harmony 鸿蒙Cross-Device Sync of RDB Stores
Cross-Device Sync of RDB Stores
When to Use
You can sync the application data in a local RDB store on a device to other devices that form a Super Device.
Basic Concepts
OpenHamony supports sync of the relational data of an application across multiple devices.
If a table created for an application in the database is set as a distributed table, when data is queried from the RDB store of a remote device, the distributed table name of the remote device can be obtained based on the local table name.
Data can be synced between devices in either of the following ways:
- Pushing data from a local device to a remote device.
- Pulling data from a remote device to a local device.
Working Principles
After completing device discovery and authentication, the underlying communication component notifies the application that the device goes online. The DatamgrService then establishes an encrypted transmission channel to synchronize data between the two devices.
Cross-Device Data Sync Mechanism
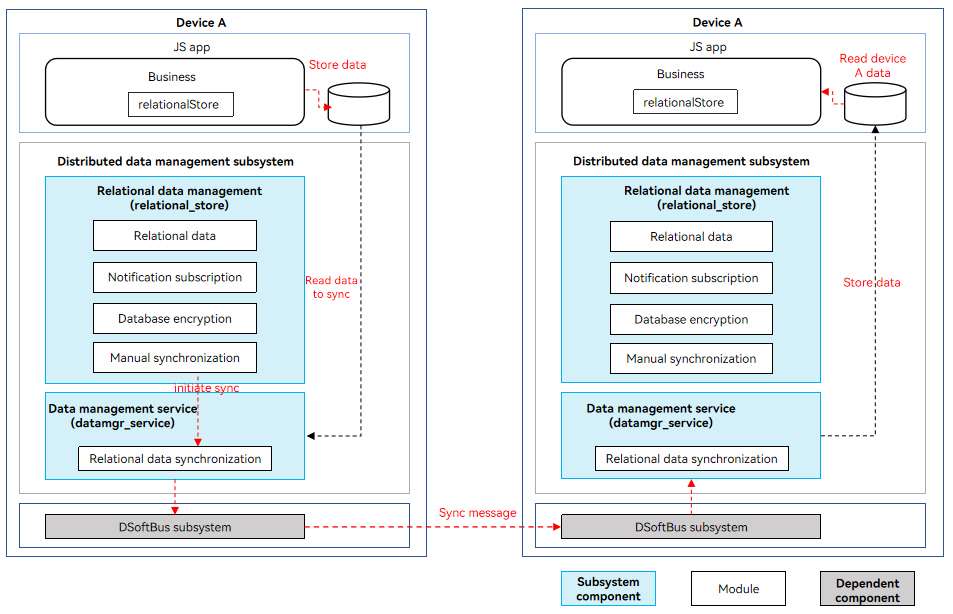
After writing data to an RDB store, the service sends a sync request to the DatamgrService.
The DatamgrService reads the data to be synced from the application sandbox and sends the data to the DatamgrService of the target device based on the deviceId of the peer device. Then, the DatamgrService writes the data to the RDB of the same application.
Data Change Notification Mechanism
When data is added, deleted, or modified, a notification is sent to the subscriber. The notifications can be classified into the following types:
Local data change notification: subscription of the application data changes on the local device. When the data in the local KV store is added, deleted, or modified in the database, a notification is received.
Distributed data change notification: subscription of the application data changes of other devices in the network. When the data in the local RDB store changes after being synced with data from another device in the same network, a notification is received.
Constraints
A maximum of 16 RDB stores can be opened simultaneously for an application.
Each RDB store supports a maximum of eight callbacks for subscription of data change notifications.
A table containing composite keys cannot be set as a distributed table.
Available APIs
Most of the APIs for cross-device data sync of RDB stores are executed asynchronously, using a callback or promise to return the result. The following table uses the callback-based APIs as an example. For more information about the APIs, see RDB Store.
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| setDistributedTables(tables: Array<string>, callback: AsyncCallback<void>): void | Sets the distributed tables to be synced. |
| sync(mode: SyncMode, predicates: RdbPredicates, callback: AsyncCallback<Array<[string, number]>>): void | Synchronizes data across devices. |
| on(event: ‘dataChange’, type: SubscribeType, observer: Callback<Array<string>>): void | Subscribes to changes in the distributed data. |
| off(event:‘dataChange’, type: SubscribeType, observer: Callback<Array<string>>): void | Unsubscribe from changes in the distributed data. |
| obtainDistributedTableName(device: string, table: string, callback: AsyncCallback<string>): void | Obtains the table name on the specified device based on the local table name. |
| remoteQuery(device: string, table: string, predicates: RdbPredicates, columns: Array<string> , callback: AsyncCallback<ResultSet>): void | Queries data from the RDB store of a remote device based on specified conditions. |
How to Develop
NOTE
The security level of the destination device (to which data is synced) cannot be higher than that of the source device. For details, see Access Control Mechanism in Cross-Device Sync.
- Import the module.
import { relationalStore } from '@kit.ArkData';
Request permissions.
- Declare the ohos.permission.DISTRIBUTED_DATASYNC permission. For details, see Declaring Permissions.
- Display a dialog box to ask for user authorization when the application is started for the first time. For details, see Requesting User Authorization.
Create an RDB store and set a table for distributed sync.
import { UIAbility } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
import { window } from '@kit.ArkUI';
class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
onWindowStageCreate(windowStage: window.WindowStage) {
const STORE_CONFIG: relationalStore.StoreConfig = {
name: "RdbTest.db",
securityLevel: relationalStore.SecurityLevel.S3
};
relationalStore.getRdbStore(this.context, STORE_CONFIG, (err: BusinessError, store: relationalStore.RdbStore) => {
store.executeSql('CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS EMPLOYEE (ID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, NAME TEXT NOT NULL, AGE INTEGER, SALARY REAL, CODES BLOB)', (err) => {
// Set the table for distributed sync.
store.setDistributedTables(['EMPLOYEE']);
// Perform related operations.
})
})
}
}
- Synchronize data across devices. After sync() is called to trigger a sync, data is synced from the local device to all other devices on the network.
// Construct the predicate object for synchronizing the distributed table.
let predicates = new relationalStore.RdbPredicates('EMPLOYEE');
// Call sync() to synchronize data.
if(store != undefined)
{
(store as relationalStore.RdbStore).sync(relationalStore.SyncMode.SYNC_MODE_PUSH, predicates, (err, result) => {
// Check whether data sync is successful.
if (err) {
console.error(`Failed to sync data. Code:${err.code},message:${err.message}`);
return;
}
console.info('Succeeded in syncing data.');
for (let i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
console.info(`device:${result[i][0]},status:${result[i][1]}`);
}
})
}
- Subscribe to changes in the distributed data. The data sync triggers the observer callback registered in on(). The input parameter of the callback is the ID of the device whose data changes.
let devices: string|undefined = undefined;
try {
// Register an observer to listen for the changes of the distributed data.
// When data in the RDB store changes, the registered callback will be invoked to return the data changes.
if(store != undefined) {
(store as relationalStore.RdbStore).on('dataChange', relationalStore.SubscribeType.SUBSCRIBE_TYPE_REMOTE, (storeObserver)=>{
if(devices != undefined){
for (let i = 0; i < devices.length; i++) {
console.info(`The data of device:${devices[i]} has been changed.`);
}
}
});
}
} catch (err) {
console.error('Failed to register observer. Code:${err.code},message:${err.message}');
}
// You can unsubscribe from the data changes if required.
try {
if(store != undefined) {
(store as relationalStore.RdbStore).off('dataChange', relationalStore.SubscribeType.SUBSCRIBE_TYPE_REMOTE, (storeObserver)=>{
});
}
} catch (err) {
console.error('Failed to register observer. Code:${err.code},message:${err.message}');
}
- Query data across devices. If data sync is not complete or triggered, an application can call remoteQuery() to query data from a remote device.
NOTE
The value of deviceIds can be obtained by using deviceManager.getAvailableDeviceListSync method.
// Obtain device IDs.
import { distributedDeviceManager } from '@kit.DistributedServiceKit';
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
let dmInstance: distributedDeviceManager.DeviceManager;
let deviceId: string|undefined = undefined ;
try {
dmInstance = distributedDeviceManager.createDeviceManager("com.example.appdatamgrverify");
let devices = dmInstance.getAvailableDeviceListSync();
deviceId = devices[0].networkId;
// Construct a predicate object for querying the distributed table.
let predicates = new relationalStore.RdbPredicates('EMPLOYEE');
// Query data from the specified remote device and return the query result.
if(store != undefined && deviceId != undefined) {
(store as relationalStore.RdbStore).remoteQuery(deviceId, 'EMPLOYEE', predicates, ['ID', 'NAME', 'AGE', 'SALARY', 'CODES'],
(err: BusinessError, resultSet: relationalStore.ResultSet) => {
if (err) {
console.error(`Failed to remoteQuery data. Code:${err.code},message:${err.message}`);
return;
}
console.info(`ResultSet column names: ${resultSet.columnNames}, column count: ${resultSet.columnCount}`);
}
)
}
} catch (err) {
let code = (err as BusinessError).code;
let message = (err as BusinessError).message;
console.error("createDeviceManager errCode:" + code + ",errMessage:" + message);
}
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙ArkData (Ark Data Management)
harmony 鸿蒙Access Control by Device and Data Level
harmony 鸿蒙Application Data Vectorization
harmony 鸿蒙Application Data Persistence Overview
harmony 鸿蒙Database Backup and Restore
harmony 鸿蒙Introduction to ArkData
harmony 鸿蒙Persisting Graph Store Data (for System Applications Only)
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: