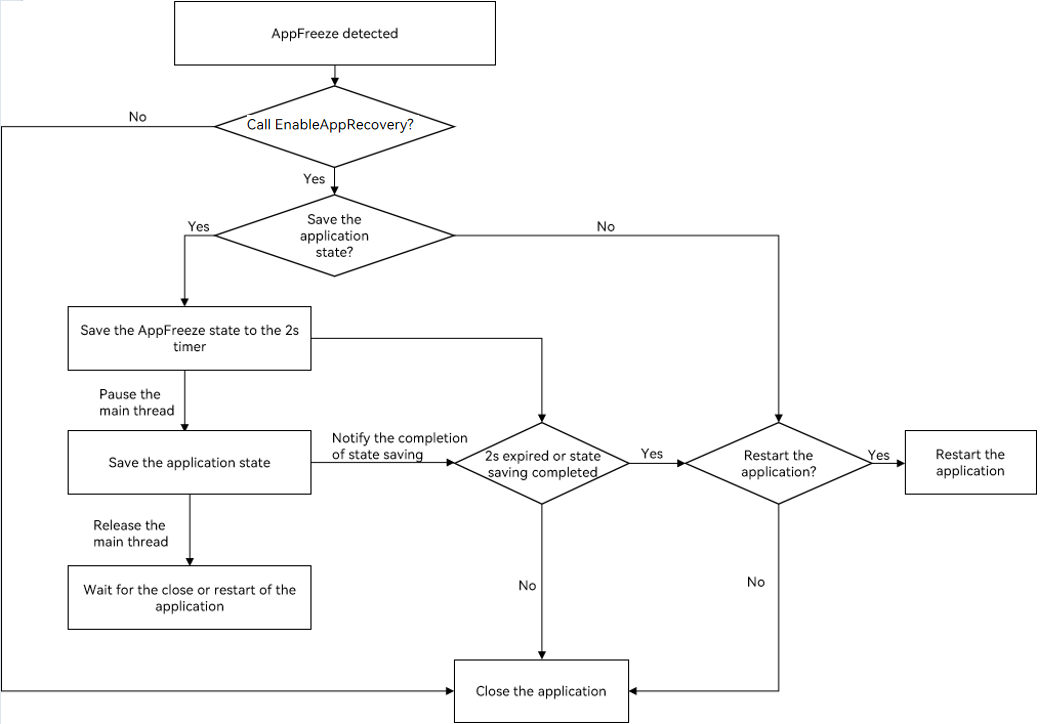
When the application is suspended, the callback is not executed in the JS thread. Therefore, you are advised not to use the imported dynamic Native library or access the thread_local object created by the main thread in the code of the onSaveState callback.
Framework Fault Management
Fault management is an important way for applications to deliver a better user experience. The application framework offers three methods for application fault management: fault listening, fault rectification, and fault query.
Fault listening refers to the process of registering an ErrorObserver via errorManager, listening for faults, and notifying the listener of the faults.
Fault rectification refers to the process of restoring the application state and data through appRecovery.
Fault query is the process of calling APIs of faultLogger to obtain the fault information.
The figure below does not illustrate the time when faultLogger is called. You can refer to the LastExitReason passed during application initialization to determine whether to call faultLogger to query information about the previous fault.
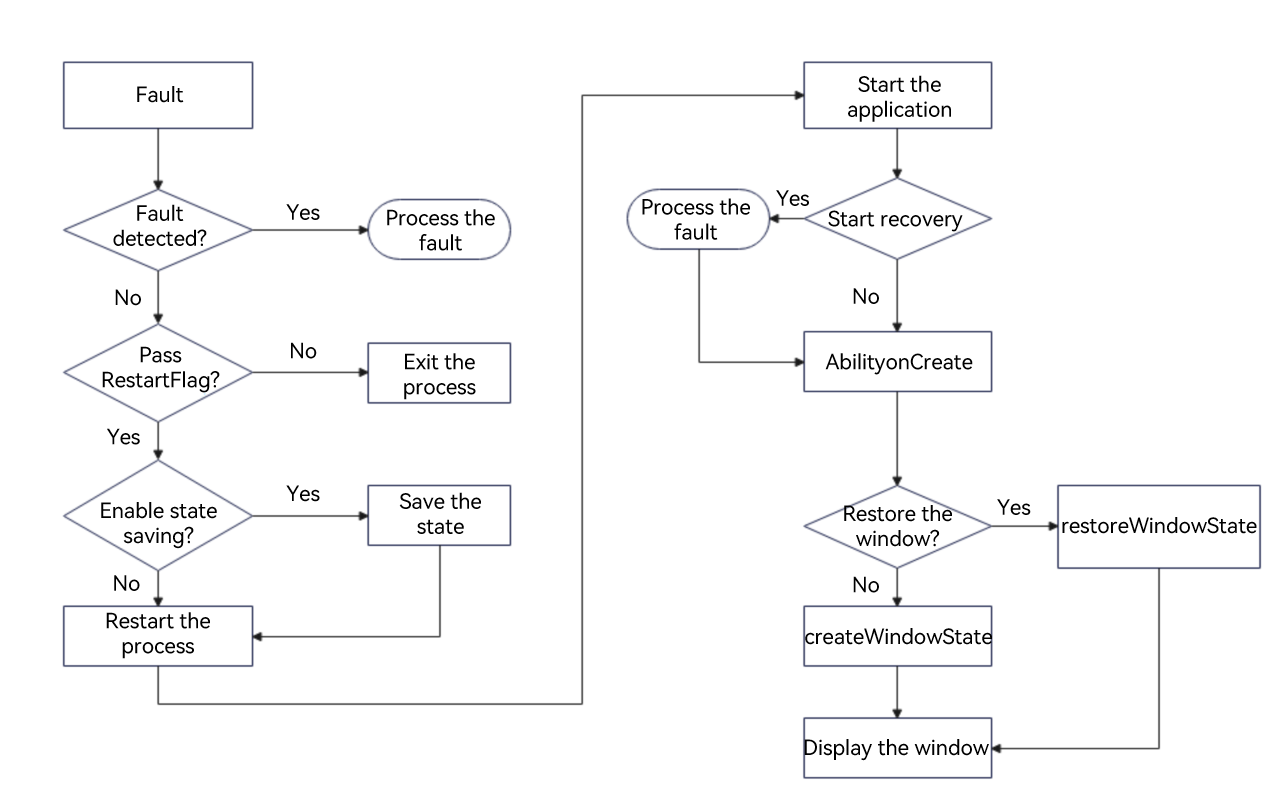
It is recommended that you call errorManager to handle the exception. After the processing is complete, you can call the saveAppState API and restart the application. If you do not register an ErrorObserver instance or enable application recovery, the application process will exit according to the default processing logic of the system. Users can restart the application from the home screen. If you have enabled application recovery, the recovery framework first checks whether application state saving is supported and whether the application state saving is enabled. If so, the recovery framework invokes onSaveState of the ability. Finally, the application is restarted.
Supported Application Recovery Scenarios
Common fault types include JavaScript application crash, application freezing, and C++ application crash. Generally, an application is closed when a crash occurs. Application freezing occurs when the application does not respond. The fault type can be ignored for the upper layer of an application. The recovery framework implements fault management in different scenarios based on the fault type.
| Fault | Fault Listening | State Saving | Automatic Restart | Log Query |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JS_CRASH | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| APP_FREEZE | This fault is supported since API version 18. | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| CPP_CRASH | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported | Supported |
State Saving in the table header means saving of the application state when a fault occurs. To protect user data as much as possible when an AppFreeze occurs, you can adopt either the periodic or automatic way, and the latter will save user data when an ability is switched to the background.
Development Example
Enabling Application Recovery
Enable appRecovery during application initialization. The following is an example of AbilityStage:
import { AbilityStage, appRecovery } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
export default class MyAbilityStage extends AbilityStage {
onCreate() {
console.info("[Demo] MyAbilityStage onCreate");
appRecovery.enableAppRecovery(appRecovery.RestartFlag.ALWAYS_RESTART,
appRecovery.SaveOccasionFlag.SAVE_WHEN_ERROR|appRecovery.SaveOccasionFlag.SAVE_WHEN_BACKGROUND,
appRecovery.SaveModeFlag.SAVE_WITH_FILE);
}
}
Enabling Application Recovery for the Specified Abilities
Generally, the ability configuration list is named module.json5.
{
"abilities": [
{
"name": "EntryAbility",
"recoverable": true,
}]
}
Saving and Restoring Data
After enabling appRecovery, you can use this function by either actively or passively saving the application state and restoring data in the ability. The following is an example of EntryAbility:
Importing the Service Package
import { AbilityConstant, appRecovery, errorManager } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
Actively Saving the Application State and Restoring Data
- Define and register the ErrorObserver callback. For details about its usage, see errorManager.
import { appRecovery, errorManager, UIAbility } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
import { window } from '@kit.ArkUI';
let registerId = -1;
let callback: errorManager.ErrorObserver = {
onUnhandledException(errMsg) {
console.log(errMsg);
appRecovery.saveAppState();
appRecovery.restartApp();
}
}
export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
onWindowStageCreate(windowStage: window.WindowStage) {
// Main window is created, set main page for this ability
console.log("[Demo] EntryAbility onWindowStageCreate");
registerId = errorManager.on('error', callback);
windowStage.loadContent("pages/index", (err, data) => {
if (err.code) {
console.error('Failed to load the content. Cause:' + JSON.stringify(err));
return;
}
console.info('Succeeded in loading the content. Data: ' + JSON.stringify(data));
})
}
}
- Save data.
After the callback triggers appRecovery.saveAppState(), onSaveState(state, wantParams) of EntryAbility is triggered.
import { AbilityConstant, UIAbility } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
onSaveState(state:AbilityConstant.StateType, wantParams: Record<string, Object>) {
// Ability has called to save app data
console.log("[Demo] EntryAbility onSaveState");
wantParams["myData"] = "my1234567";
return AbilityConstant.OnSaveResult.ALL_AGREE;
}
}
- Restore data.
After the callback triggers appRecovery.restartApp(), the application is restarted. After the restart, onCreate(want, launchParam) of EntryAbility is called, and the saved data is stored in parameters of want.
import { AbilityConstant, UIAbility, Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
let abilityWant: Want;
export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
storage: LocalStorage|undefined = undefined;
onCreate(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam) {
console.log("[Demo] EntryAbility onCreate");
abilityWant = want;
if (launchParam.launchReason == AbilityConstant.LaunchReason.APP_RECOVERY) {
this.storage = new LocalStorage();
if (want.parameters) {
let recoveryData = want.parameters["myData"];
this.storage.setOrCreate("myData", recoveryData);
this.context.restoreWindowStage(this.storage);
}
}
}
}
- Unregister the ErrorObserver callback.
import { errorManager, UIAbility } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
let registerId = -1;
export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
onWindowStageDestroy() {
// Main window is destroyed, release UI related resources
console.log("[Demo] EntryAbility onWindowStageDestroy");
errorManager.off('error', registerId, (err) => {
console.error("[Demo] err:", err);
});
}
}
Passively Saving the Application State and Restoring Data
This is triggered by the recovery framework. You do not need to register an ErrorObserver callback. You only need to implement onSaveState for application state saving and onCreate for data restore.
import { AbilityConstant, UIAbility, Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
let abilityWant: Want;
export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
storage: LocalStorage|undefined = undefined
onCreate(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam) {
console.log("[Demo] EntryAbility onCreate");
abilityWant = want;
if (launchParam.launchReason == AbilityConstant.LaunchReason.APP_RECOVERY) {
this.storage = new LocalStorage();
if (want.parameters) {
let recoveryData = want.parameters["myData"];
this.storage.setOrCreate("myData", recoveryData);
this.context.restoreWindowStage(this.storage);
}
}
}
onSaveState(state:AbilityConstant.StateType, wantParams: Record<string, Object>) {
// Ability has called to save app data
console.log("[Demo] EntryAbility onSaveState");
wantParams["myData"] = "my1234567";
return AbilityConstant.OnSaveResult.ALL_AGREE;
}
}
Restart Flag for the Failed Ability
If the failed ability is restarted again, the ABILITY_RECOVERY_RESTART flag will be added as a parameters member for the want parameter in onCreate and its value is true.
import { AbilityConstant, UIAbility, Want, wantConstant } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
onCreate(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam) {
if (want.parameters === undefined) {
return;
}
if (want.parameters[wantConstant.Params.ABILITY_RECOVERY_RESTART] != undefined &&
want.parameters[wantConstant.Params.ABILITY_RECOVERY_RESTART] == true) {
console.log("This ability need to recovery");
}
}
}
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Performance Analysis Kit
harmony 鸿蒙Analyzing Application Freeze
harmony 鸿蒙Development of Error Manager
harmony 鸿蒙Introduction to HiAppEvent
harmony 鸿蒙Subscribing to Address Sanitizer Events (ArkTS)
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: